chapter8
... In 1864 the English chemist John Newlands noticed that when the known elements were arranged in order of atomic mass, every eighth element had similar properties. Newlands referred to this peculiar relationship as the law of octaves. This turned out to be inadequate for elements beyond calcium, and ...
... In 1864 the English chemist John Newlands noticed that when the known elements were arranged in order of atomic mass, every eighth element had similar properties. Newlands referred to this peculiar relationship as the law of octaves. This turned out to be inadequate for elements beyond calcium, and ...
Chemistry
... - Groups 1A through 7A and group 0 make up the representative elements (wide variety of properties) - Group B elements are the transition metals - Two rows of elements below the periodic table are the lanthanides and actinides - The periodic law states that when elements are arranged in order of inc ...
... - Groups 1A through 7A and group 0 make up the representative elements (wide variety of properties) - Group B elements are the transition metals - Two rows of elements below the periodic table are the lanthanides and actinides - The periodic law states that when elements are arranged in order of inc ...
Ionization energy
... 2) The law did not work for very low or very high massed elements such as F, Cl, and Br. 3) As techniques improved for measuring atomic masses accurately, the law became obsolete. Dobereiner’s research made chemists look at groups of elements with similar chemical and physical properties. ...
... 2) The law did not work for very low or very high massed elements such as F, Cl, and Br. 3) As techniques improved for measuring atomic masses accurately, the law became obsolete. Dobereiner’s research made chemists look at groups of elements with similar chemical and physical properties. ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... The s-block elements consist of the elements in groups 1 and 2 of the periodic table. Electrons from these elements fill the s orbital of each period. Group 1 (ALKALI METALS) fill the s orbital with 1 electron. These elements are considered to be reactive metals because they are not readily found in ...
... The s-block elements consist of the elements in groups 1 and 2 of the periodic table. Electrons from these elements fill the s orbital of each period. Group 1 (ALKALI METALS) fill the s orbital with 1 electron. These elements are considered to be reactive metals because they are not readily found in ...
C1 - Powerpoint - tonyconnett.com
... 1. What happens to the boiling point of the metals as you move down group 1 2. Group 1 atoms want to loose an electron, do you think it would be easier to remove an electron from Lithium or Cs? 3. What is the most reactive element in group 1? 4. Group 7 atoms want to gain an electron, which atom wou ...
... 1. What happens to the boiling point of the metals as you move down group 1 2. Group 1 atoms want to loose an electron, do you think it would be easier to remove an electron from Lithium or Cs? 3. What is the most reactive element in group 1? 4. Group 7 atoms want to gain an electron, which atom wou ...
Ionization Energy
... On the periodic table, elements are arranged least to greatest by atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. The periodic table is also arranged in groups which are vertical columns of elements, and periods, which are the horizontal rows of elements. Each element has ionization en ...
... On the periodic table, elements are arranged least to greatest by atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. The periodic table is also arranged in groups which are vertical columns of elements, and periods, which are the horizontal rows of elements. Each element has ionization en ...
periodic table
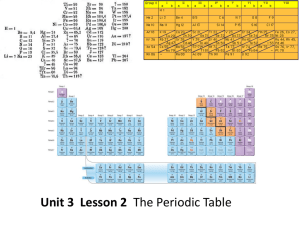
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
Ch. 14 notes (teacher)3
... gases – ___________ are not listed in Table 14.2 since form _____________ compounds ! they do not ________ ...
... gases – ___________ are not listed in Table 14.2 since form _____________ compounds ! they do not ________ ...
physical science
... 5. TSW describe the evidence for energy levels and distinguish the ground state from excited states of an atom based on electron configurations. (p. 113 – 118) 6. TSW explain how the arrangement of Mendeleev’s periodic table made it useful to predict and discover new elements. (p. 126 – 129) 7. TSW ...
... 5. TSW describe the evidence for energy levels and distinguish the ground state from excited states of an atom based on electron configurations. (p. 113 – 118) 6. TSW explain how the arrangement of Mendeleev’s periodic table made it useful to predict and discover new elements. (p. 126 – 129) 7. TSW ...
Chapter 6- The Periodic Table
... remove an electron from its atom. • Almost, but not quite like electronegativity • Electronegativity is how well it takes someone else’s electron • Ionization energy is how well it holds on to its own electrons ...
... remove an electron from its atom. • Almost, but not quite like electronegativity • Electronegativity is how well it takes someone else’s electron • Ionization energy is how well it holds on to its own electrons ...
An element
... • The Periodic table was designed to classify elements according to their properties and to show trends in their physical and chemical properties • The main groups are: I – Alkali metals; II – Alkaline earth metals; VII – Halogens; VIII (also called group ...
... • The Periodic table was designed to classify elements according to their properties and to show trends in their physical and chemical properties • The main groups are: I – Alkali metals; II – Alkaline earth metals; VII – Halogens; VIII (also called group ...
Electrons in Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... Name the block and group in which each of the following elements is located in the periodic table. Then, use the periodic table to name each element. Identify each element as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. Finally, describe whether each element has high reactivity or low reactivity ...
... Name the block and group in which each of the following elements is located in the periodic table. Then, use the periodic table to name each element. Identify each element as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. Finally, describe whether each element has high reactivity or low reactivity ...
The Periodic Law
... The Modern Periodic Table • It is an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column or group. • The most significant additions were the noble gases. Helium was discovered in 1868. Argon was discovered by Ramsey in 1894. ...
... The Modern Periodic Table • It is an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column or group. • The most significant additions were the noble gases. Helium was discovered in 1868. Argon was discovered by Ramsey in 1894. ...
315`01-01
... C. T____Sulfur is an element that is brittle and does not conduct hear or electricity well D. T____Out of Se, Si, P and Mg, only Mg is soft and malleable in its solid state E. F____Most Halogens are solid at room temperature 19. Transition Metals - d-Block Elements Transition metals generally have 2 ...
... C. T____Sulfur is an element that is brittle and does not conduct hear or electricity well D. T____Out of Se, Si, P and Mg, only Mg is soft and malleable in its solid state E. F____Most Halogens are solid at room temperature 19. Transition Metals - d-Block Elements Transition metals generally have 2 ...
Periodic Table Name: Practice Review H
... grouped in A) periods C) horizontal rows E) horizontal families ...
... grouped in A) periods C) horizontal rows E) horizontal families ...
Ionization energy
... Dobereiner’s research made chemists look at groups of elements with similar chemical and physical properties. ...
... Dobereiner’s research made chemists look at groups of elements with similar chemical and physical properties. ...
virtual lab- Atoms on periodic table student
... In the late 1800’s, _____________ ___________________, a Russian ____________, ______________ all the ________________ known at that time in the _______________ of _________________ _____________________ ____________. He_____________________ that there was a _________________ to the ________________ ...
... In the late 1800’s, _____________ ___________________, a Russian ____________, ______________ all the ________________ known at that time in the _______________ of _________________ _____________________ ____________. He_____________________ that there was a _________________ to the ________________ ...
periodic classification of elements
... In his periodic table the elements with similar chemical properties were grouped together due to which the order of atomic masses for some elements was wrong i.e, decreasing order instead of increasing. Like Cobalt ...
... In his periodic table the elements with similar chemical properties were grouped together due to which the order of atomic masses for some elements was wrong i.e, decreasing order instead of increasing. Like Cobalt ...
Daily 40 no. – 15 John Newlands
... create an early periodic table. His organization led to the modern periodic table. He realized that every eighth element had similar characteristics. His incomplete table predicted other undiscovered elements. -Eric John Newlands was born in 1837 and died in 1898. He is known for creating the first ...
... create an early periodic table. His organization led to the modern periodic table. He realized that every eighth element had similar characteristics. His incomplete table predicted other undiscovered elements. -Eric John Newlands was born in 1837 and died in 1898. He is known for creating the first ...
Unit Six: Atomic structure
... 1. Dimitri Mendeleev , a Russian scientist, is credits for creating the first periodic table in 1869. At that time, there were only 60 known element and Mendeleev organized them according to their atomic mass. Mendeleev was able to predict the properties of missing elements which were later discover ...
... 1. Dimitri Mendeleev , a Russian scientist, is credits for creating the first periodic table in 1869. At that time, there were only 60 known element and Mendeleev organized them according to their atomic mass. Mendeleev was able to predict the properties of missing elements which were later discover ...
Better Understanding of Element Property Trends
... Property trend patterns - physical, electrical, or chemical aspects of adjacent elements of the periodic table - increase or decrease in different directions, but often not strictly continuous. The main trends are: ionization energy, electron affinity, metallic character, atomic radius, electronegat ...
... Property trend patterns - physical, electrical, or chemical aspects of adjacent elements of the periodic table - increase or decrease in different directions, but often not strictly continuous. The main trends are: ionization energy, electron affinity, metallic character, atomic radius, electronegat ...
Chapter 5 The Periodic Table
... break the elements into rows • Key Concept: Mendeleev arranged the elements into rows in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. ...
... break the elements into rows • Key Concept: Mendeleev arranged the elements into rows in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. ...
Patterns of Behavior of Main Group Elements (cont.) Patterns of
... for Electrons (cont.) • Noble gases are considered to have electronegativity values of zero and do not follow periodic trends. • Shielding effect is the tendency for the electrons in the inner energy levels to block the attraction of the nucleus for the valence electrons. ...
... for Electrons (cont.) • Noble gases are considered to have electronegativity values of zero and do not follow periodic trends. • Shielding effect is the tendency for the electrons in the inner energy levels to block the attraction of the nucleus for the valence electrons. ...
10TH CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CHEMISRY As a large
... b) Newland placed two elements in the same slot in a particular group. He could not offer any explanation for such an arrangement. c) Newland thought that only 50 elements existed in nature and no more elements were likely to be discovered. But he was proved wrong. d) When noble gas elements were di ...
... b) Newland placed two elements in the same slot in a particular group. He could not offer any explanation for such an arrangement. c) Newland thought that only 50 elements existed in nature and no more elements were likely to be discovered. But he was proved wrong. d) When noble gas elements were di ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.