Section 2 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Chapter 5
... • In many compounds, the negative charge of the valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. • Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. • Electronegativities tend to increase acros ...
... • In many compounds, the negative charge of the valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. • Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. • Electronegativities tend to increase acros ...
The Periodic Table
... Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons (True, False) Ionization energy is the energy required to remove and electron from an atom (True, False) An atom with high electronegativity easily gives up an electron (True, False) ...
... Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons (True, False) Ionization energy is the energy required to remove and electron from an atom (True, False) An atom with high electronegativity easily gives up an electron (True, False) ...
Unit Two Test Review
... very low reactivity. good conductivity. very high reactivity. metallic character. ...
... very low reactivity. good conductivity. very high reactivity. metallic character. ...
The physical characteristics of the atom of an element are called
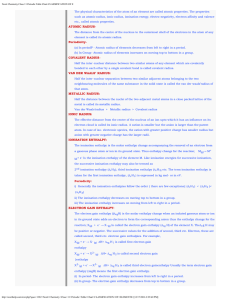
... the atomic radius increases regularly with atomic number as). as we descend the groups, the principal quantum number (n) increases and the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. This happens because the inner energy levels are filled with electrons, which serve to shield the outer electrons ...
... the atomic radius increases regularly with atomic number as). as we descend the groups, the principal quantum number (n) increases and the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. This happens because the inner energy levels are filled with electrons, which serve to shield the outer electrons ...
Group 16: The Oxygen Family - Chemwiki
... Tellurium is the metalloid of the oxygen family, with a silvery white color and a metallic luster similar to that of tin at room temperature. Like selenium, it is also displays photoconductivity. Tellurium is an extremely rare element, and is most commonly found as a telluride of gold. It is often u ...
... Tellurium is the metalloid of the oxygen family, with a silvery white color and a metallic luster similar to that of tin at room temperature. Like selenium, it is also displays photoconductivity. Tellurium is an extremely rare element, and is most commonly found as a telluride of gold. It is often u ...
Microsoft product template
... Explore the Periodic Table found on the Bing page (Hover your mouse over parts of the table, click on the different tabs, click on the table, etc). Which elements are familiar to you? In which contexts have you heard of these elements? ...
... Explore the Periodic Table found on the Bing page (Hover your mouse over parts of the table, click on the different tabs, click on the table, etc). Which elements are familiar to you? In which contexts have you heard of these elements? ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... Mendeleev’s work was published first; he did more to show periodic trends; and he predicted properties of several yet-to-be-discovered elements. ...
... Mendeleev’s work was published first; he did more to show periodic trends; and he predicted properties of several yet-to-be-discovered elements. ...
Lesson 3 - St John Brebeuf
... More energy shells. More energy shells (layers)…thus farther from nucleus (Positively charged)…..thus there is less attraction the farther away you go….so less energy to pull electrons away. ...
... More energy shells. More energy shells (layers)…thus farther from nucleus (Positively charged)…..thus there is less attraction the farther away you go….so less energy to pull electrons away. ...
Chemical Matter: Elements and Their Classification
... the orbital with the lower principal quantum n number is more stable, which means that the stability decreases as follows: 1s>2s>3s>4s, and so on. Similarly, if n is constant the orbital with lower l number is more stable, which means that the stability decreases as follows: 4s>4p>4d>4f, and so on. ...
... the orbital with the lower principal quantum n number is more stable, which means that the stability decreases as follows: 1s>2s>3s>4s, and so on. Similarly, if n is constant the orbital with lower l number is more stable, which means that the stability decreases as follows: 4s>4p>4d>4f, and so on. ...
Periodic_Tendancies
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
Periodic Table Notes.notebook
... Why? Elements near the top of the period table have few electrons to begin with; every electron is a big deal. They have a stronger desire to acquire more electrons. Elements near the bottom of the chart have so many electrons that loosing or acquiring an electron is not as big a deal. This is du ...
... Why? Elements near the top of the period table have few electrons to begin with; every electron is a big deal. They have a stronger desire to acquire more electrons. Elements near the bottom of the chart have so many electrons that loosing or acquiring an electron is not as big a deal. This is du ...
Periodic Table Notes
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
unit 6: periodic table - St. Dominic High School
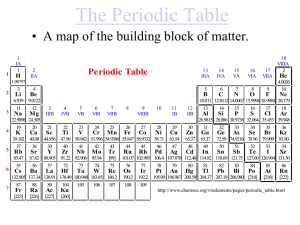
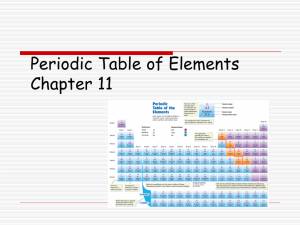
... Lists elements according to their atomic number Still used columns called families which consist of elements with similar properties Still uses rows called periods . Elements increase by 1 moving from left to right. Periodic table lists 118 element. May need to be revised as new elements are di ...
... Lists elements according to their atomic number Still used columns called families which consist of elements with similar properties Still uses rows called periods . Elements increase by 1 moving from left to right. Periodic table lists 118 element. May need to be revised as new elements are di ...
Inorganic Chemistry ELEMENTS AND
... penultimate shell is progressively filled form 1 to 10 while the s-sublevel of ultimate shell is already filled up. The general electronic configuration of d-block elements can be given as (n-1) d1-10ns1-2. These are also known as transation elements since their properties of s- & p-block elements. ...
... penultimate shell is progressively filled form 1 to 10 while the s-sublevel of ultimate shell is already filled up. The general electronic configuration of d-block elements can be given as (n-1) d1-10ns1-2. These are also known as transation elements since their properties of s- & p-block elements. ...
Target 3 – Identify the 3 main classes of
... atomic radius DECREASES. 2. Why? As you go across the periodic table, the atomic number increases by one proton. 3. Remember that one proton has a charge of +1…As the charge of the nucleus increases as you move across a period, it creates a stronger pull on the electrons. 4. This stronger pull of el ...
... atomic radius DECREASES. 2. Why? As you go across the periodic table, the atomic number increases by one proton. 3. Remember that one proton has a charge of +1…As the charge of the nucleus increases as you move across a period, it creates a stronger pull on the electrons. 4. This stronger pull of el ...
Placing Elements on the Periodic Table
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
Periodic Table
... Two variable determine the atomic radius of a atom: the number of protons in the nucleus the number of electron energy levels in the atom. The number protons and radius are inversely proportional. As protons increase, the radius decreases. The number of energy levels and radius are proportional. As ...
... Two variable determine the atomic radius of a atom: the number of protons in the nucleus the number of electron energy levels in the atom. The number protons and radius are inversely proportional. As protons increase, the radius decreases. The number of energy levels and radius are proportional. As ...
The periodic table and electron structure - Chemistry
... The actinoids go on the f block below the lanthanoids, outside the main body of the table. You will not find these elements in common household products such as oven cleaners or air fresheners as they are radioactive and artificially produced. Groups of Elements Each group has characteristic propert ...
... The actinoids go on the f block below the lanthanoids, outside the main body of the table. You will not find these elements in common household products such as oven cleaners or air fresheners as they are radioactive and artificially produced. Groups of Elements Each group has characteristic propert ...
3. classification of elements and periodicity in properties
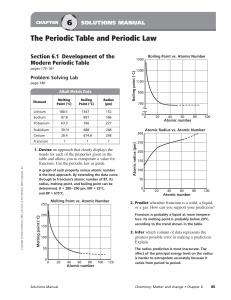
... In this periodic table, the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number. It contains 7 horizontal rows called periods and 18 vertical columns called groups. Elements having similar outer electronic configurations are arranged in same group or family. The groups are numbered ...
... In this periodic table, the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number. It contains 7 horizontal rows called periods and 18 vertical columns called groups. Elements having similar outer electronic configurations are arranged in same group or family. The groups are numbered ...
File
... elements had been determined. John Newlands: – hypothesized that the chemistry of the elements might be related to their masses; – arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic masses; – discovered that every 7th element had similar properties (noble gases were still unknown during this ...
... elements had been determined. John Newlands: – hypothesized that the chemistry of the elements might be related to their masses; – arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic masses; – discovered that every 7th element had similar properties (noble gases were still unknown during this ...
Record: 1 THE EVOLUTION OF THE PERIODIC SYSTEM Page 1 of
... intense effort could chemists and physicists successfully incorporate the noble gases into the table. In the new arrangement, an additional column was introduced between the halogens (the gaseous elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine) and the alkali metals (lithium, sodium, potas ...
... intense effort could chemists and physicists successfully incorporate the noble gases into the table. In the new arrangement, an additional column was introduced between the halogens (the gaseous elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine) and the alkali metals (lithium, sodium, potas ...
1 - Wiki Home
... Session 1 DIRECTIONS: This session contains twenty multiple choice questions and two open response questions. Mark your answers to these questions in the spaces provided in your Student Answer Booklet. You may work out solutions to multiple choice questions in the test booklet. ...
... Session 1 DIRECTIONS: This session contains twenty multiple choice questions and two open response questions. Mark your answers to these questions in the spaces provided in your Student Answer Booklet. You may work out solutions to multiple choice questions in the test booklet. ...
day4-periodictrends
... 1. Which family is least reactive? 2. Which family is most metallic? 3. Where are the nonmetals on the periodic table? ...
... 1. Which family is least reactive? 2. Which family is most metallic? 3. Where are the nonmetals on the periodic table? ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.