Objectives - Warren County Public Schools
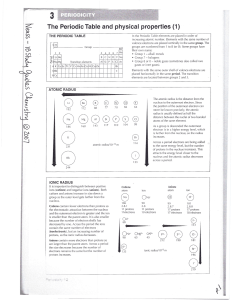
... 2. Circle the elements that are representative elements: Al, Fe, Br , Ag Explain how you know this. 3. Circle the elements below that have similar chemical properties: Explain how you know this. Carbon (C), Nitrogen, (N), Silicon (Si), Boron (B) 4. What is the name of the group of elements that are ...
... 2. Circle the elements that are representative elements: Al, Fe, Br , Ag Explain how you know this. 3. Circle the elements below that have similar chemical properties: Explain how you know this. Carbon (C), Nitrogen, (N), Silicon (Si), Boron (B) 4. What is the name of the group of elements that are ...
Ch 14 power point
... oxygen, with 8 protons, gains/steals two eand then has 10 e-. The superscript is telling you that it has two too many electrons relative to its neutral form. ...
... oxygen, with 8 protons, gains/steals two eand then has 10 e-. The superscript is telling you that it has two too many electrons relative to its neutral form. ...
The Periodic Table and physical properties (1)
... Trends in first ionization energy On moving down a group, the atomic radius increases as additional electron shells are added. This causes the shielding effect to increase. The further the outer or valence shell is from the nucleus, the smaller the attractive force exerted by the protons in the nucl ...
... Trends in first ionization energy On moving down a group, the atomic radius increases as additional electron shells are added. This causes the shielding effect to increase. The further the outer or valence shell is from the nucleus, the smaller the attractive force exerted by the protons in the nucl ...
Lesson Plan
... remembering chemical and physical properties of elements. The structure of the periodic table is a direct result of the periodic nature of elemental properties, which is very important for chemistry students to understand. Elements in the same column have the same number of valance electrons; they o ...
... remembering chemical and physical properties of elements. The structure of the periodic table is a direct result of the periodic nature of elemental properties, which is very important for chemistry students to understand. Elements in the same column have the same number of valance electrons; they o ...
Electron Configuration And Periodic Properties
... hydrogen. Increased nuclear charge causes this: For example, the 1s orbital of H is higher in energy than 1s orbital of He. Different subshells within each principle energy level (n) no longer have the same energy. For a given n: s electrons closer than p electrons, s orbital lower in energy more st ...
... hydrogen. Increased nuclear charge causes this: For example, the 1s orbital of H is higher in energy than 1s orbital of He. Different subshells within each principle energy level (n) no longer have the same energy. For a given n: s electrons closer than p electrons, s orbital lower in energy more st ...
1 - DarringtonScience
... What physical and chemical properties are found among the nonmetals? What happens to the atoms of most nonmetals when they react with other elements? How do the physical and chemical properties of halogens compare with those of the noble gases? Where in the periodic table are the metalloids found? ...
... What physical and chemical properties are found among the nonmetals? What happens to the atoms of most nonmetals when they react with other elements? How do the physical and chemical properties of halogens compare with those of the noble gases? Where in the periodic table are the metalloids found? ...
Initial Pages.pmd - Sakshieducation.com
... In the chapter ‘Structure of atom’ you have learnt that ‘s’ sub-shell with one orbital contains a maximum of two electrons. Each ‘p’ sub-shell contains 3 orbitals and accommodates a maximum of six electrons. The‘d’ sub-shell contains 5 orbitals and accommodates a maximum of 10 electrons and ‘f’ sub- ...
... In the chapter ‘Structure of atom’ you have learnt that ‘s’ sub-shell with one orbital contains a maximum of two electrons. Each ‘p’ sub-shell contains 3 orbitals and accommodates a maximum of six electrons. The‘d’ sub-shell contains 5 orbitals and accommodates a maximum of 10 electrons and ‘f’ sub- ...
Pre-AP Chemistry Exam 4 - Harding Charter Preparatory High School
... horizontal row in the periodic table vertical column in the periodic table A repetition of properties occurs when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. type of element that is a good conductor of heat and electric current type of element characterized by the presence of electro ...
... horizontal row in the periodic table vertical column in the periodic table A repetition of properties occurs when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. type of element that is a good conductor of heat and electric current type of element characterized by the presence of electro ...
The Periodic Table
... With the ever-increasing number of elements, chemists recognized that there may be some kind of systematic way to organize the elements. The question was: how? A logical way to begin to group elements together was by their chemical properties. In other words, putting elements in separate groups base ...
... With the ever-increasing number of elements, chemists recognized that there may be some kind of systematic way to organize the elements. The question was: how? A logical way to begin to group elements together was by their chemical properties. In other words, putting elements in separate groups base ...
File - VarsityField
... Bohr model – the energy of H-atom depends on n ….(E = - Rhc/n2) • Atoms with more than 1 electron, sub-shell energies depend on both n and ℓ. • Subshell energy order – 2 general rules • Electrons assigned to sub-shells of increasing ‘n + ℓ’ value • For 2 sub-shells with the same ‘n + ℓ’ value, elect ...
... Bohr model – the energy of H-atom depends on n ….(E = - Rhc/n2) • Atoms with more than 1 electron, sub-shell energies depend on both n and ℓ. • Subshell energy order – 2 general rules • Electrons assigned to sub-shells of increasing ‘n + ℓ’ value • For 2 sub-shells with the same ‘n + ℓ’ value, elect ...
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... minerals important for your health, are examples of alkaline earth metals. Because magnesium is solid and relatively light, it is used in the fabrication of electronic devices, such as the laptop shown in Figure 6.4. ...
... minerals important for your health, are examples of alkaline earth metals. Because magnesium is solid and relatively light, it is used in the fabrication of electronic devices, such as the laptop shown in Figure 6.4. ...
84.443/543 Advanced Inorganic Chemistry
... There is a large decrease in atomic size between La (169pm) and Hf (144 pm). This is due to the filling of the f orbitals of the Lanthanide series. As a result, the elements Hf and beyond appear to be unusually small. The decrease in size is called the lanthanide contraction, and is simply due to th ...
... There is a large decrease in atomic size between La (169pm) and Hf (144 pm). This is due to the filling of the f orbitals of the Lanthanide series. As a result, the elements Hf and beyond appear to be unusually small. The decrease in size is called the lanthanide contraction, and is simply due to th ...
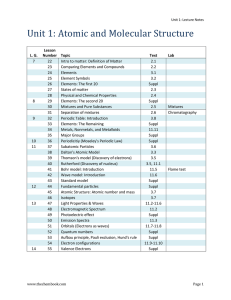
Unit 1: Lecture Notes
... 1e. Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. The volume of the hydrogen nucleus is about one trillion times less than the volume of the hydrogen atom, yet the nucleus contains almost all the mass in the form of one proton. The diameter of an ...
... 1e. Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. The volume of the hydrogen nucleus is about one trillion times less than the volume of the hydrogen atom, yet the nucleus contains almost all the mass in the form of one proton. The diameter of an ...
Concerning Electronegativity as a Basic Elemental Property and
... Fig. 4 Atomic number, Z, increases across (left-to-right) and down the Janet Left-Step formulation. Physical and chemical properties show periodicity down the Groups. There is no general left-to-right periodicity. Consider elements 9, 10, 11, 12 that correspond to the distinctly non-periodic: F, Ne, ...
... Fig. 4 Atomic number, Z, increases across (left-to-right) and down the Janet Left-Step formulation. Physical and chemical properties show periodicity down the Groups. There is no general left-to-right periodicity. Consider elements 9, 10, 11, 12 that correspond to the distinctly non-periodic: F, Ne, ...
periodic table II 016
... larger than the radius of the atom. (3) The ion is negatively charged and its radius is smaller than the radius of the atom. (4) The ion is negatively charged and its radius is larger than the radius of the atom. ...
... larger than the radius of the atom. (3) The ion is negatively charged and its radius is smaller than the radius of the atom. (4) The ion is negatively charged and its radius is larger than the radius of the atom. ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... used to break down compounds into their components, and the development of the spectrometer, which was used to identify the newly isolated elements, played major roles in the advancement of chemistry. The industrial revolution of the mid-1800s also played a major role, which led to the development o ...
... used to break down compounds into their components, and the development of the spectrometer, which was used to identify the newly isolated elements, played major roles in the advancement of chemistry. The industrial revolution of the mid-1800s also played a major role, which led to the development o ...
Ionization energy
... As the size of the atom increases the outermost electrons are held less tightly by the nucleus (attractive force between the electron and the nucleus is inversely proportional to the distance). As a result it becomes easier to remove the electron and therefore the ionization energy decreases with th ...
... As the size of the atom increases the outermost electrons are held less tightly by the nucleus (attractive force between the electron and the nucleus is inversely proportional to the distance). As a result it becomes easier to remove the electron and therefore the ionization energy decreases with th ...
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
... It may be (i)electrovalency or (ii)covalency . When the proper sign is associated with valency it becomes oxidation number(ON). It is mostly a theoretical concept particularly for covalent compounds and ions. Definition: It is the theoetical charge which an atom will possess when all the atoms in a ...
... It may be (i)electrovalency or (ii)covalency . When the proper sign is associated with valency it becomes oxidation number(ON). It is mostly a theoretical concept particularly for covalent compounds and ions. Definition: It is the theoetical charge which an atom will possess when all the atoms in a ...
Electrons and Periodicity
... The inner transition metals are the two rows at the bottom of the periodic table. They include the lanthanide and actinide series. Here are some characteristics of the inner transition metals. They are very dense compared to most other metals. Many of the inner transition metals are radioactive. ...
... The inner transition metals are the two rows at the bottom of the periodic table. They include the lanthanide and actinide series. Here are some characteristics of the inner transition metals. They are very dense compared to most other metals. Many of the inner transition metals are radioactive. ...
Atomic Theory and Atomic Structure PowerPoint
... Far right of the periodic table These elements are extremely unreactive or inert They rarely form compounds with other elements ...
... Far right of the periodic table These elements are extremely unreactive or inert They rarely form compounds with other elements ...
Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams
... the same energy sublevel must have an electron before electrons begin pairing up inside the same orbital; this is known as Hund's rule. The diagram below represents the so-called orbital diagram for chromium. The 24 electrons of a chromium atom will fill each of the atomic orbitals in the manner sho ...
... the same energy sublevel must have an electron before electrons begin pairing up inside the same orbital; this is known as Hund's rule. The diagram below represents the so-called orbital diagram for chromium. The 24 electrons of a chromium atom will fill each of the atomic orbitals in the manner sho ...
C H A P T E R
... compounds are white solids that dissolve in water to form solutions that conduct electricity. Similarly, the elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine can combine with sodium in a 1:1 ratio to form NaF, NaCl, NaBr, and NaI. These compounds are also white solids that can dissolve in water to f ...
... compounds are white solids that dissolve in water to form solutions that conduct electricity. Similarly, the elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine can combine with sodium in a 1:1 ratio to form NaF, NaCl, NaBr, and NaI. These compounds are also white solids that can dissolve in water to f ...
Chapter 6 Section 3 Periodic Trends
... charged electrons, the sodium ion has a net positive charge. An ion with a positive charge is called a cation. The charge for a cation is written as a number followed by a plus sign. If the charge is 1, the number in 1à is usually omitted from the symbol for the ion. For example, Na1à is written as ...
... charged electrons, the sodium ion has a net positive charge. An ion with a positive charge is called a cation. The charge for a cation is written as a number followed by a plus sign. If the charge is 1, the number in 1à is usually omitted from the symbol for the ion. For example, Na1à is written as ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.