The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... • The metals of the p block are generally harder and denser than the s-block alkaline-earth metals, but softer and less dense than the dblock metals. • The Noble Gases round out the p block elements and are in general, very un-reactive or inert gases. We have no known compounds of He, Ne, and Ar. ...
... • The metals of the p block are generally harder and denser than the s-block alkaline-earth metals, but softer and less dense than the dblock metals. • The Noble Gases round out the p block elements and are in general, very un-reactive or inert gases. We have no known compounds of He, Ne, and Ar. ...
17.3 The periodic table
... The periodic law The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing the atomic number, a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of the elements are noticed. ...
... The periodic law The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing the atomic number, a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of the elements are noticed. ...
The Periodic Table
... the elements fit into patterns better when they were arranged according to atomic number, rather than atomic weight. • The Periodic Law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. ...
... the elements fit into patterns better when they were arranged according to atomic number, rather than atomic weight. • The Periodic Law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. ...
Study Guide Chapter 6
... 7. List the various levels of stability from most stable to least stable (see Zones of Stability chart in the notebook). The Zones of Stability (see Zones of Stability chart in the notebook) shows that some electron configurations are more stable than others. The most stable electron configuration i ...
... 7. List the various levels of stability from most stable to least stable (see Zones of Stability chart in the notebook). The Zones of Stability (see Zones of Stability chart in the notebook) shows that some electron configurations are more stable than others. The most stable electron configuration i ...
lanthanides - schultz915
... Where are the most reactive metals located on the Periodic Table? a. b. c. d. ...
... Where are the most reactive metals located on the Periodic Table? a. b. c. d. ...
Relationships in The PeriodicTable
... 3. Periodic variation in the physical properties of the elements reflect differences in atomic structure. The metallic character of elements decreases across a period from metals through the metalloids and increases from top to bottom within a particular group of representative elements. 4. Atomic ...
... 3. Periodic variation in the physical properties of the elements reflect differences in atomic structure. The metallic character of elements decreases across a period from metals through the metalloids and increases from top to bottom within a particular group of representative elements. 4. Atomic ...
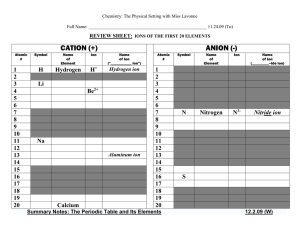
IONS OF THE FIRST 20 ELEMENTS
... The alkaline earth elements are metallic elements found in the second group of the periodic table. All alkaline earth elements have an oxidation number of +2, making them very reactive. Because of their reactivity, the alkaline metals are not found free in nature. The Alkaline Earth Metals are: Bery ...
... The alkaline earth elements are metallic elements found in the second group of the periodic table. All alkaline earth elements have an oxidation number of +2, making them very reactive. Because of their reactivity, the alkaline metals are not found free in nature. The Alkaline Earth Metals are: Bery ...
Science 2nd prep. 1st term Lesson 2 Graduation of the properties of
... reaction. To reach the nearest inert gas next them in the periodic table, ...
... reaction. To reach the nearest inert gas next them in the periodic table, ...
File
... d. Be sure to include the charge of the particles, the location where the particles are found, and their mass in relation to each other”. Word atom element atomic symbol proton electron neutron nucleus atomic number mass number average atomic mass isotope ions valence electrons atomic energy levels ...
... d. Be sure to include the charge of the particles, the location where the particles are found, and their mass in relation to each other”. Word atom element atomic symbol proton electron neutron nucleus atomic number mass number average atomic mass isotope ions valence electrons atomic energy levels ...
The Periodic Table
... periodic table (cont) • Dimitri Mendeleev, in 1869, used this information and produced the first orderly arrangement of all 63 known elements. • He arranged them in a similar way to Newlands and created the first periodic table. • Mendeleev started a new row each time he noticed that the chemical pr ...
... periodic table (cont) • Dimitri Mendeleev, in 1869, used this information and produced the first orderly arrangement of all 63 known elements. • He arranged them in a similar way to Newlands and created the first periodic table. • Mendeleev started a new row each time he noticed that the chemical pr ...
chem 1411 – chapter 8
... incompletely filled (n-1) d sub shells. Elements of 2B have completely filled (n-1) d sub shells. But are studied along with transition metals because their properties are similar to that of transition metals. 4. Lanthanides and Actinides Lanthanides constitute a group of elements with atomic number ...
... incompletely filled (n-1) d sub shells. Elements of 2B have completely filled (n-1) d sub shells. But are studied along with transition metals because their properties are similar to that of transition metals. 4. Lanthanides and Actinides Lanthanides constitute a group of elements with atomic number ...
LessonPlans_BowmanC_Sci8th_Dec 5 Teacher Bowman Class 8th
... (Then First Letter of Mendeleev Video Last Name) IV. Count the Compare Days of Table (How many the Week, Groups, How many Calendars, Cards Periods) II. Periodic Table with A Video Series about Mendeleev: Mendeleev Video III. Review Atomic Symbols, Atomic Mass, Atomic Number IV. We Do: Periodic Tabl ...
... (Then First Letter of Mendeleev Video Last Name) IV. Count the Compare Days of Table (How many the Week, Groups, How many Calendars, Cards Periods) II. Periodic Table with A Video Series about Mendeleev: Mendeleev Video III. Review Atomic Symbols, Atomic Mass, Atomic Number IV. We Do: Periodic Tabl ...
Section 6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
Untitled
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
Properties of Periodic Table and Periodic Trends
... Families (groups) had similar chemical and physical properties Discovered all elements in same family had same number of valence e- -- outermost electrons in highest energy level Why? ...
... Families (groups) had similar chemical and physical properties Discovered all elements in same family had same number of valence e- -- outermost electrons in highest energy level Why? ...
Elements and Their Properties
... isolated atoms. They are stable because their outermost energy levels are full. No naturally occurring noble gas compounds are known. ...
... isolated atoms. They are stable because their outermost energy levels are full. No naturally occurring noble gas compounds are known. ...
Unit 3 Test Review – Periodic Table (Yes, this is worth a grade!) Fill
... A) Valence electrons are attracted more to atoms containing a lot of protons. B) Valence electrons in larger atoms are more loosely held. C) Atoms with fewer protons will lose electrons easily. D) Atoms with more protons will lose electrons easily. 7. Which group tends to have the highest ionization ...
... A) Valence electrons are attracted more to atoms containing a lot of protons. B) Valence electrons in larger atoms are more loosely held. C) Atoms with fewer protons will lose electrons easily. D) Atoms with more protons will lose electrons easily. 7. Which group tends to have the highest ionization ...
the Periodic Table Regents Review Worksheets with answers.
... 10. Which element is a noble gas? A. krypton B. chlorine ...
... 10. Which element is a noble gas? A. krypton B. chlorine ...
Regents Chemistry NOTE PACKET
... Reason: SAME NUCLEAR CHARGE pulling on MORE e Electrons outnumber Protons ...
... Reason: SAME NUCLEAR CHARGE pulling on MORE e Electrons outnumber Protons ...
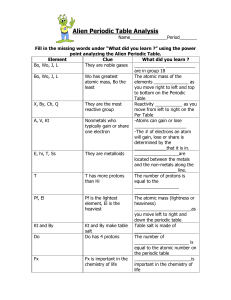
Alien Periodic Table Analysis
... They are the most Reactivity ___________ as you reactive group move from left to right on the Per Table A, V, Kt Nonmetals who -Atoms can gain or lose typically gain or share _____________________ one electron -The # of electrons an atom will gain, lose or share is determined by the _____________tha ...
... They are the most Reactivity ___________ as you reactive group move from left to right on the Per Table A, V, Kt Nonmetals who -Atoms can gain or lose typically gain or share _____________________ one electron -The # of electrons an atom will gain, lose or share is determined by the _____________tha ...
Families on the Periodic Table
... 1. The most reactive metallic element is x. 2. The most reactive nonmetallic element is !. 3. Inert gases (like our noble gases) are $, %, a, and d. a has the highest ionization energy of this group and the least dense, $ has the lowest ionization energy for this group, and d has a smaller atomic ra ...
... 1. The most reactive metallic element is x. 2. The most reactive nonmetallic element is !. 3. Inert gases (like our noble gases) are $, %, a, and d. a has the highest ionization energy of this group and the least dense, $ has the lowest ionization energy for this group, and d has a smaller atomic ra ...
Unit 4 Periodic Table Packet 2016-2017
... 1. The most reactive metallic element is x. 2. The most reactive nonmetallic element is !. 3. Inert gases (like our noble gases) are $, %, a, and d. a has the highest ionization energy of this group and the least dense, $ has the lowest ionization energy for this group, and d has a smaller atomic ra ...
... 1. The most reactive metallic element is x. 2. The most reactive nonmetallic element is !. 3. Inert gases (like our noble gases) are $, %, a, and d. a has the highest ionization energy of this group and the least dense, $ has the lowest ionization energy for this group, and d has a smaller atomic ra ...
Periodic Table Organization Comprehension Questions
... Why does the size of an atom increase as you move from top to bottom on the periodic table? 7. Why does the size of an atom decrease as you move from left to right on the periodic table? 8. Metals, non-metals, and metalloids are grouped on the periodic table. What type of properties do metals share? ...
... Why does the size of an atom increase as you move from top to bottom on the periodic table? 7. Why does the size of an atom decrease as you move from left to right on the periodic table? 8. Metals, non-metals, and metalloids are grouped on the periodic table. What type of properties do metals share? ...
Section 4 Powerpoint review lecure
... • Each kind of atom has its own distinct atomic number. Only atoms of that element have the same atomic number. • Atomic number equals number of protons • Uncharged atom – equal number of protons and electrons, atomic number = number of electrons • For Example GOLD, has a atomic number of 79. Gold h ...
... • Each kind of atom has its own distinct atomic number. Only atoms of that element have the same atomic number. • Atomic number equals number of protons • Uncharged atom – equal number of protons and electrons, atomic number = number of electrons • For Example GOLD, has a atomic number of 79. Gold h ...
File
... Mendeleev had noticed a periodic relationship between increasing atomic mass and chemical properties of elements. His work provided a logical organization for a huge amount of data about the elements, but no one could explain why the elements showed their amazing periodicity. By about 1915, chemists ...
... Mendeleev had noticed a periodic relationship between increasing atomic mass and chemical properties of elements. His work provided a logical organization for a huge amount of data about the elements, but no one could explain why the elements showed their amazing periodicity. By about 1915, chemists ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.