File
... the alkali metals in the same period! • So Mg is less reactive than Na, but more reactive than Be!!! • Location allows prediction of reactivity! ...
... the alkali metals in the same period! • So Mg is less reactive than Na, but more reactive than Be!!! • Location allows prediction of reactivity! ...
the modern periodic law
... vigorously with water to release hydrogen from water. Sodium is so active that it must be kept under an oil layer; this prevents it from any contact with the humidity and the oxygen contained in the air. All alkali metals react with chlorine to form colourless compounds which crystallize in cubic sh ...
... vigorously with water to release hydrogen from water. Sodium is so active that it must be kept under an oil layer; this prevents it from any contact with the humidity and the oxygen contained in the air. All alkali metals react with chlorine to form colourless compounds which crystallize in cubic sh ...
Chapter 5 - EZWebSite
... Helium ends in s2. However, it is more closely related to elements in group VIIIA. Since the first energy level has only an s orbital, and two electrons fill it, helium has a full outer energy level. This gives it the same stability and unreactivity as a noble gas. ...
... Helium ends in s2. However, it is more closely related to elements in group VIIIA. Since the first energy level has only an s orbital, and two electrons fill it, helium has a full outer energy level. This gives it the same stability and unreactivity as a noble gas. ...
TRENDS in the PERIODIC TABLE
... all atoms for that electron gain. Fluorine is given the rating of 4.0 on the E-N scale, the highest Electronegativity of all elements. Electro-negativity is on Table S. You don’t have to memorize the trend, you can look it up anytime you want to. ...
... all atoms for that electron gain. Fluorine is given the rating of 4.0 on the E-N scale, the highest Electronegativity of all elements. Electro-negativity is on Table S. You don’t have to memorize the trend, you can look it up anytime you want to. ...
Periodic Table – Organizing the Elements
... Regardless of the “Block,” the number of electrons in the highest sub-level is equal to the element’s column number within its block. –Ex: Nitrogen is in the 3rd column of the p block and its configuration ends in p3. –Ex: Iron is in the 6th column of the d block and it ends in d6. ...
... Regardless of the “Block,” the number of electrons in the highest sub-level is equal to the element’s column number within its block. –Ex: Nitrogen is in the 3rd column of the p block and its configuration ends in p3. –Ex: Iron is in the 6th column of the d block and it ends in d6. ...
Ch. 4.3 – Distinguishing Among Atoms
... element, multiply the mass of each isotope by its percent relative abundance, expressed as a decimal, and then add the products. ...
... element, multiply the mass of each isotope by its percent relative abundance, expressed as a decimal, and then add the products. ...
(halogens group) 4-write down the electronic configuration
... 1- choose the correct answer : 1-the number of known elements till now is 118 2- the scientist Bohr had discovered the main energy level. 3- the scientist who discovered the positive proton in the nucleus is Rutherford 4- the scientist who left gaps in his table is Mendeleev 5-element of d-block are ...
... 1- choose the correct answer : 1-the number of known elements till now is 118 2- the scientist Bohr had discovered the main energy level. 3- the scientist who discovered the positive proton in the nucleus is Rutherford 4- the scientist who left gaps in his table is Mendeleev 5-element of d-block are ...
Ch. 11.4 Notes (Periodicity) teacher
... gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
... gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
Ch. 13 Notes---Electrons in Atoms
... gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
... gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
File
... • Have shared properties of both metals and non metals • Metallic luster • Brittle or crumbly ...
... • Have shared properties of both metals and non metals • Metallic luster • Brittle or crumbly ...
Increasing Radii
... brittle-break into pieces when hit or are gases dull looking solids if not a gas Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids: elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals (these are also called semiconductors) B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te ...
... brittle-break into pieces when hit or are gases dull looking solids if not a gas Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids: elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals (these are also called semiconductors) B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te ...
Ch. 6 PPT
... • Group 17 is composed of highly reactive elements called halogens. • Group 18 gases are extremely unreactive and commonly called noble gases. ...
... • Group 17 is composed of highly reactive elements called halogens. • Group 18 gases are extremely unreactive and commonly called noble gases. ...
Periodic Table Properties Notes s1
... An ion is an atom that has lost or gained electrons and has a negative or positive charge. • Atoms that lose electrons have a positive charge. Atoms that gain electrons have a negative charge. • What ion an atom will form can be determined by its group on the periodic table. ...
... An ion is an atom that has lost or gained electrons and has a negative or positive charge. • Atoms that lose electrons have a positive charge. Atoms that gain electrons have a negative charge. • What ion an atom will form can be determined by its group on the periodic table. ...
Questions on Chapter 7
... 1) In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) O, S, Se B) N, O, F C) Na, Mg, K D) S, Se, Si E) Ne, Na, Mg 2) In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) P, Se, I B) Cl, Br, Na C) Si, As, ...
... 1) In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) O, S, Se B) N, O, F C) Na, Mg, K D) S, Se, Si E) Ne, Na, Mg 2) In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) P, Se, I B) Cl, Br, Na C) Si, As, ...
groups - Orangefield ISD
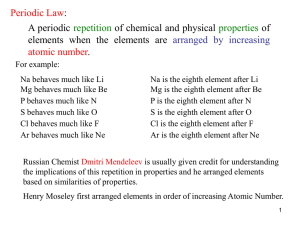
... ◦ Periodic law – states that there is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of the elements when they are arranged by increasing atomic number ◦ Arranged in order of increasing atomic number into a series of columns, called groups, and rows, called periods ◦ Groups are labeled 1- ...
... ◦ Periodic law – states that there is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of the elements when they are arranged by increasing atomic number ◦ Arranged in order of increasing atomic number into a series of columns, called groups, and rows, called periods ◦ Groups are labeled 1- ...
The Periodic Table
... He revised atomic weights and staked his whole career, Predicting that several new elements would appear. A few years passed and sure enough they came, Gallium, scandium, germanium were their names. Chemists everywhere were impressed with what they saw. There really must be something to this periodi ...
... He revised atomic weights and staked his whole career, Predicting that several new elements would appear. A few years passed and sure enough they came, Gallium, scandium, germanium were their names. Chemists everywhere were impressed with what they saw. There really must be something to this periodi ...
File - Unit #1-0
... 18. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Elements? 19. Elements within a group have a similar number of 20. Elements across a series have the same number of 21. A colored ion generally indicates a 22. As you go down a group, the elements generally become ( more / less) metallic. 23. The ...
... 18. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Elements? 19. Elements within a group have a similar number of 20. Elements across a series have the same number of 21. A colored ion generally indicates a 22. As you go down a group, the elements generally become ( more / less) metallic. 23. The ...
The Periodic Table
... Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons. This identifies them as the element that they are. But all atoms of an element don’t have to have the same number of neutrons. For example, all boron atoms have 5 protons. However, four-fifths of them have 6 neutrons and one-fifth of ...
... Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons. This identifies them as the element that they are. But all atoms of an element don’t have to have the same number of neutrons. For example, all boron atoms have 5 protons. However, four-fifths of them have 6 neutrons and one-fifth of ...
Lesson 7.8 Basic Properties of the Main Group Elements Suggested
... The elements also tend to increase in metallic character going down any column of elements. Some groups show this tendency more clearly than others. For example, Group IVA starts with carbon (nonmetal), and goes to silicon and germanium (metalloids), and concludes with tin and lead (metal). The tren ...
... The elements also tend to increase in metallic character going down any column of elements. Some groups show this tendency more clearly than others. For example, Group IVA starts with carbon (nonmetal), and goes to silicon and germanium (metalloids), and concludes with tin and lead (metal). The tren ...
ElementsPeriodicTable Notes
... Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain six protons and six electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon12 is the most common isotope. ...
... Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain six protons and six electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon12 is the most common isotope. ...
Organizing the periodic table
... The vertical columns of the periodic table are known as a group. Another name for each group is a “family”. Each group is filled with atoms which have similar characteristics. There are eighteen groups in the periodic table. The lanthanides and actinides do not fit in the periodic table because the ...
... The vertical columns of the periodic table are known as a group. Another name for each group is a “family”. Each group is filled with atoms which have similar characteristics. There are eighteen groups in the periodic table. The lanthanides and actinides do not fit in the periodic table because the ...
Chapter 5
... Electron Affinity - the energy change associated with the addition of an electron Affinity tends to increase across a period Affinity tends to decrease down a group Electrons farther from the nucleus experience less nuclear attraction Some irregularities due to repulsive forces in the relatively sm ...
... Electron Affinity - the energy change associated with the addition of an electron Affinity tends to increase across a period Affinity tends to decrease down a group Electrons farther from the nucleus experience less nuclear attraction Some irregularities due to repulsive forces in the relatively sm ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.