Chapter 28: Inside the Atom
... 28.2 Pauli exclusion principle According to the quantum theory, two electrons in an atom can never be in the same quantum state at the same time. This rule is known as the Pauli exclusion principle after Wolfgang Pauli, the physicist who discovered it. Once all the quantum states in the first ...
... 28.2 Pauli exclusion principle According to the quantum theory, two electrons in an atom can never be in the same quantum state at the same time. This rule is known as the Pauli exclusion principle after Wolfgang Pauli, the physicist who discovered it. Once all the quantum states in the first ...
Regents Chemistry - Scarsdale Schools
... smaller and smaller), the wavelength of the electron must become shorter and shorter so that it can “fit” into the confining space. As its wavelength becomes shorter, the electron’s energy increases. Eventually, the energy possessed by the electron due to its confinement becomes sufficiently great t ...
... smaller and smaller), the wavelength of the electron must become shorter and shorter so that it can “fit” into the confining space. As its wavelength becomes shorter, the electron’s energy increases. Eventually, the energy possessed by the electron due to its confinement becomes sufficiently great t ...
mineral
... 1. An __________ is a substance that can not be broken down into simpler substance by chemical or physical means. atom is the smallest particle of matter that contains the 2. An _____ characteristics of an element. protons 3. The number of __________ in a nucleus of an atom is called the atomic numb ...
... 1. An __________ is a substance that can not be broken down into simpler substance by chemical or physical means. atom is the smallest particle of matter that contains the 2. An _____ characteristics of an element. protons 3. The number of __________ in a nucleus of an atom is called the atomic numb ...
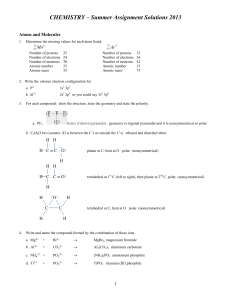
CHEMISTRY – Summer Assignment Solutions 2013
... states the arrangement of electrons within the electron cloud; includes the energy level, orbital type and number of electrons. examples: H = 1s1 N = 1s2 2s2 2p3 Notes All families have the same valence electron configuration noble gas configuration ns2np6 halogen configuration ns2np5 chalcogen (O-f ...
... states the arrangement of electrons within the electron cloud; includes the energy level, orbital type and number of electrons. examples: H = 1s1 N = 1s2 2s2 2p3 Notes All families have the same valence electron configuration noble gas configuration ns2np6 halogen configuration ns2np5 chalcogen (O-f ...
Ch. 41 Atomic Structure
... This is consistent with our model of multielectron atoms. Bombarding an atom with a high-energy electron can knock an atomic electron out of the innermost K shell. K x rays are produced when an electron from the L shell falls into the K-shell vacancy. The energy of an electron in each shell depends ...
... This is consistent with our model of multielectron atoms. Bombarding an atom with a high-energy electron can knock an atomic electron out of the innermost K shell. K x rays are produced when an electron from the L shell falls into the K-shell vacancy. The energy of an electron in each shell depends ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... mixtures such as those in blood. The centrifuge spins rapidly and causes the solid to settle to the bottom. Ex. Separating blood ...
... mixtures such as those in blood. The centrifuge spins rapidly and causes the solid to settle to the bottom. Ex. Separating blood ...
General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... chemist John Dalton, is defined as one twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12. Because the isotopes of an element do not occur with equal frequency, the average atomic mass unit (the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes) is used. For example, hydrogen has th ...
... chemist John Dalton, is defined as one twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12. Because the isotopes of an element do not occur with equal frequency, the average atomic mass unit (the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes) is used. For example, hydrogen has th ...
chem100chapter5 - Imperial Valley College Faculty Websites
... mass units” was devised to express the masses of elements using simple ...
... mass units” was devised to express the masses of elements using simple ...
2007 local exam - American Chemical Society
... HCl? (Assume all graphs are plotted on the same scale as the one shown above.) (A) ...
... HCl? (Assume all graphs are plotted on the same scale as the one shown above.) (A) ...
chemical reaction
... Expressing Chemical Reactions Ex.: Silver tarnishing (reaction between silver and the sulfur in air) Word equation: silver + sulfur -> silver sulfide Chemical Equation: Ag +S8 -> Ag2S ...
... Expressing Chemical Reactions Ex.: Silver tarnishing (reaction between silver and the sulfur in air) Word equation: silver + sulfur -> silver sulfide Chemical Equation: Ag +S8 -> Ag2S ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... A metal cation, such as Cu2+ gains electrons to become neutral metal: e.g. Cu2+ + 2e Cu. Choices I and II increase the number of electrons moving through the system, so more metal is deposited. As the metal’s charge increases, more e-’s are required per mole of metal… so less metal is deposited. ...
... A metal cation, such as Cu2+ gains electrons to become neutral metal: e.g. Cu2+ + 2e Cu. Choices I and II increase the number of electrons moving through the system, so more metal is deposited. As the metal’s charge increases, more e-’s are required per mole of metal… so less metal is deposited. ...
CHEMISTRY
... • Dalton’s atomic theory easily explained conservation of mass in a reaction as the result of the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms. ...
... • Dalton’s atomic theory easily explained conservation of mass in a reaction as the result of the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms. ...
CHEMISTRY
... • Dalton’s atomic theory easily explained conservation of mass in a reaction as the result of the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms. ...
... • Dalton’s atomic theory easily explained conservation of mass in a reaction as the result of the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms. ...
Structure and Bonding
... A group of an atom’s electrons with the same principal quantum number Each orbital can be occupied by two electrons First shell contains one s orbital, denoted 1s, which holds only two electrons Second shell contains four orbitals, one s orbital (2s) and three p orbitals (2p), which hold a total of ...
... A group of an atom’s electrons with the same principal quantum number Each orbital can be occupied by two electrons First shell contains one s orbital, denoted 1s, which holds only two electrons Second shell contains four orbitals, one s orbital (2s) and three p orbitals (2p), which hold a total of ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... From his experiments and observations, as well as the work from peers of his time, Dalton proposed a new theory of the atom. This later became known as Dalton’s atomic theory. The general tenets of this theory were as follows: • All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • Ato ...
... From his experiments and observations, as well as the work from peers of his time, Dalton proposed a new theory of the atom. This later became known as Dalton’s atomic theory. The general tenets of this theory were as follows: • All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • Ato ...
Elements, Molecules, and Ions Chapter 2 CHEMA1301
... chemical reaction is the same as before the reaction. Dalton used his theory to explain the law of multiple proportions: If two elements A and B are combined to form more than one compound, the masses of B that can combine with the same mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... chemical reaction is the same as before the reaction. Dalton used his theory to explain the law of multiple proportions: If two elements A and B are combined to form more than one compound, the masses of B that can combine with the same mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. ...
wahideh chemistry eportfolio hw
... sometimes explosively. However, many sodium compounds have a variety of uses in industry, medicine, and everyday life. Physical Properties: Sodium is a silvery-white metal with a waxy appearance. It is soft enough to be cut with a knife. The surface is bright and shiny when first cut, but quickly be ...
... sometimes explosively. However, many sodium compounds have a variety of uses in industry, medicine, and everyday life. Physical Properties: Sodium is a silvery-white metal with a waxy appearance. It is soft enough to be cut with a knife. The surface is bright and shiny when first cut, but quickly be ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... • This quantum number defines the shape of the orbital. • Allowed values of l are integers ranging from 0 to n − 1. • We use letter designations to communicate the different values of l and, therefore, the shapes and types of orbitals. ...
... • This quantum number defines the shape of the orbital. • Allowed values of l are integers ranging from 0 to n − 1. • We use letter designations to communicate the different values of l and, therefore, the shapes and types of orbitals. ...
College Chemistry 1 Note Guide(free download)
... 6. give a brief description of how a basic mass spectrometer works. 7. give a general overview of the periodic table and point out where types of elements and families/groups of elements are found. 8. introduce the concept of the mole roadmap and demonstrate how to use this concept in chemical calcu ...
... 6. give a brief description of how a basic mass spectrometer works. 7. give a general overview of the periodic table and point out where types of elements and families/groups of elements are found. 8. introduce the concept of the mole roadmap and demonstrate how to use this concept in chemical calcu ...
Chapter 3 Reading
... A mixture of 1.50 mol of Al and 3.00 mol of Cl2 is •Often, one or more reactants is present in excess. allowed to react. (a) Which is the limiting reactant? •Therefore, at the end of reaction those reactants present in excess will (b) How many moles of AlCl3 are formed? still be in the reaction mixt ...
... A mixture of 1.50 mol of Al and 3.00 mol of Cl2 is •Often, one or more reactants is present in excess. allowed to react. (a) Which is the limiting reactant? •Therefore, at the end of reaction those reactants present in excess will (b) How many moles of AlCl3 are formed? still be in the reaction mixt ...
AP Chemistry Ch. 3 Sections 3.7-3.8 Notes Chemical Equations
... Check your answer to see if: The number of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios (reduced). ...
... Check your answer to see if: The number of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios (reduced). ...
OCR A Level Physics B Delivery Guide Learner Resource 1: Atomic
... © OCR 2015 - This resource may be freely copied and distributed, as long as the OCR logo and this message remain intact and OCR is acknowledged as the originator of this work. OCR acknowledges the use of the following content: Please get in touch if you want to discuss the accessibility of resources ...
... © OCR 2015 - This resource may be freely copied and distributed, as long as the OCR logo and this message remain intact and OCR is acknowledged as the originator of this work. OCR acknowledges the use of the following content: Please get in touch if you want to discuss the accessibility of resources ...
Midterm 1 Spring 2004
... __A liter is a volume equal to 100 cm3. __The discovery of the nucleus assisted Dalton in his development of atomic theory. __A free proton has a mass of exactly one atomic mass unit. __Oxygen, sulfur and bromine are all nonmetallic elements. __Isotopes of the same element always have the same numbe ...
... __A liter is a volume equal to 100 cm3. __The discovery of the nucleus assisted Dalton in his development of atomic theory. __A free proton has a mass of exactly one atomic mass unit. __Oxygen, sulfur and bromine are all nonmetallic elements. __Isotopes of the same element always have the same numbe ...