File - eScience@Kings
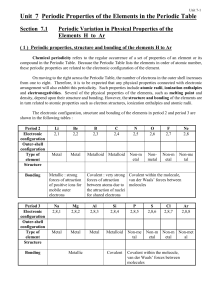
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
Chapter 7 - Wikispaces
... As we move across the periodic table, the number of core electrons remains constant, however, the nuclear charge increases. Therefore, there is an increased attraction between the nucleus and the outermost electrons. This attraction causes the atomic radius to decrease. ...
... As we move across the periodic table, the number of core electrons remains constant, however, the nuclear charge increases. Therefore, there is an increased attraction between the nucleus and the outermost electrons. This attraction causes the atomic radius to decrease. ...
groups - Northside Middle School
... – Full set of valence electrons: most elements have 8 valence electrons, except Helium with 2 valence electrons, but it is still associated with this group because its properties match these elements. – Extremely stable and occur as monoatomic gases in nature – Although they do not readily combine w ...
... – Full set of valence electrons: most elements have 8 valence electrons, except Helium with 2 valence electrons, but it is still associated with this group because its properties match these elements. – Extremely stable and occur as monoatomic gases in nature – Although they do not readily combine w ...
The Modern Periodic Table (cont.)
... • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
... • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
Unit 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements in the Periodic Table
... expected, the most electronegative elements are the reactive non-metals in the top right-hand corner of the periodic table. In contrast, the least electronegative elements are the reactive metals in the bottom left-hand corner. Moving from one element to the next across a period, the nuclear charge ...
... expected, the most electronegative elements are the reactive non-metals in the top right-hand corner of the periodic table. In contrast, the least electronegative elements are the reactive metals in the bottom left-hand corner. Moving from one element to the next across a period, the nuclear charge ...
Chapter Three: Periodic Table
... Atomic mass, Atomic number, Oxidation states, and Electron Configurations are all listed in the Reference Table On The Periodic Table. ...
... Atomic mass, Atomic number, Oxidation states, and Electron Configurations are all listed in the Reference Table On The Periodic Table. ...
Groups and Families
... Shellat (Valence Electrons): 1 or 2 bottom of periodic Actinides: radioactive table Less to keep table (unstable) Elements after Reactivity: reactive than from being toooccur wide. plutonium do not in alkaline-earth nature in similar a lab) Each(created row has metals properties Other Shared Propert ...
... Shellat (Valence Electrons): 1 or 2 bottom of periodic Actinides: radioactive table Less to keep table (unstable) Elements after Reactivity: reactive than from being toooccur wide. plutonium do not in alkaline-earth nature in similar a lab) Each(created row has metals properties Other Shared Propert ...
Revising the Periodic Table
... 1. The Periodic Table is a way of arranging what we know about the chemical elements. 2. Each element in the Periodic Table is a different type of atom. 3. Each element has a different atomic number. 4. The Periodic Table is arranged in atomic number order. 5. Each atom has an atomic number. 6. An e ...
... 1. The Periodic Table is a way of arranging what we know about the chemical elements. 2. Each element in the Periodic Table is a different type of atom. 3. Each element has a different atomic number. 4. The Periodic Table is arranged in atomic number order. 5. Each atom has an atomic number. 6. An e ...
Chapter #5 Notes
... • Put in other words, when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their properties. ...
... • Put in other words, when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their properties. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Atoms, the Periodic Table & more review!
... F, Cl, Br, I, At very reactive They are very reactive because have 7 valence electrons, this means they are ALMOST full and can combine with many elements. • Nonmetals • Halogen elements combine with metals to form compounds called salts. ...
... F, Cl, Br, I, At very reactive They are very reactive because have 7 valence electrons, this means they are ALMOST full and can combine with many elements. • Nonmetals • Halogen elements combine with metals to form compounds called salts. ...
The Periodic Table
... ∙ First to notice the element's periodic repetition of properties. ∙ Designed the first periodic table ...
... ∙ First to notice the element's periodic repetition of properties. ∙ Designed the first periodic table ...
d) Ramsay. The idea of arranging the elements in the periodic table
... The ionization energies for removing successive electrons from sodium are 496 kJ/mol, 4562 kJ/mol, 6912 kJ/mol, and 9544 kJ/mol. The great jump in ionization energy after the first electron is removed indicates that a) sodium has four or five electrons. ...
... The ionization energies for removing successive electrons from sodium are 496 kJ/mol, 4562 kJ/mol, 6912 kJ/mol, and 9544 kJ/mol. The great jump in ionization energy after the first electron is removed indicates that a) sodium has four or five electrons. ...
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table Essential Question: How are
... is called a group, or family. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. ...
... is called a group, or family. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. ...
Chemical Periodicity
... b) Non-metals: opposite properties of metals, poor conductor of electricity and heat, exist in all three states of matter, the majority are gases, the solids are brittle and not lustrous, and melting points are lower than metals, broad variety of uses, gain electrons easily. c) metalloids or semimet ...
... b) Non-metals: opposite properties of metals, poor conductor of electricity and heat, exist in all three states of matter, the majority are gases, the solids are brittle and not lustrous, and melting points are lower than metals, broad variety of uses, gain electrons easily. c) metalloids or semimet ...
Learn About the Different Types of Elements on the Periodic Table
... Because they possess the properties of metals, the transition elements are also known as the transition metals. These elements are very hard, with high melting points and boiling points. Moving from left to right across the periodic table, the five d orbitals become more filled. The d electrons are ...
... Because they possess the properties of metals, the transition elements are also known as the transition metals. These elements are very hard, with high melting points and boiling points. Moving from left to right across the periodic table, the five d orbitals become more filled. The d electrons are ...
The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties
... All the alkali metals are highly reactive (Figure 2.16), and reactivity increases as you go down the group. Alkali metals react with both oxygen and water. They have low melting points, all of which are below 200°C. The alkali metals are soft and can be cut with a knife. Cesium is softer and more ...
... All the alkali metals are highly reactive (Figure 2.16), and reactivity increases as you go down the group. Alkali metals react with both oxygen and water. They have low melting points, all of which are below 200°C. The alkali metals are soft and can be cut with a knife. Cesium is softer and more ...
UNIT-3 Classification of elements and periodicity
... 9. How many elements are there in the 4th period of long form of periodic table? 10. Write the atomic number of the element unniltrium. 11. Give the IUPAC name of the element whose atomic number is 109? 12. Which one of the following subshell is not filled in the 5th period (5s, 5p, 5d, 4d)? 13. In ...
... 9. How many elements are there in the 4th period of long form of periodic table? 10. Write the atomic number of the element unniltrium. 11. Give the IUPAC name of the element whose atomic number is 109? 12. Which one of the following subshell is not filled in the 5th period (5s, 5p, 5d, 4d)? 13. In ...
Chemical Periodicity
... • Heath Chemistry: Experiments and Principles, Chapter 7 Order Among Atomsdels of Atomic ...
... • Heath Chemistry: Experiments and Principles, Chapter 7 Order Among Atomsdels of Atomic ...
Science Questions
... Reason: Any metal will combine chemically with any non-metal to form ionic bonds that hold the molecule together. ...
... Reason: Any metal will combine chemically with any non-metal to form ionic bonds that hold the molecule together. ...
Question Bank Periodic Table and Periodic Properties
... valence shell. Furthermore, this valence electron is far removed from the nucleus because the elements in this group have maximum atomic volume. As these elements can easily donate their valence electrons, therefore they are very active metals. 22. Why are the elements lying in a group prior to zero ...
... valence shell. Furthermore, this valence electron is far removed from the nucleus because the elements in this group have maximum atomic volume. As these elements can easily donate their valence electrons, therefore they are very active metals. 22. Why are the elements lying in a group prior to zero ...
Chem Ch 5 Release Test
... 1. The idea of arranging the elements in the periodic table according to their chemical and physical properties is attributed to a. Mendeleev. c. Bohr. b. Moseley. d. Ramsay. 2. Mendeleev left spaces in his periodic table and predicted several elements and their a. atomic numbers. c. properties. b. ...
... 1. The idea of arranging the elements in the periodic table according to their chemical and physical properties is attributed to a. Mendeleev. c. Bohr. b. Moseley. d. Ramsay. 2. Mendeleev left spaces in his periodic table and predicted several elements and their a. atomic numbers. c. properties. b. ...
Chapter 13 Homework
... when electrons move to a lower energy level, the energy is released in the form of light (photons). The energy of the light is related to the difference in the starting and ending energy levels of the electron. in the quantum or wave model of the atom, an atomic orbital is a region in space with ...
... when electrons move to a lower energy level, the energy is released in the form of light (photons). The energy of the light is related to the difference in the starting and ending energy levels of the electron. in the quantum or wave model of the atom, an atomic orbital is a region in space with ...
Periodic Table - Mrs. Sousa`s Science Site
... Very Unreactive because they have full electron levels ...
... Very Unreactive because they have full electron levels ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.