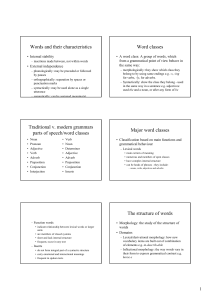
Words and their characteristics Word classes Traditional v. modern
... down into grammatical parts e.g. yes, boy, • affixes: meaningful dependent elements added before or after the base form – prefixes: pure lexical role; allow construction of many new words – suffixes: most purely lexical: change meaning of base form e.g. -ness, -ship, -able • few are purely grammatic ...
... down into grammatical parts e.g. yes, boy, • affixes: meaningful dependent elements added before or after the base form – prefixes: pure lexical role; allow construction of many new words – suffixes: most purely lexical: change meaning of base form e.g. -ness, -ship, -able • few are purely grammatic ...
Grammar Notes - Trimble County Schools
... • Correlative Conjunctions- must be used together to join words or clauses. – Either/or – Neither/ nor – Both/ and – Not only/ but also – Whether/ or ...
... • Correlative Conjunctions- must be used together to join words or clauses. – Either/or – Neither/ nor – Both/ and – Not only/ but also – Whether/ or ...
Phrases: Prepositional, Verbal, Absolute, and Appositive
... 1. Prepositional Phrases, which are phrases that begin with a preposition followed by a noun or pronoun, along with any words that modify that noun. Ex: a) Jim went to school without his books. b) Behind the cushions John found more bits of food and other debris then he imagined possible. ...
... 1. Prepositional Phrases, which are phrases that begin with a preposition followed by a noun or pronoun, along with any words that modify that noun. Ex: a) Jim went to school without his books. b) Behind the cushions John found more bits of food and other debris then he imagined possible. ...
KEY P. 1
... 449: prepositions after particular words and expressions: you explain something to somebody 386.5 / 389.15: singular forms are used as modifiers before nouns in plural measuring expressions 559.2b: when we use a longer phrase as an adjective before a noun, we use hyphens ...
... 449: prepositions after particular words and expressions: you explain something to somebody 386.5 / 389.15: singular forms are used as modifiers before nouns in plural measuring expressions 559.2b: when we use a longer phrase as an adjective before a noun, we use hyphens ...
Grammar Glossary
... A pronoun is a word that stands in for a noun. There are different classes ofpronoun, the main types are: 1. Personal pronouns refer to people or things, such as ‘I’ or ‘you’. 2. Reflexive pronouns refer to people or things that are also the subject of the sentence and end with ‘-self’ or ‘-selves’. ...
... A pronoun is a word that stands in for a noun. There are different classes ofpronoun, the main types are: 1. Personal pronouns refer to people or things, such as ‘I’ or ‘you’. 2. Reflexive pronouns refer to people or things that are also the subject of the sentence and end with ‘-self’ or ‘-selves’. ...
The Parts of Speech - Welcome to The World of S
... An adjective describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. Answers the questions: ...
... An adjective describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. Answers the questions: ...
VERB - Ms. Stanton: English (GHS)
... ▫ They [S] waited for the lunch period to come. ▫ They [S] were anxious. ...
... ▫ They [S] waited for the lunch period to come. ▫ They [S] were anxious. ...
Year 1: Terminology Taught • Letter • Capital letter • Word • Singular
... Verb: The easiest way to identify verbs is by the ways they can be used: they usually have a tense, either present or past. Sometimes, we think of verbs as being action or ‘doing’ words. They show what someone or something is, has or does. e.g. I jumped into the swimming pool. My brother likes choc ...
... Verb: The easiest way to identify verbs is by the ways they can be used: they usually have a tense, either present or past. Sometimes, we think of verbs as being action or ‘doing’ words. They show what someone or something is, has or does. e.g. I jumped into the swimming pool. My brother likes choc ...
Year 4 - Crossley Fields
... Pronoun: A pronoun is a word that stands in for a noun or noun phrase. The most common type of pronoun is the personal pronoun, but many other words can also be used as pronouns, for example: ‘this’, ‘that’, ‘who’ and ‘which’. Pronouns can be singular (for example: ‘I’, ‘she’) or plural (for example ...
... Pronoun: A pronoun is a word that stands in for a noun or noun phrase. The most common type of pronoun is the personal pronoun, but many other words can also be used as pronouns, for example: ‘this’, ‘that’, ‘who’ and ‘which’. Pronouns can be singular (for example: ‘I’, ‘she’) or plural (for example ...
Phrases, Clauses, and Appositives
... A sentence requires a subject, predicate and a complete thought. Phrases, subordinate clauses, and appositives are missing the complete thought, and sometimes a subject and predicate. Let’s take a look at each one. 1. A phrase is a group of words that don’t have both a subject and a predicate. Phras ...
... A sentence requires a subject, predicate and a complete thought. Phrases, subordinate clauses, and appositives are missing the complete thought, and sometimes a subject and predicate. Let’s take a look at each one. 1. A phrase is a group of words that don’t have both a subject and a predicate. Phras ...
ELA THE 12 STEVEN AND TOMMY
... • A predicate adjective is an adjective that follows a linking verb and describes the subject. • A sentence for predicate adjective is: • The golf ball is white and round. ...
... • A predicate adjective is an adjective that follows a linking verb and describes the subject. • A sentence for predicate adjective is: • The golf ball is white and round. ...
A - Parts of Sentence Intro 11
... Follow the chart on the second page of the DGP notes for help APPOSITIVE - noun or pronoun that follows or renames another noun/pronoun. Ex. My son Beck likes trains. (place an = sign) ...
... Follow the chart on the second page of the DGP notes for help APPOSITIVE - noun or pronoun that follows or renames another noun/pronoun. Ex. My son Beck likes trains. (place an = sign) ...
verbs - SCHOOLinSITES
... Singular nominative: I, you, he, she, it Plural Nominative: we, you, they Singular objective: me, you, him, her, it Plural objective: us, you, them Singular possessive: my, your, his, her, its, mine, yours Plural possessive: our, your, their, ours, yours, theirs ...
... Singular nominative: I, you, he, she, it Plural Nominative: we, you, they Singular objective: me, you, him, her, it Plural objective: us, you, them Singular possessive: my, your, his, her, its, mine, yours Plural possessive: our, your, their, ours, yours, theirs ...
Newletter style - Monday
... Pronoun – takes the place of a noun Pe rso na l pro n ou n s – refers to a particular person, place, or thing 1st person pronouns—having to do with “ me ” (I, me, mine, we, us, our, ours) 2nd person—having to do with “ you ” (you, your, yours) 3rd person—having to do with “everyone else” (he, she, ...
... Pronoun – takes the place of a noun Pe rso na l pro n ou n s – refers to a particular person, place, or thing 1st person pronouns—having to do with “ me ” (I, me, mine, we, us, our, ours) 2nd person—having to do with “ you ” (you, your, yours) 3rd person—having to do with “everyone else” (he, she, ...
Parts of Speech and Their Function
... Article: a, an, the Pronoun: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they Adjective: small, exhausted, disgusting Verb: is building, moves, bought, has lived, had expected Adverb: very, unusually, fast, quickly Preposition: in, on, at, over, under, etc. Conjunction: and, but, for, or, nor, so, yet (coordintin ...
... Article: a, an, the Pronoun: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they Adjective: small, exhausted, disgusting Verb: is building, moves, bought, has lived, had expected Adverb: very, unusually, fast, quickly Preposition: in, on, at, over, under, etc. Conjunction: and, but, for, or, nor, so, yet (coordintin ...
Name - Scarsdale Schools
... 2. Possessive: Locate apostrophes. Nouns with apostrophes are probably possessive. Once you locate a noun with an apostrophe, check that it owns, possesses or “has,” something else. This means it’s possessive. There may be more than one possessive noun in a sentence, but sentences don’t have to have ...
... 2. Possessive: Locate apostrophes. Nouns with apostrophes are probably possessive. Once you locate a noun with an apostrophe, check that it owns, possesses or “has,” something else. This means it’s possessive. There may be more than one possessive noun in a sentence, but sentences don’t have to have ...
Prepositions
... 3- Phrasal (more than one word working as one preposition): on top of/ together with/ by means of/ in back of/ on behalf of/ in between NOTE: the first pronoun or noun following a preposition is its object. Ex. The bug was clinging to the girl’s upper lip. ...
... 3- Phrasal (more than one word working as one preposition): on top of/ together with/ by means of/ in back of/ on behalf of/ in between NOTE: the first pronoun or noun following a preposition is its object. Ex. The bug was clinging to the girl’s upper lip. ...
nouns, verbs, adjectives…
... Pronouns substitute for nouns, noun phrases, or other pronouns, and can also refer to people (I, you), places (that), things ...
... Pronouns substitute for nouns, noun phrases, or other pronouns, and can also refer to people (I, you), places (that), things ...