File
... POSSESSIVE PERSONAL PRONOUNS: my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, theirs INDEFINITE PRONOUNS: Anybody, anyone, each, either, none, someone, somebody, both, everyone, no one, neither, many, few, several, one. INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS: who, whom, what, which, whose DEMO ...
... POSSESSIVE PERSONAL PRONOUNS: my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, theirs INDEFINITE PRONOUNS: Anybody, anyone, each, either, none, someone, somebody, both, everyone, no one, neither, many, few, several, one. INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS: who, whom, what, which, whose DEMO ...
IDO
... When the movie comes out, I will have read the book. When you graduate, you will have been in school 13 years. ...
... When the movie comes out, I will have read the book. When you graduate, you will have been in school 13 years. ...
Semi-auxiliaries
... auxiliary with nearly the same meaning. Example: I am able to go = I can go. Have to ...
... auxiliary with nearly the same meaning. Example: I am able to go = I can go. Have to ...
5. SC = Subject Complement (“completes” or complements the
... (verb + ing) used as noun verb used as adjective ...
... (verb + ing) used as noun verb used as adjective ...
POS
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. The word it stands for is the antecedent. Personal Pronouns (refers to a specific person or thing) I, me, we, us, you, he, him, she, her, it, they them Indefinite Pronouns (refers to persons, ...
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. The word it stands for is the antecedent. Personal Pronouns (refers to a specific person or thing) I, me, we, us, you, he, him, she, her, it, they them Indefinite Pronouns (refers to persons, ...
Participles
... A participle is a form of a verb, but it is not a used as a verb. Participles can be used as adjectives because they modify, or describe, nouns. To form most participles, use the -ed or -ing forms for regular verbs. Examples: ...
... A participle is a form of a verb, but it is not a used as a verb. Participles can be used as adjectives because they modify, or describe, nouns. To form most participles, use the -ed or -ing forms for regular verbs. Examples: ...
Grammar Definition Example Conjunction Used to join two ideas
... A clause using who, whom, which, whose to relate back to the noun. Clause does not make sense by itself. ...
... A clause using who, whom, which, whose to relate back to the noun. Clause does not make sense by itself. ...
WORD PLAY
... WORD PLAY By Peter Gauthier In correct grammar every verb in a clause or sentence must agree in number and person with its subject. Most nouns (subjects) indicate a plural by an ‘s’ ending. For verbs, the third person singular usually has the ‘s’ ending. Beyond this, there are a few odd or special c ...
... WORD PLAY By Peter Gauthier In correct grammar every verb in a clause or sentence must agree in number and person with its subject. Most nouns (subjects) indicate a plural by an ‘s’ ending. For verbs, the third person singular usually has the ‘s’ ending. Beyond this, there are a few odd or special c ...
REFERRING TO THE PAST, PRESENT AND FUTURE THROUGH
... WORDS WHICH, IN SOME SENSES, MAY BE CONSIDERED OPPOSITES OR EXTREMES. ...
... WORDS WHICH, IN SOME SENSES, MAY BE CONSIDERED OPPOSITES OR EXTREMES. ...
Verb Review
... c. writes a sentence on the board that describes a group of those verbs i. Things we do with our feet ii. Things we do alone, etc. d. asks students to make a list of the verbs that fit into that sentence (either individually or in groups) e. gives the students a specific amount of time to complete t ...
... c. writes a sentence on the board that describes a group of those verbs i. Things we do with our feet ii. Things we do alone, etc. d. asks students to make a list of the verbs that fit into that sentence (either individually or in groups) e. gives the students a specific amount of time to complete t ...
Grammar Points Summary by Chapter: Para Empezar
... Conjugation of IR (to go) tan / tantos (making comparisons) saber and conocer (TO KNOW) Hace + time (to tell how long something has been going on) ...
... Conjugation of IR (to go) tan / tantos (making comparisons) saber and conocer (TO KNOW) Hace + time (to tell how long something has been going on) ...
Sentence 2 - Wed 1
... coordinating conjunction (1), linking verb (2), participle (2), pronoun (3), proper noun (2) ...
... coordinating conjunction (1), linking verb (2), participle (2), pronoun (3), proper noun (2) ...
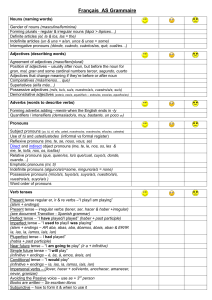
Français AS Grammaire
... Gender of nouns (masculine/feminine) Forming plurals - regular & irregular nouns (lápiz > lápices…) Definite articles (el, la & los, las = the) Indefinite articles (un & una = a/an, unos & unas = some) Interrogative pronouns (dónde, cuándo, cuántos/as, qué, cual/es…) Adjectives (describing words) Ag ...
... Gender of nouns (masculine/feminine) Forming plurals - regular & irregular nouns (lápiz > lápices…) Definite articles (el, la & los, las = the) Indefinite articles (un & una = a/an, unos & unas = some) Interrogative pronouns (dónde, cuándo, cuántos/as, qué, cual/es…) Adjectives (describing words) Ag ...
-ing forms in English
... I am talking to you right now. (present progressive or present continuous) I have been thinking a lot about this decision. (present perfect progressive or present perfect continuous) You were already sleeping. (past progressive or past continuous) I will be taking my friend to the airport. (future p ...
... I am talking to you right now. (present progressive or present continuous) I have been thinking a lot about this decision. (present perfect progressive or present perfect continuous) You were already sleeping. (past progressive or past continuous) I will be taking my friend to the airport. (future p ...
Kirby`s POS "beachball" ppt.
... How often? Never, twice, sometimes How long? Hardly, greatly, very How much? More, less ...
... How often? Never, twice, sometimes How long? Hardly, greatly, very How much? More, less ...
sentence supplement(MP4.3)
... Sentence complement is a group of word that completes the subject. Verbs can be divided into transitive verbs, intransitive verbs and linking verbs. A transitive verb expresses action that passes from the subject of the verb to an object of the verb. The subject of the verb is the person or thing th ...
... Sentence complement is a group of word that completes the subject. Verbs can be divided into transitive verbs, intransitive verbs and linking verbs. A transitive verb expresses action that passes from the subject of the verb to an object of the verb. The subject of the verb is the person or thing th ...
NOUNS – name persons, places, things, or ideas
... Always linking verbs: Forms of be: am, is, are, was, were, has been, are being, might have been, etc., and become, and seem Can be linking verbs: appear, feel, grow, look, prove, remain, smell, sound, taste, and turn ...
... Always linking verbs: Forms of be: am, is, are, was, were, has been, are being, might have been, etc., and become, and seem Can be linking verbs: appear, feel, grow, look, prove, remain, smell, sound, taste, and turn ...
PARTS OF SPEECH ADJECTIVE: Describes a noun or pronoun
... PRONOUN: Takes the place of a person, place, or thing: can function any way a noun can function; may be nominative, objective, or possessive; may be singular or plural; may be personal (therefore, first, second or third person), demonstrative, intensive, interrogative, reflexive, relative, or indefi ...
... PRONOUN: Takes the place of a person, place, or thing: can function any way a noun can function; may be nominative, objective, or possessive; may be singular or plural; may be personal (therefore, first, second or third person), demonstrative, intensive, interrogative, reflexive, relative, or indefi ...
VERB - Minooka Community High School
... some other kind of emotion. It can also be used as a filler. • EX: Hey, like, well, ouch, oh • EX: Ouch! Did you step on my toe?= STRONG ...
... some other kind of emotion. It can also be used as a filler. • EX: Hey, like, well, ouch, oh • EX: Ouch! Did you step on my toe?= STRONG ...
verb - School District of Cambridge
... Why know the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs? It’s in the dictionary! ...
... Why know the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs? It’s in the dictionary! ...
The verbal system in Old English (grammatical categories
... can hardly be regarded as a marker of aspect, it could change the aspective meaning of the verb by making it perfective, but it could also change its lexical meaning, e.g. beran – зeberan ‘carry’ – ‘bear a child’. It follows that the prefix зe- should rather be regarded as an element of word-buildin ...
... can hardly be regarded as a marker of aspect, it could change the aspective meaning of the verb by making it perfective, but it could also change its lexical meaning, e.g. beran – зeberan ‘carry’ – ‘bear a child’. It follows that the prefix зe- should rather be regarded as an element of word-buildin ...
Nombre: Fecha: Study guide for final exam. Spanish II. Verb tenses
... a. Present, past (imperfect and preterite), future. b. Irregular preterite; unidad 3 leccion 2. c. Irregular preterite of stem changing verbs; unidad 3 leccion 2. d. Irregular preterite of the verbs that end in –car, -zar, -gar. e. All other irregular verbs in any of the tenses. Learn how to conjuga ...
... a. Present, past (imperfect and preterite), future. b. Irregular preterite; unidad 3 leccion 2. c. Irregular preterite of stem changing verbs; unidad 3 leccion 2. d. Irregular preterite of the verbs that end in –car, -zar, -gar. e. All other irregular verbs in any of the tenses. Learn how to conjuga ...
Gerunds
... Participles Participles are adjectives that look like verbs. They usually end in ing or ed, but can also have irregular forms. Ex. Walking in the rain, the traveler searched for shelter. ...
... Participles Participles are adjectives that look like verbs. They usually end in ing or ed, but can also have irregular forms. Ex. Walking in the rain, the traveler searched for shelter. ...