Power Point Chapter 5
... • In 1829, the German chemist J. W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. ...
... • In 1829, the German chemist J. W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. ...
Document
... A scientific problem. A periodic pattern to be discovered. Two detectives. One answer found and reformulated. Now, for the “rest” of the story… The Russian scientist Dmitri Medeleev was the first chemist responsible for “creating” the periodic chart of elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were ...
... A scientific problem. A periodic pattern to be discovered. Two detectives. One answer found and reformulated. Now, for the “rest” of the story… The Russian scientist Dmitri Medeleev was the first chemist responsible for “creating” the periodic chart of elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were ...
Elements are the building blocks of matter.
... An element is a __________________________ that cannot be broken down or separated into ___________substances. Each element is made up of only _____ kind of ________. There are just over ________ different kinds of elements. Elements are the same everywhere. ...
... An element is a __________________________ that cannot be broken down or separated into ___________substances. Each element is made up of only _____ kind of ________. There are just over ________ different kinds of elements. Elements are the same everywhere. ...
Periodic Trends C12-2-07
... Periodic Trends Graphing Activity The periodic table is arranged according to the periodic law. The periodic law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. Students can discover these patterns by exami ...
... Periodic Trends Graphing Activity The periodic table is arranged according to the periodic law. The periodic law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. Students can discover these patterns by exami ...
TCSS Physical Science Unit 2 – Atomic Structure Information
... Essential* Atom Atomic Mass EQ1: How do subatomic Atomic Number Electron particles of an atom affect its characteristics? Element Isotope Neutron EQ2: What properties can Proton be used to compare Proton Number subatomic particles? Supplemental** EQ3: How are isotopes of Electron Cloud Energy Level ...
... Essential* Atom Atomic Mass EQ1: How do subatomic Atomic Number Electron particles of an atom affect its characteristics? Element Isotope Neutron EQ2: What properties can Proton be used to compare Proton Number subatomic particles? Supplemental** EQ3: How are isotopes of Electron Cloud Energy Level ...
KS4 Chemistry The Periodic Table 1 of 47 © Boardworks Ltd 2005
... electron arrangement – A shorthand way of writing the number of electrons in an atom’s electron shells. element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. pe ...
... electron arrangement – A shorthand way of writing the number of electrons in an atom’s electron shells. element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. pe ...
The Periodic Table - Prairie Rose School Division No. 8
... electron arrangement – A shorthand way of writing the number of electrons in an atom’s electron shells. element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. pe ...
... electron arrangement – A shorthand way of writing the number of electrons in an atom’s electron shells. element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. pe ...
Graphing Periodic Trends
... Graphing the Periodic Trends Background The Periodic Table is arranged according to Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. These patterns can be discovered by examinin ...
... Graphing the Periodic Trends Background The Periodic Table is arranged according to Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. These patterns can be discovered by examinin ...
KS4 The Periodic Table 3548KB
... electron arrangement – A shorthand way of writing the number of electrons in an atom’s electron shells. element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. pe ...
... electron arrangement – A shorthand way of writing the number of electrons in an atom’s electron shells. element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. pe ...
File - CCHS Chemistry
... Octet Rule – an atom w/ 8 e-’s in their outer level is chemically stable ◦ He is also considered stable bec. Its out level is full Can only hold 2 e-’s ...
... Octet Rule – an atom w/ 8 e-’s in their outer level is chemically stable ◦ He is also considered stable bec. Its out level is full Can only hold 2 e-’s ...
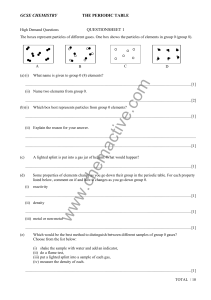
Periodic_table_questions
... (iv) The symbol for chlorine is C1, iodine is I and sodium Na. Chlorine combines with sodium to make sodium chloride, NaC1. Iodine also reacts with sodium. What will be the name and formula of the ...
... (iv) The symbol for chlorine is C1, iodine is I and sodium Na. Chlorine combines with sodium to make sodium chloride, NaC1. Iodine also reacts with sodium. What will be the name and formula of the ...
Chapter 5
... • Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. • Repeating patterns are referred to as periodic. • Mendeleev created a table in which elements with similar properties were g ...
... • Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. • Repeating patterns are referred to as periodic. • Mendeleev created a table in which elements with similar properties were g ...
Practice Packet Unit: 5 Periodic Table
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
Chem1Unit4-7.14.15 - Grainger County Schools
... SPI 3221.1.3 Describe the trends found in the periodic table with respect to atomic size, ionization energy, or electronegativity. CLE 3221.1.3 Describe an atom in terms of its composition and electron characteristics. 3221.1.8 Explain the formation of anions and cations, and predict the charge of a ...
... SPI 3221.1.3 Describe the trends found in the periodic table with respect to atomic size, ionization energy, or electronegativity. CLE 3221.1.3 Describe an atom in terms of its composition and electron characteristics. 3221.1.8 Explain the formation of anions and cations, and predict the charge of a ...
CHAPTER 6
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
chapter5
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
Document
... Procedures: In this activity you will be creating 4 graphs using Excel. Each graph will use the data found on the abridged Periodic Table on the next page. Trendlines are not necessary for these graphs. Excel Graph 1: ATOMIC RADIUS 1. Open an Excel Workbook 2. In Cell A1, type Element Symbol a. If t ...
... Procedures: In this activity you will be creating 4 graphs using Excel. Each graph will use the data found on the abridged Periodic Table on the next page. Trendlines are not necessary for these graphs. Excel Graph 1: ATOMIC RADIUS 1. Open an Excel Workbook 2. In Cell A1, type Element Symbol a. If t ...
CHAPTER 6
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
... • Atomic radii decrease within a row going from left to right on the periodic table. – This last fact seems contrary to intuition. – How does nature make the elements smaller even though the electron number is increasing? ...
The d-and f-Block Elements
... The d and f-Block Elements Top 15 Concepts 1. d -Block elements: The elements lying in the middle of periodic table belonging to groups 3 to 12 are known as d – block elements. Their general electronic configuration is (n – 1)d1-10 ns1-2 where (n – 1) stands for penultimate (last but one) shell. 2. ...
... The d and f-Block Elements Top 15 Concepts 1. d -Block elements: The elements lying in the middle of periodic table belonging to groups 3 to 12 are known as d – block elements. Their general electronic configuration is (n – 1)d1-10 ns1-2 where (n – 1) stands for penultimate (last but one) shell. 2. ...
8th Grade Chap 4 Study Guide Answer Section
... c. varying ability to conduct electricitic current. b. tendency to be unreactive. d. ability to be pulled out into long wires. 4. The elements that do not ordinarily form compounds are a. elements in the carbon family. c. metals. b. inert gases. d. halogens. 5. In the periodic table, the most reacti ...
... c. varying ability to conduct electricitic current. b. tendency to be unreactive. d. ability to be pulled out into long wires. 4. The elements that do not ordinarily form compounds are a. elements in the carbon family. c. metals. b. inert gases. d. halogens. 5. In the periodic table, the most reacti ...
Page 8: Review 1
... The tendency to lose electrons ____ as we move down a column. a. increases b. remains the same c. bigger than ...
... The tendency to lose electrons ____ as we move down a column. a. increases b. remains the same c. bigger than ...
The Periodic Table
... Robert Boyle (born Ireland, 1627) First to suggest that there were ‘elements’ that could not be further separated into different substances. ...
... Robert Boyle (born Ireland, 1627) First to suggest that there were ‘elements’ that could not be further separated into different substances. ...
(Periodic Trends) - stroh
... Discovered by boiling urine There are 2 forms: white and red The white forms combusts in air ...
... Discovered by boiling urine There are 2 forms: white and red The white forms combusts in air ...
Solution - Welcome To Badhan Education
... •€Cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from the parent atom. •€As a result the no of electrons and decreased and no: of protons remains the same. •€The no of positive charges becomes greater than the negative changes which results in greater nuclear attraction (increase in effecti ...
... •€Cations are formed by the loss of one or more electrons from the parent atom. •€As a result the no of electrons and decreased and no: of protons remains the same. •€The no of positive charges becomes greater than the negative changes which results in greater nuclear attraction (increase in effecti ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.