Chapter 8 Reading Guide Name: AP Chemistry 2016
... Understanding the arrangement of the elements in the periodic table is key foundational knowledge in chemistry. The relationships and patterns observed explain trends of the elements. The emphasis in AP Chemistry is the explanation of the concepts, not memorizing trends. For example, the size of the ...
... Understanding the arrangement of the elements in the periodic table is key foundational knowledge in chemistry. The relationships and patterns observed explain trends of the elements. The emphasis in AP Chemistry is the explanation of the concepts, not memorizing trends. For example, the size of the ...
Periodic Table
... the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. • Both left vacant spaces where unknown elements should fit. So why is Mendeleev called the “Father of the Periodic Table” and not Meyer, or both? Could it be his dashing good looks?! ...
... the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. • Both left vacant spaces where unknown elements should fit. So why is Mendeleev called the “Father of the Periodic Table” and not Meyer, or both? Could it be his dashing good looks?! ...
Periodic Table
... the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. • Both left vacant spaces where unknown elements should fit. So why is Mendeleev called the “Father of the Periodic Table” and not Meyer, or both? Could it be his dashing good looks?! ...
... the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. • Both left vacant spaces where unknown elements should fit. So why is Mendeleev called the “Father of the Periodic Table” and not Meyer, or both? Could it be his dashing good looks?! ...
Practice Questions
... 14) Most atoms prefer to fulfill the ______________ rule (having the valence shell comprise of 8 electrons). Elements on the left side of the Periodic Table have less than a half-full valence shell. Thus it is easier (takes less energy) to lose electrons to create a full valence shell, rather than g ...
... 14) Most atoms prefer to fulfill the ______________ rule (having the valence shell comprise of 8 electrons). Elements on the left side of the Periodic Table have less than a half-full valence shell. Thus it is easier (takes less energy) to lose electrons to create a full valence shell, rather than g ...
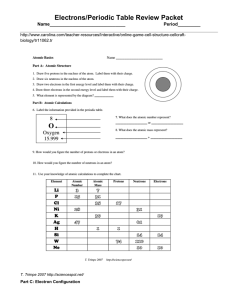
Electrons/Periodic Table Review Packet Name______________________________ Period_________
... b. metals with unpredictable properties c. a halogen d. make good semiconductors e. alkali metals f. ...
... b. metals with unpredictable properties c. a halogen d. make good semiconductors e. alkali metals f. ...
Chapter 6 Periodic Table Lecture Notes
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
Study guide for periodic table trends. A. By referring to electron
... a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? a. The number of occupied electron energy levels b. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope c. The number of electron ...
... a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? a. The number of occupied electron energy levels b. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope c. The number of electron ...
appendix: 2 - Shodhganga
... from one element to the next in the order of increasing atomic number. Rule 2 The orbital with a lower energy is filled up first before the filling up of the orbital with the higher energy commences. (Aufbau Principle) Rule 3 Electron pairing in any orbital is not possible until all die available or ...
... from one element to the next in the order of increasing atomic number. Rule 2 The orbital with a lower energy is filled up first before the filling up of the orbital with the higher energy commences. (Aufbau Principle) Rule 3 Electron pairing in any orbital is not possible until all die available or ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... Organizing the Elements Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Elements From Stardust ...
... Organizing the Elements Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Elements From Stardust ...
ch 6 ppt - Madison County Schools
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
D. - Telluride Middle/High School
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
Chapter 6 PP
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
Document
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
Chapter 8 Electron Configurations and Periodicity
... elements by increasing atomic mass and with similar properties in columns. In some places, there were missing elements whose properties he predicted. When gallium, scandium, and germanium were isolated and characterized, their properties were almost identical to those predicted by Mendeleev for eka- ...
... elements by increasing atomic mass and with similar properties in columns. In some places, there were missing elements whose properties he predicted. When gallium, scandium, and germanium were isolated and characterized, their properties were almost identical to those predicted by Mendeleev for eka- ...
Chapter 6
... Representative Elements: Main Group A Elements (elements in Groups IA-VIIIA) Know these names for these groups: Group IA: alkali metals Group IIA: alkaline earth metals Group VIIA: halogens Group VIIIA: noble gases Transition Metals: Group B elements (in middle of the Periodic Table) The behavior an ...
... Representative Elements: Main Group A Elements (elements in Groups IA-VIIIA) Know these names for these groups: Group IA: alkali metals Group IIA: alkaline earth metals Group VIIA: halogens Group VIIIA: noble gases Transition Metals: Group B elements (in middle of the Periodic Table) The behavior an ...
Section 1 How Are Elements Organized
... • A transition metal is one of the metals that can use the inner shell before using the outer shell to bond. • A transition metal may lose one, two, or even three valence electrons depending on the element with which it reacts. • Generally, the transition metals are less reactive than the alkali met ...
... • A transition metal is one of the metals that can use the inner shell before using the outer shell to bond. • A transition metal may lose one, two, or even three valence electrons depending on the element with which it reacts. • Generally, the transition metals are less reactive than the alkali met ...
Ex. 41 Answer
... Thus, compared with O, the effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost shell electrons of F is greater. The electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus. So, the atomic radius of F is smaller than that of O. O and S belong to the same group. An atom of S has 1 more occupied electron shell than an a ...
... Thus, compared with O, the effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost shell electrons of F is greater. The electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus. So, the atomic radius of F is smaller than that of O. O and S belong to the same group. An atom of S has 1 more occupied electron shell than an a ...
Elements, Periodic Trends and Lewis Dot Diagrams
... – Steel (iron-‐carbon alloy) 1200 BC (Iron Age) ...
... – Steel (iron-‐carbon alloy) 1200 BC (Iron Age) ...
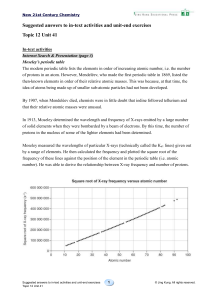
Periodic Table 2015
... • 3.1.1 Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. • 3.1.2 Distinguish between the terms group and period. • 3.1.3 Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table up to Z = 20. • 3.1.4 ...
... • 3.1.1 Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. • 3.1.2 Distinguish between the terms group and period. • 3.1.3 Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table up to Z = 20. • 3.1.4 ...
Coloring the Periodic Table - Families
... After laying all of his cards out he noticed that by arranging them according to their properties they were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. Mendeleev was even able to use the patterns in his table to predict the properties of undiscovered elements. The first periodic table was published ...
... After laying all of his cards out he noticed that by arranging them according to their properties they were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. Mendeleev was even able to use the patterns in his table to predict the properties of undiscovered elements. The first periodic table was published ...
Period
... Finding Your Way Around the Periodic Table Worksheet 1. What is the atomic number of cobalt? __________ 2. What is the atomic number of osmium? __________ 3. What is the atomic mass of germanium? __________ 4. What element is in group 1 and period 2? __________ 5. What element is in group 6 and per ...
... Finding Your Way Around the Periodic Table Worksheet 1. What is the atomic number of cobalt? __________ 2. What is the atomic number of osmium? __________ 3. What is the atomic mass of germanium? __________ 4. What element is in group 1 and period 2? __________ 5. What element is in group 6 and per ...
Document
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
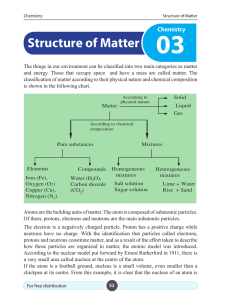
Structure of Matter - e
... carbon. In no other element, the atomic number is equal to 6. The atomic number of an element is symbolised by Z. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in it. So, it implies that the atomic number of an element is equal to the number of electrons in an atom of ...
... carbon. In no other element, the atomic number is equal to 6. The atomic number of an element is symbolised by Z. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in it. So, it implies that the atomic number of an element is equal to the number of electrons in an atom of ...
File - eScience@Kings
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
11. Patterns in the Periodic Table
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.