How the Viruses Can Evade Host Defense Mechanisms
... stimulate the production of cytokines such as TNF-_, IL-1, and IL-6 by macrophages or endothelial cells. These cytokines can activate macrophages. Phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages and other phagocytic cells is another highly effective line of innate defense. However, some types of bacteria t ...
... stimulate the production of cytokines such as TNF-_, IL-1, and IL-6 by macrophages or endothelial cells. These cytokines can activate macrophages. Phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages and other phagocytic cells is another highly effective line of innate defense. However, some types of bacteria t ...
ppt - med.muni
... • Mesangioproliferative GN with deposits of IgA, event. C3 • Etiology: - unknown, clinical manifestation is associated with infection – with latent period 2-3 days - association with HLA (DQ, DP) T-lymphocytes produce levels of IL-2 (+ IR-2R) and they ...
... • Mesangioproliferative GN with deposits of IgA, event. C3 • Etiology: - unknown, clinical manifestation is associated with infection – with latent period 2-3 days - association with HLA (DQ, DP) T-lymphocytes produce levels of IL-2 (+ IR-2R) and they ...
Hypersensitivities
... Type IV Hypersensitivity Does not involve antibody Develops 24-72 hours after exposure Examples o Acute graft rejection, skin test for TB, contact allergic reactions, and some autoimmune diseases Management includes allergen avoidance, corticosteroids and immunosuppressives. Autoimmunity ...
... Type IV Hypersensitivity Does not involve antibody Develops 24-72 hours after exposure Examples o Acute graft rejection, skin test for TB, contact allergic reactions, and some autoimmune diseases Management includes allergen avoidance, corticosteroids and immunosuppressives. Autoimmunity ...
IgM - Akademik Ciamik 2010
... Agglutination assay that test for the presence of an ab depend on the availability of a particle that is coated with the appropriate ag. The particle can be an RBC (hemaglutination), synthetic particle (latex agglutination) and can be seen in the tube, microtitres well or ...
... Agglutination assay that test for the presence of an ab depend on the availability of a particle that is coated with the appropriate ag. The particle can be an RBC (hemaglutination), synthetic particle (latex agglutination) and can be seen in the tube, microtitres well or ...
Nobel Prize of physiology or medicine (1984) (4) Part I The
... The second theory: (Reactivity against self antigen creates diversity) It was known that the immune system learns to be tolerant to the individual's own self; Jerns postulated that this learning took place in the thymus. (1971) Thymus gland ...
... The second theory: (Reactivity against self antigen creates diversity) It was known that the immune system learns to be tolerant to the individual's own self; Jerns postulated that this learning took place in the thymus. (1971) Thymus gland ...
Slide 1
... • Newborn babies receive antibodies from colostrum • Stimulates baby’s immune system – Studies demonstrate benefits for humans, at any age ...
... • Newborn babies receive antibodies from colostrum • Stimulates baby’s immune system – Studies demonstrate benefits for humans, at any age ...
The Human Immune System: Basics and then some…
... • In the case of tissue implants, they may be rejected if the tissue cells don’t have the proper proteins to inactivate the complement system in a different humans body. So the complement kills the cells! • In order for tissues to be accepted they also must have the proper MHC complex to pass as hum ...
... • In the case of tissue implants, they may be rejected if the tissue cells don’t have the proper proteins to inactivate the complement system in a different humans body. So the complement kills the cells! • In order for tissues to be accepted they also must have the proper MHC complex to pass as hum ...
Lecture notes
... The Y-shaped Ig molecule is composed of four polypeptide chains (held together by disulphide bonds) – two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. The N-terminal regions of paired heavy and light chains form an antigen combining site. Each chain is composed of a sequence of globular ...
... The Y-shaped Ig molecule is composed of four polypeptide chains (held together by disulphide bonds) – two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. The N-terminal regions of paired heavy and light chains form an antigen combining site. Each chain is composed of a sequence of globular ...
cellular basis of immunity
... determine ABO blood types and to detect influenza and measles viruses. 2. Opsonization: Antigen (microbe) is covered with antibodies that enhances its ingestion and lysis by phagocytic cells. ...
... determine ABO blood types and to detect influenza and measles viruses. 2. Opsonization: Antigen (microbe) is covered with antibodies that enhances its ingestion and lysis by phagocytic cells. ...
Topic 6.3 Defence against infectious disease
... microbes successfully invade body fluids or tissues damaged cells release histamine and other chemicals initiating inflammation ...
... microbes successfully invade body fluids or tissues damaged cells release histamine and other chemicals initiating inflammation ...
Streptococcal Serology powerpoint
... • Associated with large amount of M protein and a capsule • Due to immune response against Strep antigens similar to heart antigens. ...
... • Associated with large amount of M protein and a capsule • Due to immune response against Strep antigens similar to heart antigens. ...
T4 helper cell
... Drugs to Treat HIV Current drugs prevent the virus from replicating once it is inside T4 helper cells Other drugs block HIV at other stages of its infection and reproduction cycle Combinations of these drugs successful in slowing or stopping progress of HIV Serious side effects, drug-resist ...
... Drugs to Treat HIV Current drugs prevent the virus from replicating once it is inside T4 helper cells Other drugs block HIV at other stages of its infection and reproduction cycle Combinations of these drugs successful in slowing or stopping progress of HIV Serious side effects, drug-resist ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... serum, contains no cells or clotting proteins. Serum does, however, contain a high concentration of other proteins, including soluble antibody proteins, and is widely used in immunological investigations. The use of serum antibodies to detect antigens in vitro is called serology. • A variety of leuk ...
... serum, contains no cells or clotting proteins. Serum does, however, contain a high concentration of other proteins, including soluble antibody proteins, and is widely used in immunological investigations. The use of serum antibodies to detect antigens in vitro is called serology. • A variety of leuk ...
Surname 1 Name Instructor Course Date Human Immune System
... entirely physical sealed against the disease causing organisms. Other systems are therefore present to protect the body openings including lungs genitourinary tract and intestines. Lungs get protection from factors like sneezing and coughing that mechanically remove pathogens and other irritating su ...
... entirely physical sealed against the disease causing organisms. Other systems are therefore present to protect the body openings including lungs genitourinary tract and intestines. Lungs get protection from factors like sneezing and coughing that mechanically remove pathogens and other irritating su ...
Immunology Terms Phagocytosis- method of engulfing and
... Epitope- the specific aspect of an antigen that is recognized by a T cell B cell or antibody Immunoglobulins (Igs)- B cells there are five families of B cells IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE, and IgG Monoclonal Antibodies- antibodies specifically generated for the purpose of binding to specific targets used ofte ...
... Epitope- the specific aspect of an antigen that is recognized by a T cell B cell or antibody Immunoglobulins (Igs)- B cells there are five families of B cells IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE, and IgG Monoclonal Antibodies- antibodies specifically generated for the purpose of binding to specific targets used ofte ...
Vaccine
... adaptive immunity against fungal infections. – CD4+ and CD8+ T cells cooperate to eliminate the yeast ...
... adaptive immunity against fungal infections. – CD4+ and CD8+ T cells cooperate to eliminate the yeast ...
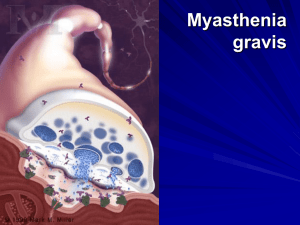
Myasthenia gravis
... The role of B-cell activating factor (BAFF) in myasthenia gravis B-cell activating factor (BAFF) is important in the differentiation and maturation of B cells and plasma cells. Although the mechanism(s) by which BAFF and its receptors help regulate B-cell function and tolerance is not known, it may ...
... The role of B-cell activating factor (BAFF) in myasthenia gravis B-cell activating factor (BAFF) is important in the differentiation and maturation of B cells and plasma cells. Although the mechanism(s) by which BAFF and its receptors help regulate B-cell function and tolerance is not known, it may ...
Cardiovascular System
... E. Factor VII, Calcium ions and platelet phospholipids combine to form prothrombin activator. Vitamin K is necessary for the liver to produce prothrombin and other clotting factors. F. Prothrombin activator combines with calcium ions and converts the inactive protein, Prothrombin, into its active fo ...
... E. Factor VII, Calcium ions and platelet phospholipids combine to form prothrombin activator. Vitamin K is necessary for the liver to produce prothrombin and other clotting factors. F. Prothrombin activator combines with calcium ions and converts the inactive protein, Prothrombin, into its active fo ...
Complement system
The complement system is a part of the immune system that helps or complements the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism. It is part of the innate immune system, which is not adaptable and does not change over the course of an individual's lifetime. However, it can be recruited and brought into action by the adaptive immune system.The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, in general synthesized by the liver, and normally circulating as inactive precursors (pro-proteins). When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end-result of this activation cascade is massive amplification of the response and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex. Over 30 proteins and protein fragments make up the complement system, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors. They account for about 5% of the globulin fraction of blood serum and can serve as opsonins.Three biochemical pathways activate the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the lectin pathway.