Lab 1.2
... your ideas in #2? If not, readjust your statement to explain you new ideas about the behavior of the electron. ...
... your ideas in #2? If not, readjust your statement to explain you new ideas about the behavior of the electron. ...
atom
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are comb ...
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are comb ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at http://www.ck12.org/about/ terms-of-use. ...
... licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at http://www.ck12.org/about/ terms-of-use. ...
Chapter 4 Elements and the Periodic Table The Periodic Table
... Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain six protons and six electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon12 is the most common isotope. ...
... Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain six protons and six electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon12 is the most common isotope. ...
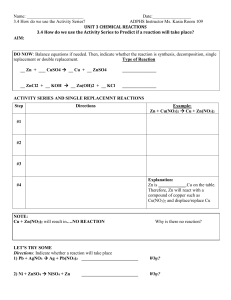
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
... 3.4 How do we use the Activity Series to Predict if a reaction will take place? AIM: ...
1 - KFUPM Faculty List
... orbitals in a subshell with a particular l value (ech ml refers to a different orbital) each orbital holds maximum of 2 electrons total number of orbitals in a shell is equal to n2 ...
... orbitals in a subshell with a particular l value (ech ml refers to a different orbital) each orbital holds maximum of 2 electrons total number of orbitals in a shell is equal to n2 ...
Metals
... exist as an array of ions or atoms bound to each other but with no recognisable molecules. The formula NaCl instead tells us that throughout a sample of NaCl sodium and chlorine atoms are present in the ratio 1:1. Because ionic compounds do not contain molecules the sum of the relative atomic masses ...
... exist as an array of ions or atoms bound to each other but with no recognisable molecules. The formula NaCl instead tells us that throughout a sample of NaCl sodium and chlorine atoms are present in the ratio 1:1. Because ionic compounds do not contain molecules the sum of the relative atomic masses ...
Unit 6 1 Quantum Mechanics
... NOT absolute. There are exceptions to the Aufbau Principle, although these exceptions are not tested on the AP exam. Hund’s Rule: When a sublevel contains degenerate orbitals, electrons are configured into the orbitals, one at a time, and are paired only when energy concerns become dominant. Pauli E ...
... NOT absolute. There are exceptions to the Aufbau Principle, although these exceptions are not tested on the AP exam. Hund’s Rule: When a sublevel contains degenerate orbitals, electrons are configured into the orbitals, one at a time, and are paired only when energy concerns become dominant. Pauli E ...
KISS Notes
... From the Medieval to the Modern After the collapse of the Roman Empire the various cultures that dominated the “Dark Ages” still had ironbased technologies. The next great technological change was the “Industrial Revolution” which began about 1750 in England. This had many aspects, but the big chang ...
... From the Medieval to the Modern After the collapse of the Roman Empire the various cultures that dominated the “Dark Ages” still had ironbased technologies. The next great technological change was the “Industrial Revolution” which began about 1750 in England. This had many aspects, but the big chang ...
CHEMISTRY
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
CHEMISTRY
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
discovery of atomic structure
... (neutral). Electrons (-) move in space around the nucleus (in the “planetary” model). The number of electrons always equals the number of protons when an atom is neutral. Atomic Number (Z): the number of protons in an atom. Mass Number (A): the total of protons and ...
... (neutral). Electrons (-) move in space around the nucleus (in the “planetary” model). The number of electrons always equals the number of protons when an atom is neutral. Atomic Number (Z): the number of protons in an atom. Mass Number (A): the total of protons and ...
II.I Corhon compounds lI.2 Hydrocorhons
... and correct structures for organic molecules. As you can see,the molecular formula of methane is CHa.However,molecular formulas are not very useful in organic chemistry.Molecular formulas cannot, by themselves,contain enough information about a molecule, such as the €rrangement of the atoms and the ...
... and correct structures for organic molecules. As you can see,the molecular formula of methane is CHa.However,molecular formulas are not very useful in organic chemistry.Molecular formulas cannot, by themselves,contain enough information about a molecule, such as the €rrangement of the atoms and the ...
5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure Chapter Outline Early Theories
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or more atoms of different elements. 5. Atoms combine to form compounds in simple whole number ratios. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or more atoms of different elements. 5. Atoms combine to form compounds in simple whole number ratios. ...
Ch 3 Sec 3 Highlighted
... Mass Number: the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope. From the periodic table the Mass Number is the atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 3 Given the identity of a nuclide, determine its number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
... Mass Number: the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope. From the periodic table the Mass Number is the atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 3 Given the identity of a nuclide, determine its number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
CI-754E_08FL_OneTopicManyLessons_Student1
... students. It allows students to get up and move around the room. This technique would probably be very memorable for the students, because they would know if they were a proton or neutron and if they were in the center or an electron surrounding the nucleus. Finally, lesson number five uses a more t ...
... students. It allows students to get up and move around the room. This technique would probably be very memorable for the students, because they would know if they were a proton or neutron and if they were in the center or an electron surrounding the nucleus. Finally, lesson number five uses a more t ...
Thermochemistry
... Hess’ Law- states that in going from a particular set of reactants to a particular set of products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or a series of steps. Hess’ Law allows scientists to determine the enthalpy of formation in a reaction they are unable t ...
... Hess’ Law- states that in going from a particular set of reactants to a particular set of products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or a series of steps. Hess’ Law allows scientists to determine the enthalpy of formation in a reaction they are unable t ...
Discussion 8
... Next to that scale, we use horizontal lines and arrows to show either a particular value of energy, or a change in energy. The size of the horizontal lines do not matter, only their vertal location along the scale. The size of the vertial arrows, however, show a specific range on the energy scale an ...
... Next to that scale, we use horizontal lines and arrows to show either a particular value of energy, or a change in energy. The size of the horizontal lines do not matter, only their vertal location along the scale. The size of the vertial arrows, however, show a specific range on the energy scale an ...
Document
... 8. A weighed sample of crystalline sodium carbonate Na2 CO3 and H2O, was heated in a crucible until there was no further change in mass. The mass of the sample reduced by 145%. Calculate the number of moles (n) of the water of crystallization ( Na = 23, O=16, C = 12 H = 1 ) ( 3 Marks ) ...
... 8. A weighed sample of crystalline sodium carbonate Na2 CO3 and H2O, was heated in a crucible until there was no further change in mass. The mass of the sample reduced by 145%. Calculate the number of moles (n) of the water of crystallization ( Na = 23, O=16, C = 12 H = 1 ) ( 3 Marks ) ...
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure and Properties
... Core electrons shield valence electrons better than do other valence electrons. The nuclear charge experienced by an electron affects the size and energy of its orbitals, so it is an important factor in determining the properties of the valence electrons and orbitals. However, a valence electron is ...
... Core electrons shield valence electrons better than do other valence electrons. The nuclear charge experienced by an electron affects the size and energy of its orbitals, so it is an important factor in determining the properties of the valence electrons and orbitals. However, a valence electron is ...
2. CHEMICAL ACTIVITY of the METALS 3. PATTERNS of the
... • brass, a mixture of z).................... and ................... • aa)...................................., with a very low melting point, is an alloy of ab).................................. and .................................... and is used in ac)..................................... and ... ...
... • brass, a mixture of z).................... and ................... • aa)...................................., with a very low melting point, is an alloy of ab).................................. and .................................... and is used in ac)..................................... and ... ...
Chemistry Simulations
... CH.2 The student will investigate and understand that the placement of elements on the periodic table is a function of their atomic structure. CH.3 The student will investigate and understand how conservation of energy and matter is expressed in chemical formulas and balanced equations. CH.4 The stu ...
... CH.2 The student will investigate and understand that the placement of elements on the periodic table is a function of their atomic structure. CH.3 The student will investigate and understand how conservation of energy and matter is expressed in chemical formulas and balanced equations. CH.4 The stu ...
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
... 3. • Only change the coefficient ( the number in front of the formula ) when balancing. This tells us how many of each molecule or atom we have in the balanced equation. If there is no number in front, a " 1 " is there but we usually leave out the 1's. • Do not change subscripts to balance. They are ...
... 3. • Only change the coefficient ( the number in front of the formula ) when balancing. This tells us how many of each molecule or atom we have in the balanced equation. If there is no number in front, a " 1 " is there but we usually leave out the 1's. • Do not change subscripts to balance. They are ...