Redox - Plusnet
... Rules for assigning: (these rarely change) F is always -1 O is -2, except in OF2 Group 7 are -1, except with O or F Group 1 metals are +1 Group 2 metals are +2 H is +1, except in hydrides, e.g. NaH Al is +3 The total for an ion is its charge (e.g. -1 for CN-) More electronegative atoms get negative ...
... Rules for assigning: (these rarely change) F is always -1 O is -2, except in OF2 Group 7 are -1, except with O or F Group 1 metals are +1 Group 2 metals are +2 H is +1, except in hydrides, e.g. NaH Al is +3 The total for an ion is its charge (e.g. -1 for CN-) More electronegative atoms get negative ...
ACHM 111,Week 2 Atoms and molecules
... Element and compounds are the only pure substances that can exist. If two or more kinds of molecules are present together they form a mixture. Most of the materials encountered are mixtures: air, earth, sea water, plants. One of the chemicals most important and difficulty jobs is to sort out the nat ...
... Element and compounds are the only pure substances that can exist. If two or more kinds of molecules are present together they form a mixture. Most of the materials encountered are mixtures: air, earth, sea water, plants. One of the chemicals most important and difficulty jobs is to sort out the nat ...
Document
... infinity)only integers and never zero. Orbital-that part of the atom where the electron wave has a high probability of being found. Sometimes referred to as a sublevel. This is a feature of the quantum mechanical model of the atom proposed by Schrodinger. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle-states th ...
... infinity)only integers and never zero. Orbital-that part of the atom where the electron wave has a high probability of being found. Sometimes referred to as a sublevel. This is a feature of the quantum mechanical model of the atom proposed by Schrodinger. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle-states th ...
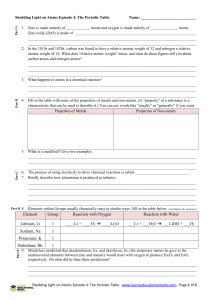
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... 9. Mendeleev predicted that ekaaluminium, Ea, and ekasilicon, Es, (the temporary names he gave to the undiscovered elements between zinc and arsenic) would react with oxygen to produce Ea2O3 and EsO2 respectively. On what did he base these predictions? ...
... 9. Mendeleev predicted that ekaaluminium, Ea, and ekasilicon, Es, (the temporary names he gave to the undiscovered elements between zinc and arsenic) would react with oxygen to produce Ea2O3 and EsO2 respectively. On what did he base these predictions? ...
Document
... Dalton’s Postulates 2. Atoms of an element cannot be created, destroyed, broken into smaller parts or transformed into atoms of another element • The discovery of nuclear processes showed that it was possible to transform atoms from one element into atoms of another. But we don't consider processes ...
... Dalton’s Postulates 2. Atoms of an element cannot be created, destroyed, broken into smaller parts or transformed into atoms of another element • The discovery of nuclear processes showed that it was possible to transform atoms from one element into atoms of another. But we don't consider processes ...
Objectives: early history, laws for calculations, atoms, molecules
... Representative or main group VIII: noble gases (not diatomic, but mono-atomic gases) Between groups II and III: transition metals Starting from Lanthanum La: rare earths or lanthanides Starting from Actinium Ac: actinides, all radioactive, beyond uranium all man made ...
... Representative or main group VIII: noble gases (not diatomic, but mono-atomic gases) Between groups II and III: transition metals Starting from Lanthanum La: rare earths or lanthanides Starting from Actinium Ac: actinides, all radioactive, beyond uranium all man made ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... • From Coulomb’s law we would expect that the IE for an electron in 3d would be greater than that for an electron in 3p. • But PES indicates that the IE3s>IE3p>IE3d • Due to an increase in the shielding effect. ...
... • From Coulomb’s law we would expect that the IE for an electron in 3d would be greater than that for an electron in 3p. • But PES indicates that the IE3s>IE3p>IE3d • Due to an increase in the shielding effect. ...
UNIT 1 - MATTER AND CHEMICAL BONDING
... e) lead(II) hydroxide lead(II) oxide + water f) ammonia + sulphuric acid ammonium sulphate g) potassium phosphate + magnesium chloride magnesium phosphate + potassium chloride 6. For each of the following, use an activity series to determine which single displacement reactions will proceed. Fo ...
... e) lead(II) hydroxide lead(II) oxide + water f) ammonia + sulphuric acid ammonium sulphate g) potassium phosphate + magnesium chloride magnesium phosphate + potassium chloride 6. For each of the following, use an activity series to determine which single displacement reactions will proceed. Fo ...
What is matter made of?
... describes all of the physical substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, air or all solids liquids & gasses. Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) Made up of different kinds of atoms ...
... describes all of the physical substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, air or all solids liquids & gasses. Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) Made up of different kinds of atoms ...
History of the atom -naperville north
... atoms. Atoms of an element are identical. Each element has different atoms. Atoms of different elements combine to form compounds. Atoms are rearranged in reactions Atoms cannot be split. ...
... atoms. Atoms of an element are identical. Each element has different atoms. Atoms of different elements combine to form compounds. Atoms are rearranged in reactions Atoms cannot be split. ...
chem 4 outline for exam 1
... Identify examples of ionic and covalent compounds using chemical formulas. In what ways do the characteristics of ionic and covalent compounds differ? General Properties and Changes of Matter (Ch. 2, p. 21-23) Distinguish between physical and chemical properties. Distinguish between physical and che ...
... Identify examples of ionic and covalent compounds using chemical formulas. In what ways do the characteristics of ionic and covalent compounds differ? General Properties and Changes of Matter (Ch. 2, p. 21-23) Distinguish between physical and chemical properties. Distinguish between physical and che ...
The Chemistry of Life Chapter 2
... • Mass of an atom. • Approximately equal to the number of protons and neutrons • Find number of neutrons by subtracting the number of protons from the mass. ...
... • Mass of an atom. • Approximately equal to the number of protons and neutrons • Find number of neutrons by subtracting the number of protons from the mass. ...
Relative Atomic Mass
... What does ‘h’ stand for in the equation relating energy of light and its frequency. 24. Name the instrument used to study emission line spectra? 25. Give another word to explain ‘quantised’, with reference to energy of an electron? 26. E = hf. What does ‘f’ stand for? 27. What electron transitions g ...
... What does ‘h’ stand for in the equation relating energy of light and its frequency. 24. Name the instrument used to study emission line spectra? 25. Give another word to explain ‘quantised’, with reference to energy of an electron? 26. E = hf. What does ‘f’ stand for? 27. What electron transitions g ...
1 | Page Chemistry Lecture #19: Atomic Number, Isotopes, and
... For now, ignore the 14.0067 (I’ll explain what this number is in another lecture). The number 7 is the atomic number of nitrogen. Thus, nitrogen has 7 protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of electrons. ...
... For now, ignore the 14.0067 (I’ll explain what this number is in another lecture). The number 7 is the atomic number of nitrogen. Thus, nitrogen has 7 protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of electrons. ...
Name: Chemistry Notes: Chapter 1.1
... Atoms do not have a shell or anything else separating them from the rest of the world. The negatively charged e ...
... Atoms do not have a shell or anything else separating them from the rest of the world. The negatively charged e ...
SECTION 3-2: THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... 1. Nucleus: * Has at least one positively charged particle called a proton and generally one or more neutral particles called neutrons. * Very small region located near the center of the atom 2. Electrons: Surrounds the nucleus (electron cloud) and are negatively charged Protons, neutrons, and elect ...
... 1. Nucleus: * Has at least one positively charged particle called a proton and generally one or more neutral particles called neutrons. * Very small region located near the center of the atom 2. Electrons: Surrounds the nucleus (electron cloud) and are negatively charged Protons, neutrons, and elect ...
Unit 2 - Test Review
... Electrons are about 2000 times smaller than protons or neutrons. 6. Understand how atomic structure is represented on the periodic table. You should be able to find the atomic number and atomic mass of an element from the periodic table. 7. Identify a given element as a metal or a non-metal based on ...
... Electrons are about 2000 times smaller than protons or neutrons. 6. Understand how atomic structure is represented on the periodic table. You should be able to find the atomic number and atomic mass of an element from the periodic table. 7. Identify a given element as a metal or a non-metal based on ...
Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
... orbits a fixed distance from the nucleus. This is similar to the way the planets orbit the sun. However, electrons do not have neat orbits like the planets. Diagram of Bohr model: ...
... orbits a fixed distance from the nucleus. This is similar to the way the planets orbit the sun. However, electrons do not have neat orbits like the planets. Diagram of Bohr model: ...
atom
... isotopes are radioactive, meaning that their nuclei are unstable and break down at a constant rate over time. Although the radiation these isotopes give off can be dangerous, they have important scientific and practical uses. ...
... isotopes are radioactive, meaning that their nuclei are unstable and break down at a constant rate over time. Although the radiation these isotopes give off can be dangerous, they have important scientific and practical uses. ...
Mongar Higher Secondary School
... iii) Ionic compounds are bad conductors in solid state but are good conductiors in molten state or in their aqueous solutions. iv) The atomic size decreases across the period. v) Sodium chloride solution is neutral. ...
... iii) Ionic compounds are bad conductors in solid state but are good conductiors in molten state or in their aqueous solutions. iv) The atomic size decreases across the period. v) Sodium chloride solution is neutral. ...