CHMR_AYS_U4AlienPeriodicTableAnalysis_V01
... Table salt is made of _________. The number of ______________ is equal to the atomic number on the Periodic Table. ___________________ is important in the chemistry of life. The further to the right you move on the Periodic Table, the __________ _____________ the element is. As you move across the p ...
... Table salt is made of _________. The number of ______________ is equal to the atomic number on the Periodic Table. ___________________ is important in the chemistry of life. The further to the right you move on the Periodic Table, the __________ _____________ the element is. As you move across the p ...
File
... • Only valence electrons are shown. • Dots representing valence electrons are placed around the element symbols (on 4 sides, imagine a box around the symbol). • Electron dots are placed singularly, then they are paired. ...
... • Only valence electrons are shown. • Dots representing valence electrons are placed around the element symbols (on 4 sides, imagine a box around the symbol). • Electron dots are placed singularly, then they are paired. ...
Element Project - Dover Bay
... group 1, period 1, which is just down the street. Hydrogen has two siblings isotopes, deuterium and tritium, who has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. He also has a neighbor, the Alkali Metals who lives in the same street. Their names are Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidi ...
... group 1, period 1, which is just down the street. Hydrogen has two siblings isotopes, deuterium and tritium, who has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. He also has a neighbor, the Alkali Metals who lives in the same street. Their names are Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidi ...
Periodic Table (Wiki)
... periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's perio ...
... periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's perio ...
Periodic Table – Organizing the Elements
... The group with Li, Na, K etc is called Group 1A Group 1A elements are called the alkali metals Alkali metals are the MOST active metals ...
... The group with Li, Na, K etc is called Group 1A Group 1A elements are called the alkali metals Alkali metals are the MOST active metals ...
Atomic Structure - RHS Encore Academy
... as a model for the periodic table? (page 127) 4. Why did Mendeleev leave spaces in his table? (page 128) 5. How was Mendeleev able to predict the properties of elements that had not yet been discovered? (page 128) 6. How did the discovery of new elements such as gallium demonstrate the usefulness of ...
... as a model for the periodic table? (page 127) 4. Why did Mendeleev leave spaces in his table? (page 128) 5. How was Mendeleev able to predict the properties of elements that had not yet been discovered? (page 128) 6. How did the discovery of new elements such as gallium demonstrate the usefulness of ...
Metals
... • high luster (shiny), conductive (heat and electricity), malleable (bendable), ductile (stretchable), high density, high melting point • All except Hg are solids at room temperature • Chemical properties ...
... • high luster (shiny), conductive (heat and electricity), malleable (bendable), ductile (stretchable), high density, high melting point • All except Hg are solids at room temperature • Chemical properties ...
Periodic Table
... Distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outer edge of it’s electron cloud. ...
... Distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outer edge of it’s electron cloud. ...
Algebra - Militant Grammarian
... elements, shown as dots, and each colored different colors, shrink as the groups near the noble gases. In other words, the noble gases are the smallest dots. This is from left to right. If the picture is looked at from top to bottom, the dots grow larger as they near the bottom. The radii of the ele ...
... elements, shown as dots, and each colored different colors, shrink as the groups near the noble gases. In other words, the noble gases are the smallest dots. This is from left to right. If the picture is looked at from top to bottom, the dots grow larger as they near the bottom. The radii of the ele ...
chapter4problems
... 1) Classify each of the following elements as a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid. Also identify the element as an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, halogen, noble gas, or transition metal, as appropriate. a) As, b) Cl, c) Xe, d) Ba, e) Fe, f) P, g) Li, h) I, i) B, j) Si 2) What are valence electr ...
... 1) Classify each of the following elements as a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid. Also identify the element as an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, halogen, noble gas, or transition metal, as appropriate. a) As, b) Cl, c) Xe, d) Ba, e) Fe, f) P, g) Li, h) I, i) B, j) Si 2) What are valence electr ...
The Periodic Table - Palisades High School
... – Technetium (Tc) and Promethium (Pm) were detected in the stars, but not found on earth ...
... – Technetium (Tc) and Promethium (Pm) were detected in the stars, but not found on earth ...
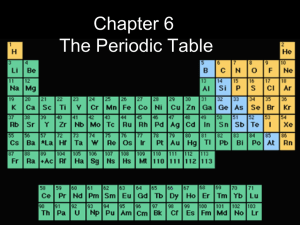
The Periodic Table
... Rows on the table are called PERIODS Columns on the table are called GROUPS or FAMILIES There are 7 periods and 18 groups. Electron config. are repeated in periods. similar e- config. in the same group. Elements in groups are also listed in order of their increasing n. ...
... Rows on the table are called PERIODS Columns on the table are called GROUPS or FAMILIES There are 7 periods and 18 groups. Electron config. are repeated in periods. similar e- config. in the same group. Elements in groups are also listed in order of their increasing n. ...
Chemistry Definitions
... A Compound is a substance that is made from the atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded. Extensive Properties depend upon the amount of matter present; do not depend upon the type of matter. (Examples: mass or volume…) Intensive Properties depend upon the type of matter do not depen ...
... A Compound is a substance that is made from the atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded. Extensive Properties depend upon the amount of matter present; do not depend upon the type of matter. (Examples: mass or volume…) Intensive Properties depend upon the type of matter do not depen ...
Core Chemistry Term 3 Final Exam 2007-08 S2
... b. substances with new chemical and physical properties are formed. c. the law of conservation of mass applies. d. all of the above. 90. What is the number that appears in front of a compound in a chemical reaction? a. subscript c. ratio b. superscript d. coefficient 91. Which equation is NOT balanc ...
... b. substances with new chemical and physical properties are formed. c. the law of conservation of mass applies. d. all of the above. 90. What is the number that appears in front of a compound in a chemical reaction? a. subscript c. ratio b. superscript d. coefficient 91. Which equation is NOT balanc ...
Notes: Unit 4: Periodic Table - Mr. Palermo`s Flipped Chemistry
... physical and chemical properties of that element. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. (3.1y) Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. ( ...
... physical and chemical properties of that element. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. (3.1y) Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. ( ...
Chemistry 1 Chapter 4, The Periodic Table
... information to produce the first orderly arrangement of all the elements known at the time (63 elements) •this arrangement is called a periodic table •He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass •he started a new row every time he noticed the properties repeated placing elements in t ...
... information to produce the first orderly arrangement of all the elements known at the time (63 elements) •this arrangement is called a periodic table •He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass •he started a new row every time he noticed the properties repeated placing elements in t ...
Periodicity - Walton High
... • Group 1 (except H) • All have only 1 valence electron • Most reactive metals; never found in pure state in nature ...
... • Group 1 (except H) • All have only 1 valence electron • Most reactive metals; never found in pure state in nature ...
Periodicity - Walton High
... • Group 1 (except H) • All have only 1 valence electron • Most reactive metals; never found in pure state in nature ...
... • Group 1 (except H) • All have only 1 valence electron • Most reactive metals; never found in pure state in nature ...
S8P1-a-and-f-study-guide
... the number of electrons each energy level can hold. The first energy level holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, the third holds 18, the fourth holds 32, and the fifth holds 50. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom is referred to as the atoms valence electrons. The numbe ...
... the number of electrons each energy level can hold. The first energy level holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, the third holds 18, the fourth holds 32, and the fifth holds 50. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom is referred to as the atoms valence electrons. The numbe ...
Period - scienceathylands
... • Each element has two fewer electrons than the next noble gas • Outer p sub-shell containing 5 electrons (needs 1 more to form a -1 ion ...
... • Each element has two fewer electrons than the next noble gas • Outer p sub-shell containing 5 electrons (needs 1 more to form a -1 ion ...
The Periodic Table - Ms. Simmons
... Mendeleev’s Contribution Mendeleev developed Periodic Law (Modern) Periodic Law: the elements, when listed in order of their atomic numbers, fall into recurring groups, so that elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals Periodic law is observed by all members of a column having the ...
... Mendeleev’s Contribution Mendeleev developed Periodic Law (Modern) Periodic Law: the elements, when listed in order of their atomic numbers, fall into recurring groups, so that elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals Periodic law is observed by all members of a column having the ...
periodic-data-and-trends-assign-2016
... 1. Based on your graphs, what is the trend in atomic radius across a period? Down a family? Observing the Atomic Number Vs. Atomic Radius graph the Alkali metals have a noticeably greater atomic radius then the other elements. Also, the noble gases have a substantially smaller atomic radius then all ...
... 1. Based on your graphs, what is the trend in atomic radius across a period? Down a family? Observing the Atomic Number Vs. Atomic Radius graph the Alkali metals have a noticeably greater atomic radius then the other elements. Also, the noble gases have a substantially smaller atomic radius then all ...
11-chemistry-exemplar-chapter-3
... electron repulsion outweighs the stability gained by achieving noble gas configuration. ...
... electron repulsion outweighs the stability gained by achieving noble gas configuration. ...
10C The Periodic Table
... 12. What does the atomic mass tell you about an element? 13. Why isn’t the atomic mass always a whole number? 14. Why don’t we include the mass of an atom’s electrons in the atomic mass? ...
... 12. What does the atomic mass tell you about an element? 13. Why isn’t the atomic mass always a whole number? 14. Why don’t we include the mass of an atom’s electrons in the atomic mass? ...
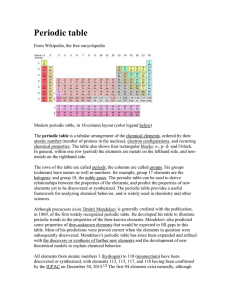
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.