CLASS NOTES- Balancing Chemical Equations.pptx
... • The Law of Conservation of Mass as it relates to chemical changes of substances • The parts of a chemical reaction Learners will be able to… • Write and balance chemical equations ...
... • The Law of Conservation of Mass as it relates to chemical changes of substances • The parts of a chemical reaction Learners will be able to… • Write and balance chemical equations ...
Various Types of RXNS
... 5. Combustion Reactions: Combustion reactions can vary a good deal as soon as one steps out of the realm of hydrocarbons but the exam seldom indulges in other combustions unless they are simple combinations like the burning of a metal in air or oxygen. For the hydrocarbon combustions, the simple rul ...
... 5. Combustion Reactions: Combustion reactions can vary a good deal as soon as one steps out of the realm of hydrocarbons but the exam seldom indulges in other combustions unless they are simple combinations like the burning of a metal in air or oxygen. For the hydrocarbon combustions, the simple rul ...
Chapter 3—Time and Geology
... geochronology (27): The study of time as applied to Earth and planetary history. half-life (38): The time in which one-half of an original amount of a radioactive atoms decays to daughter products. Holocene Series (32): A term sometimes used to designate the period of time since the last major episo ...
... geochronology (27): The study of time as applied to Earth and planetary history. half-life (38): The time in which one-half of an original amount of a radioactive atoms decays to daughter products. Holocene Series (32): A term sometimes used to designate the period of time since the last major episo ...
1.10 Atomic structure - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... All matter is made up of particles called atoms. Atoms are very, very small. It is not possible to see an atom even under the most powerful light microscope. However, scientists and engineers have developed ways of producing images of atoms using other methods. ...
... All matter is made up of particles called atoms. Atoms are very, very small. It is not possible to see an atom even under the most powerful light microscope. However, scientists and engineers have developed ways of producing images of atoms using other methods. ...
Ch 5 Electron Structure
... spectral lines, but failed to explain any other element’s lines. • The behavior of electrons is still not fully understood, but it is known they do not move around the nucleus in circular orbits. ...
... spectral lines, but failed to explain any other element’s lines. • The behavior of electrons is still not fully understood, but it is known they do not move around the nucleus in circular orbits. ...
Development of Atomic Theory
... • A given compound always has elements in exactly the same proportions by weight or mass • Water as example ( 11% H and 89% O ) • Atoms combine in whole number ratios ( H2O ) ...
... • A given compound always has elements in exactly the same proportions by weight or mass • Water as example ( 11% H and 89% O ) • Atoms combine in whole number ratios ( H2O ) ...
Vocabulary List # 2 Covalent Bonding
... (σ bond) a bond formed when two atomic orbitals combine to form a molecular orbital that is symmetrical around the axis connecting the two atomic nuclei. ...
... (σ bond) a bond formed when two atomic orbitals combine to form a molecular orbital that is symmetrical around the axis connecting the two atomic nuclei. ...
notes-part-1
... because he didn't know about subatomic particles. Today, we know that the number of protons and neutrons in an atom determines the mass of an atom. Remember the terms like electron (e ), proton (p+), and neutron (n) — (see the chart below); however, there are a number of other terms used to describe ...
... because he didn't know about subatomic particles. Today, we know that the number of protons and neutrons in an atom determines the mass of an atom. Remember the terms like electron (e ), proton (p+), and neutron (n) — (see the chart below); however, there are a number of other terms used to describe ...
Scientific Measurement
... It takes 5,210 J of heat to melt 50 g of ethanol at its melting point. What is the heat of fusion of ethanol? q = mHf 5,210 = 50(Hf) = 104.2 J/g (solving for Hf, substance is not water so you cannot use Table B value) The five parts of the Kinetic Molecular Theory are: A. Particles of an ideal gas m ...
... It takes 5,210 J of heat to melt 50 g of ethanol at its melting point. What is the heat of fusion of ethanol? q = mHf 5,210 = 50(Hf) = 104.2 J/g (solving for Hf, substance is not water so you cannot use Table B value) The five parts of the Kinetic Molecular Theory are: A. Particles of an ideal gas m ...
CHEMISTRY REVIEW - Haystack Observatory
... level. The farther out the orbit, the higher its energy. ...
... level. The farther out the orbit, the higher its energy. ...
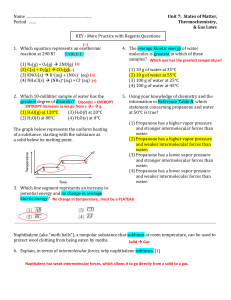
Name ………………………………………………… Unit 7: States of
... placed in the test tube, the test tube feels colder to the student’s hand. Describe the direction of heat flow between the test tube and the hand. [1] Heat flows from objects at higher temperatures to objects at lower temperatures. Heat will flow from the hand to the test tube. ...
... placed in the test tube, the test tube feels colder to the student’s hand. Describe the direction of heat flow between the test tube and the hand. [1] Heat flows from objects at higher temperatures to objects at lower temperatures. Heat will flow from the hand to the test tube. ...
Mechanism and Elementary Reactions
... simplify the rate expressions for complex reaction networks. Without further redue, let’s get into the details! The important difference between a reaction with an observed stoichiometry and an elementary reaction is that the stoichiometry of an elementary reaction defines the concentration dependen ...
... simplify the rate expressions for complex reaction networks. Without further redue, let’s get into the details! The important difference between a reaction with an observed stoichiometry and an elementary reaction is that the stoichiometry of an elementary reaction defines the concentration dependen ...
Microsoft Word
... whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen which wants 2 electrons around it). ...
... whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen which wants 2 electrons around it). ...
3-3 Molar Mass
... Atomic mass unit – exactly 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom Atomic mass of any other atom is determined by comparing it with the mass of carbon-12 ...
... Atomic mass unit – exactly 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom Atomic mass of any other atom is determined by comparing it with the mass of carbon-12 ...
Document
... 1. Work backward from the required reaction, using the reactants and products to know to manipulate the other given reactants at your disposal. 2. Reverse any reactions as needed to give the required reactants and products. ...
... 1. Work backward from the required reaction, using the reactants and products to know to manipulate the other given reactants at your disposal. 2. Reverse any reactions as needed to give the required reactants and products. ...
atomic theory - chemistryatdulwich
... approximately one hundred thousand times greater than the radius of the nucleus. The nucleus has a very high density. This is because the protons, which all have ‘like’ charges are drawn very close together by very powerful nuclear forces. These forces need to be powerful as they Topic2atomictheory ...
... approximately one hundred thousand times greater than the radius of the nucleus. The nucleus has a very high density. This is because the protons, which all have ‘like’ charges are drawn very close together by very powerful nuclear forces. These forces need to be powerful as they Topic2atomictheory ...
Redox Introduction
... 2. Oxidation is the process by which electrons are apparently removed from an atom or group of atoms. 3. Reduction is the process by which electrons are apparently added to atoms or groups of atoms. 3. Any substance in a reaction which loses electrons is a reducing agent. 4. Any substance in a react ...
... 2. Oxidation is the process by which electrons are apparently removed from an atom or group of atoms. 3. Reduction is the process by which electrons are apparently added to atoms or groups of atoms. 3. Any substance in a reaction which loses electrons is a reducing agent. 4. Any substance in a react ...
Ions and Ionic Compounds
... The Modern View of Atomic Structure The atom consists of positive, negative, and neutral entities (protons, electrons, and neutrons). Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, which is small. Most of the mass of the atom is due to the nucleus. There can be a variable number of ne ...
... The Modern View of Atomic Structure The atom consists of positive, negative, and neutral entities (protons, electrons, and neutrons). Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, which is small. Most of the mass of the atom is due to the nucleus. There can be a variable number of ne ...
Atomic structure and periodic table
... A periodic table is a horizontal and vertical arrangement of elements according to their atomic numbers. This table was successfully arranged in 1913 by the British scientist Henry Moseley from the previous work of the Russian Scientist Dmitri Mendeleev. The horizontal arrangement forms period. Atom ...
... A periodic table is a horizontal and vertical arrangement of elements according to their atomic numbers. This table was successfully arranged in 1913 by the British scientist Henry Moseley from the previous work of the Russian Scientist Dmitri Mendeleev. The horizontal arrangement forms period. Atom ...
The Wave Mechanical Model of the Atom
... Note: Now that with more orbitals available, many more electronic transitions are possible, thus explaining all the extra lines in the spectra observed earlier. The letters correspond to the first letter in each series of lines observed. The electrons fill according to the following set of rules: ...
... Note: Now that with more orbitals available, many more electronic transitions are possible, thus explaining all the extra lines in the spectra observed earlier. The letters correspond to the first letter in each series of lines observed. The electrons fill according to the following set of rules: ...
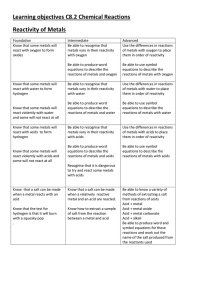
Learning objectives C8.2 Chemical Reactions Reactivity of Metals
... symbol equations for these reactions and work out the name of the salt produced from the reactants used ...
... symbol equations for these reactions and work out the name of the salt produced from the reactants used ...