History of Periodic Table
... Periodic Table Activity Directions • Work with your row to complete the activity • Arrange the known elements on the cards into the order of the periodic table • Place the unknown’s in their spot based on the properties of the elements ▫ Hint: you are only working with elements in the s and p block ...
... Periodic Table Activity Directions • Work with your row to complete the activity • Arrange the known elements on the cards into the order of the periodic table • Place the unknown’s in their spot based on the properties of the elements ▫ Hint: you are only working with elements in the s and p block ...
Unit 4 Pack
... Chemistry I - Unit 4: Chapters 5-6 - Periodic Table and Characteristics of Elements Vocab Quiz: Friday, Oct. 3 Test Date: Wednesday, Oct. 8 Vocabulary: average atomic mass metal Mendeleev ionization energy alkali metals actinides ...
... Chemistry I - Unit 4: Chapters 5-6 - Periodic Table and Characteristics of Elements Vocab Quiz: Friday, Oct. 3 Test Date: Wednesday, Oct. 8 Vocabulary: average atomic mass metal Mendeleev ionization energy alkali metals actinides ...
Periodic Table
... fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the fewer electrons needed to fill the valance are very reactive and combine easily to form compounds. Atoms with full valances do not react to form compoun ...
... fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the fewer electrons needed to fill the valance are very reactive and combine easily to form compounds. Atoms with full valances do not react to form compoun ...
File
... first element in the period. What is element Z? ________________________________ 3. Element D loses two electrons in a chemical reaction. Now it has the same number of electrons as Neon. What is element D? ________________________ 4. If the atomic numbers of Calcium and Beryllium are added together, ...
... first element in the period. What is element Z? ________________________________ 3. Element D loses two electrons in a chemical reaction. Now it has the same number of electrons as Neon. What is element D? ________________________ 4. If the atomic numbers of Calcium and Beryllium are added together, ...
Unit 3.2 Periodic Table Test
... An electron has the same mass as a proton. An electron has much more mass than a neutron. An electron has about the same mass as a neutron. An electron has much less mass than a proton. An electron has much less mass than a neutron. A proton has more mass than ...
... An electron has the same mass as a proton. An electron has much more mass than a neutron. An electron has about the same mass as a neutron. An electron has much less mass than a proton. An electron has much less mass than a neutron. A proton has more mass than ...
6 The Periodic Tableааааааааааааааааааааааааа__ /__ pts First
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table ...
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table ...
Name Pre-Test : Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Fill in the blank with the correct word from the list at the bottom of the page. Not all words from the list will be used. 1. Atomic ________________________ refers to the arrangement and number of smaller particles in an atom. 2. The ________________________ is the center or core of an ...
... Directions: Fill in the blank with the correct word from the list at the bottom of the page. Not all words from the list will be used. 1. Atomic ________________________ refers to the arrangement and number of smaller particles in an atom. 2. The ________________________ is the center or core of an ...
The Periodical Table and chemical properties
... The transition metals have several features in common: unlike representative metals, most transition metals have variable valence, meaning that they have more than one possible oxidation—or valence— state. For example, platinum exists most commonly in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, but it can als ...
... The transition metals have several features in common: unlike representative metals, most transition metals have variable valence, meaning that they have more than one possible oxidation—or valence— state. For example, platinum exists most commonly in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, but it can als ...
Chapter 6 Reading Guide
... 3. What is a picometer and why is it used? 4. What are the patterns to atomic size on the periodic table? 5. What was the book’s example of a trend? 6. What effect does the increase in the charge of the nucleus have on the size? 7. How do orbitals act as shields? 8. Why does atomic size increase in ...
... 3. What is a picometer and why is it used? 4. What are the patterns to atomic size on the periodic table? 5. What was the book’s example of a trend? 6. What effect does the increase in the charge of the nucleus have on the size? 7. How do orbitals act as shields? 8. Why does atomic size increase in ...
The Periodic Table
... • What happens to an atom if it GAINS an electron? It gets more negative (so it has a negative charge) Cl ...
... • What happens to an atom if it GAINS an electron? It gets more negative (so it has a negative charge) Cl ...
Periodic Table Presentation Lesson
... Element Properties No two elements will have the same properties. ¨ For example, Calcium has a density of 1.54g/mL with no other element having this same density. ...
... Element Properties No two elements will have the same properties. ¨ For example, Calcium has a density of 1.54g/mL with no other element having this same density. ...
CP-Chem Ch 5 PowerPoint(The Periodic Table)
... periodic table, an English chemist named Henry Moseley found a different physical basis for the arrangement of elements. • Moseley studied the lines in the X-ray spectra of 38 different elements. • Moseley’s work led to the modern definition of atomic number, and showed that atomic number, not atomi ...
... periodic table, an English chemist named Henry Moseley found a different physical basis for the arrangement of elements. • Moseley studied the lines in the X-ray spectra of 38 different elements. • Moseley’s work led to the modern definition of atomic number, and showed that atomic number, not atomi ...
3 Periodic Trends
... Affinity”, and one rectangle “Ionization Energy”. Draw TWO arrows on each labeled indicating the trends. **Indicate if the arrow is increasing or decreasing. Example ...
... Affinity”, and one rectangle “Ionization Energy”. Draw TWO arrows on each labeled indicating the trends. **Indicate if the arrow is increasing or decreasing. Example ...
Periodicity
... orbital the electron occupies; s, p, d, and f. • is read left to right; 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s.... • is arranged as representative elements (s and p block elements), transition metals (d block metals), lanthanides and actinides (f block metals). • is arranged in order of increasing energy of the sub ...
... orbital the electron occupies; s, p, d, and f. • is read left to right; 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s.... • is arranged as representative elements (s and p block elements), transition metals (d block metals), lanthanides and actinides (f block metals). • is arranged in order of increasing energy of the sub ...
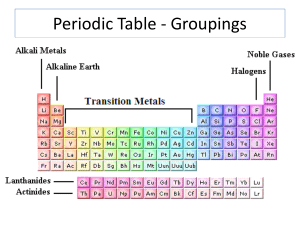
Periodic Properties
... – 1A (Alkali Metals) – 2A (Alkaline Earth Metals) – 7A (Halogens) – 8A I (Noble Gases) • The letters A and B in the group ...
... – 1A (Alkali Metals) – 2A (Alkaline Earth Metals) – 7A (Halogens) – 8A I (Noble Gases) • The letters A and B in the group ...
The Periodic Table
... • Low chemical reactivity – very stable. They have no desire to gain or lose electrons! ▫ Example – He used for blimps. ▫ Typically inert – thought to be completely unreactive. Exception: 1962, chemists were able to make some compounds with Xe. ...
... • Low chemical reactivity – very stable. They have no desire to gain or lose electrons! ▫ Example – He used for blimps. ▫ Typically inert – thought to be completely unreactive. Exception: 1962, chemists were able to make some compounds with Xe. ...
The Periodic Table
... • Low chemical reactivity – very stable. They have no desire to gain or lose electrons! ▫ Example – He used for blimps. ▫ Typically inert – thought to be completely unreactive. Exception: 1962, chemists were able to make some compounds with Xe. ...
... • Low chemical reactivity – very stable. They have no desire to gain or lose electrons! ▫ Example – He used for blimps. ▫ Typically inert – thought to be completely unreactive. Exception: 1962, chemists were able to make some compounds with Xe. ...
chapter-5-periodic-classification-of-elements
... discovered at that time. Mendeléev named them by prefixing a Sanskrit numeral, Eka (one) to the name of preceding element in the same group. It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respective ...
... discovered at that time. Mendeléev named them by prefixing a Sanskrit numeral, Eka (one) to the name of preceding element in the same group. It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respective ...
How the Periodic Table Works
... (alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, nonmetals, noble gases and so on). Within the table, the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, as you'll recall. The elements stretch across seven rows. Each row is called a period and indicates the energy levels or shells occupied by the electron ...
... (alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, nonmetals, noble gases and so on). Within the table, the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, as you'll recall. The elements stretch across seven rows. Each row is called a period and indicates the energy levels or shells occupied by the electron ...
chem ch 5 - wbm
... increasing mass. Properties are repeated in an orderly, periodic, fashion. Mendeleev’s periodic law – the properties of the elements are a periodic function of their masses. ...
... increasing mass. Properties are repeated in an orderly, periodic, fashion. Mendeleev’s periodic law – the properties of the elements are a periodic function of their masses. ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... 19. _____________ electrons are the electrons in the outer energy levels of an atom. 20. _____________ electrons are transferred or shared when atoms bond together. 21. The three main categories of elements are: ________________, ____________, and __________________. 22. Metals are good ____________ ...
... 19. _____________ electrons are the electrons in the outer energy levels of an atom. 20. _____________ electrons are transferred or shared when atoms bond together. 21. The three main categories of elements are: ________________, ____________, and __________________. 22. Metals are good ____________ ...
Biology - Mr. Julien`s Homepage
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: g.*Students know how electronegativity and ionization energy r ...
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: g.*Students know how electronegativity and ionization energy r ...
Atoms & Elements
... Structure of atom: An atom consists • of a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons. • of electrons in a large empty space around the nucleus. • a proton has a mass of about 1 (1.007) amu. • a neutron has a mass of about 1 (1.008) amu. • an electron has a very small mass, 0.000549 amu. ...
... Structure of atom: An atom consists • of a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons. • of electrons in a large empty space around the nucleus. • a proton has a mass of about 1 (1.007) amu. • a neutron has a mass of about 1 (1.008) amu. • an electron has a very small mass, 0.000549 amu. ...
Chemistry-notes-ch-5
... these three elements were discovered—scandium, gallium and germanium. 1911 Moseley published a periodic table based on atomic numbers. This was the basis for our modern periodic table. Periodic Law—the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. P ...
... these three elements were discovered—scandium, gallium and germanium. 1911 Moseley published a periodic table based on atomic numbers. This was the basis for our modern periodic table. Periodic Law—the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. P ...
The Periodic Table
... Halogens, such as chlorine, are located in Group 17 of the periodic table. Noble gases, such as neon, make up Group 18 of the periodic table. They are unreactive. ...
... Halogens, such as chlorine, are located in Group 17 of the periodic table. Noble gases, such as neon, make up Group 18 of the periodic table. They are unreactive. ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.