Chapter 4- The Periodic Table Section 1
... nucleus and its outermost electrons due to the cancellation of some of the positive charge by the negative charges of the inner electrons ...
... nucleus and its outermost electrons due to the cancellation of some of the positive charge by the negative charges of the inner electrons ...
C3 The Periodic Table
... element . • Mendeleev ordered the elements based on their atomic weights and arranged them so there was a pattern. • He left GAPS because he predicted new elements would fit in, as they were discovered. He was right! ...
... element . • Mendeleev ordered the elements based on their atomic weights and arranged them so there was a pattern. • He left GAPS because he predicted new elements would fit in, as they were discovered. He was right! ...
Periodic TABLE: Tables: PT, Table S
... atomic number. Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. 3.1v Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. 3.1w Elements can be differentiated by physical properties. Physical prop ...
... atomic number. Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. 3.1v Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. 3.1w Elements can be differentiated by physical properties. Physical prop ...
Chapter 5 - Geocities
... Alkaline-earth metals: Group 2 Transition elements: d-block elements with typical metallic properties Main-Group elements: p-block elements and s-block elements Halogens: Group 17 Section 3: Electron Configuration and Periodic Properties Atomic radius: ½ the distance between the nuclei of identical ...
... Alkaline-earth metals: Group 2 Transition elements: d-block elements with typical metallic properties Main-Group elements: p-block elements and s-block elements Halogens: Group 17 Section 3: Electron Configuration and Periodic Properties Atomic radius: ½ the distance between the nuclei of identical ...
periodic table - rosedalegrade9chemistry
... Scientists started trying to organize the known elements in the early 1800’s. Could the elements be organized based on properties like colour, smell or taste? Not really, because the characteristics or properties were not unique. Early scientists found a property unique to each element, atomic mass. ...
... Scientists started trying to organize the known elements in the early 1800’s. Could the elements be organized based on properties like colour, smell or taste? Not really, because the characteristics or properties were not unique. Early scientists found a property unique to each element, atomic mass. ...
Periodic Table Virtual Activity http://my.uzinggo.com/cplogin/ The
... 1. What is the first element of the periodic table ad why? ...
... 1. What is the first element of the periodic table ad why? ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... 21. Looking at the periodic table, which element would have similar chemical properties to Beryllium, Be? 22. Complete the following chart: Element Symbol Atomic ...
... 21. Looking at the periodic table, which element would have similar chemical properties to Beryllium, Be? 22. Complete the following chart: Element Symbol Atomic ...
The Periodic Table
... 4. Which side of the table do most of the non-metals tend to be found on? ________ 5. The only elements which are liquids are ___________________ and _________________. (hint: look in the fourth and the sixth periods ) 6. Name three elements which are found in more than one form. _____ _____ _____ 7 ...
... 4. Which side of the table do most of the non-metals tend to be found on? ________ 5. The only elements which are liquids are ___________________ and _________________. (hint: look in the fourth and the sixth periods ) 6. Name three elements which are found in more than one form. _____ _____ _____ 7 ...
p.1 - Ms Beaucage
... *3. Elements of Group (II)/2 are called: Alkaline-Earth (charge: +2) 4. Elements of Group 3-12 are called: Transition Elements(d block) *5. Group (VII)/17 elements are called: Halogens (charge: -1) *6. Group (VIII)/18 elements are called: Noble Gases 7. An element with both metallic and non metallic ...
... *3. Elements of Group (II)/2 are called: Alkaline-Earth (charge: +2) 4. Elements of Group 3-12 are called: Transition Elements(d block) *5. Group (VII)/17 elements are called: Halogens (charge: -1) *6. Group (VIII)/18 elements are called: Noble Gases 7. An element with both metallic and non metallic ...
Periodic Table Worksheet
... 4. Elements of Group 3-12 are called: Transition Elements *5. Group 17 elements are called: Halogens (charge: -1) *6. Group 18 elements are called: Noble Gases 7. An element with both metallic and non metallic properties is called a: metalloid or semi-metal 8. The majority of elements in the periodi ...
... 4. Elements of Group 3-12 are called: Transition Elements *5. Group 17 elements are called: Halogens (charge: -1) *6. Group 18 elements are called: Noble Gases 7. An element with both metallic and non metallic properties is called a: metalloid or semi-metal 8. The majority of elements in the periodi ...
Periodic Table Worksheet
... 4. Elements of Group 3-12 are called: Transition Elements *5. Group 17 elements are called: Halogens (charge: -1) *6. Group 18 elements are called: Noble Gases 7. An element with both metallic and non metallic properties is called a: metalloid or semi-metal 8. The majority of elements in the periodi ...
... 4. Elements of Group 3-12 are called: Transition Elements *5. Group 17 elements are called: Halogens (charge: -1) *6. Group 18 elements are called: Noble Gases 7. An element with both metallic and non metallic properties is called a: metalloid or semi-metal 8. The majority of elements in the periodi ...
PT objectives
... together if they react in similar ways. Examples of this in the periodic table include metals, nonmetals, and noble gases. Students know these are major groups of elements that have different physical properties. that the information that is organized in the periodic table is based on the observat ...
... together if they react in similar ways. Examples of this in the periodic table include metals, nonmetals, and noble gases. Students know these are major groups of elements that have different physical properties. that the information that is organized in the periodic table is based on the observat ...
Basics of the Periodic Table
... *Directions: Use the Periodic Table in your textbook to answer the following questions. Read carefully! ...
... *Directions: Use the Periodic Table in your textbook to answer the following questions. Read carefully! ...
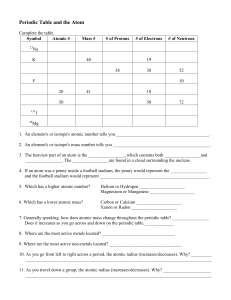
3.08_Periodic Table and the Atom
... 22. Elements of Groups 17 are called ________________________________. 23. The most active element in Group 17 is ________________________________. 24. Elements of Groups 18 are called ________________________________. 25. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Metals? ________________ 26. ...
... 22. Elements of Groups 17 are called ________________________________. 23. The most active element in Group 17 is ________________________________. 24. Elements of Groups 18 are called ________________________________. 25. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Metals? ________________ 26. ...
File
... THE PERIODIC TABLE TODAY Lesson Objective: Relate patterns in the physical and chemical properties of the elements to their positions in the periodic table. ...
... THE PERIODIC TABLE TODAY Lesson Objective: Relate patterns in the physical and chemical properties of the elements to their positions in the periodic table. ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE TODAY
... THE PERIODIC TABLE TODAY Lesson Objective: Relate patterns in the physical and chemical properties of the elements to their positions in the periodic table. ...
... THE PERIODIC TABLE TODAY Lesson Objective: Relate patterns in the physical and chemical properties of the elements to their positions in the periodic table. ...
Define the following: Electronegativity
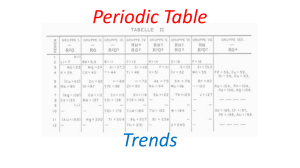
... 21. How does atomic radius change from left to right across a period in the periodic table? decreases 22. What element in the first period has the largest atomic radius? Hydrogen 23. What is the charge of a cation? + Anion? 24. What is the element with the lowest electronegativity value? Cesium 25. ...
... 21. How does atomic radius change from left to right across a period in the periodic table? decreases 22. What element in the first period has the largest atomic radius? Hydrogen 23. What is the charge of a cation? + Anion? 24. What is the element with the lowest electronegativity value? Cesium 25. ...
2- Periodic Trends
... Mendeleev (correctly) predicted the mass of elements yet to be discovered and left spaces open for them ...
... Mendeleev (correctly) predicted the mass of elements yet to be discovered and left spaces open for them ...
Subatomic Particles
... 2. have _____ charge (neutral) 3. their __________ is approximately equal to 1 __________________ (amu) • Electrons: 1. found _____________ the nucleus in the _____________ (electron cloud/orbits) 2. have a _____________ charge 3. their mass is approximately equal to _______ amu ...
... 2. have _____ charge (neutral) 3. their __________ is approximately equal to 1 __________________ (amu) • Electrons: 1. found _____________ the nucleus in the _____________ (electron cloud/orbits) 2. have a _____________ charge 3. their mass is approximately equal to _______ amu ...
UNIT 3 –TEST REVIEW 1 Atoms of which of the
... Zinc IS IN SAME GROUP AS Cd F gold (Au) G zinc (Zn) H silver (Ag) J copper (Cu) ...
... Zinc IS IN SAME GROUP AS Cd F gold (Au) G zinc (Zn) H silver (Ag) J copper (Cu) ...
Periodic Table
... Elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties Sometimes groups are called families ...
... Elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties Sometimes groups are called families ...
KEY - Unit 4 - Find Someone Who
... 4. Define ionization energy. Amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom ...
... 4. Define ionization energy. Amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.