Section 2 Electron Configuration and the Periodic
... • The number of the highest occupied energy level is 5, so the element is in the fifth period. • There are five electrons in the d sublevel, which means that it is incompletely filled. The d sublevel can hold 10 electrons. Therefore, the element is in the d block. • For d-block elements, the number ...
... • The number of the highest occupied energy level is 5, so the element is in the fifth period. • There are five electrons in the d sublevel, which means that it is incompletely filled. The d sublevel can hold 10 electrons. Therefore, the element is in the d block. • For d-block elements, the number ...
Principles of Chemistry The Development of Periodic Table
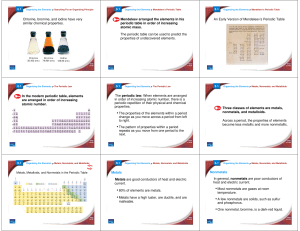
... Elements in the same column have similar chemical and physical properties? same # of valence e-s ...
... Elements in the same column have similar chemical and physical properties? same # of valence e-s ...
Periodic Classification of Elements
... years later and its properties matched very closely with the predicted properties of ekaaluminium. In this section we have learnt about the success of Mendeleev’s periodic classification and also about its merits. Does it mean that this periodic table was perfect? No. Although it was a very successf ...
... years later and its properties matched very closely with the predicted properties of ekaaluminium. In this section we have learnt about the success of Mendeleev’s periodic classification and also about its merits. Does it mean that this periodic table was perfect? No. Although it was a very successf ...
File
... S1-2-07 Investigate the characteristic properties of metals, non-metals, and metalloids and classify elements according to these properties. Examples: ductility, conductivity of heat and electricity, lustre, reactivity... Be able to: Give characteristics and properties of metals, non-metals and met ...
... S1-2-07 Investigate the characteristic properties of metals, non-metals, and metalloids and classify elements according to these properties. Examples: ductility, conductivity of heat and electricity, lustre, reactivity... Be able to: Give characteristics and properties of metals, non-metals and met ...
Chemical Periodicity
... shielding, the valence shell cannot be pulled in as close. The more shielding that occurs, the further the valence shell can spread out. For example, if you are looking at the element sodium, it has the electron configuration: Na ...
... shielding, the valence shell cannot be pulled in as close. The more shielding that occurs, the further the valence shell can spread out. For example, if you are looking at the element sodium, it has the electron configuration: Na ...
Chlorine, bromine, and iodine have very similar chemical properties
... During reactions between metals and nonmetals, metal atoms tend to lose electrons, and nonmetal atoms tend to gain electrons. The transfer has a predictable effect on the size of the ions that form. ...
... During reactions between metals and nonmetals, metal atoms tend to lose electrons, and nonmetal atoms tend to gain electrons. The transfer has a predictable effect on the size of the ions that form. ...
File
... Metals, nonmetals and metalloids ionic compound: one non-metal atom bonded with one metal atom molecular compound: two non-metal atoms bonded with each other ...
... Metals, nonmetals and metalloids ionic compound: one non-metal atom bonded with one metal atom molecular compound: two non-metal atoms bonded with each other ...
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... who is shown in Figure 6-2, proposed an organization scheme for the elements. Newlands noticed that when the elements were arranged by increasing atomic mass, their properties repeated every eighth element. In other words, the first and eighth elements had similar properties, the second and ninth el ...
... who is shown in Figure 6-2, proposed an organization scheme for the elements. Newlands noticed that when the elements were arranged by increasing atomic mass, their properties repeated every eighth element. In other words, the first and eighth elements had similar properties, the second and ninth el ...
Periodic Table Quiz 1
... ____ 15. What is the element with the highest electronegativity value? a. cesium c. calcium b. helium d. fluorine ____ 16. Which of the following elements has the smallest ionic radius? a. Li c. O b. K d. S ____ 17. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state ...
... ____ 15. What is the element with the highest electronegativity value? a. cesium c. calcium b. helium d. fluorine ____ 16. Which of the following elements has the smallest ionic radius? a. Li c. O b. K d. S ____ 17. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state ...
Missing Alien_11_12-1
... To recognize patterns in the periodic table To describe how the periodic table is arranged To describe an atom and its energy levels To learn the difference between groups and periods on the periodic table ...
... To recognize patterns in the periodic table To describe how the periodic table is arranged To describe an atom and its energy levels To learn the difference between groups and periods on the periodic table ...
6.3 Study Guide
... ____ 16. Which is the most important characteristic in detemining an element’s chemical properties? a. the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus b. which period it is found in c. the number of valence electrons it contains d. its outermost energy level ____ 17. Which property describes how m ...
... ____ 16. Which is the most important characteristic in detemining an element’s chemical properties? a. the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus b. which period it is found in c. the number of valence electrons it contains d. its outermost energy level ____ 17. Which property describes how m ...
Chemistry
... there is more than one way to distribute them. Hund's rule consists of two important ideas. Based on Model 2, circle the correct answer to each statement. a. Electrons will pair up in an orbital only when there is an even number of electrons in the sublevel all orbitals in the same sublevel have one ...
... there is more than one way to distribute them. Hund's rule consists of two important ideas. Based on Model 2, circle the correct answer to each statement. a. Electrons will pair up in an orbital only when there is an even number of electrons in the sublevel all orbitals in the same sublevel have one ...
3.62 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... other members of their respective groups. Groups 3A - 7A show a considerable variation among properties from metallic, metalloid, to nonmetallic. Transition metals do not always exhibit regular patterns in their electron configurations but have some similarities as a whole such as colored compou ...
... other members of their respective groups. Groups 3A - 7A show a considerable variation among properties from metallic, metalloid, to nonmetallic. Transition metals do not always exhibit regular patterns in their electron configurations but have some similarities as a whole such as colored compou ...
Chemical Periodicity
... weakened by shielding, the valence shell cannot be pulled in as close. The more shielding that occurs, the further the valence shell can spread out. For example, if you are looking at the element sodium, it has the electron configuration: Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 The outer energy level is n = 3 . There is ...
... weakened by shielding, the valence shell cannot be pulled in as close. The more shielding that occurs, the further the valence shell can spread out. For example, if you are looking at the element sodium, it has the electron configuration: Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 The outer energy level is n = 3 . There is ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... Which block spans 14 elemental groups? A. s-block B. p-block C. f-block D. g-block ...
... Which block spans 14 elemental groups? A. s-block B. p-block C. f-block D. g-block ...
The Modern Periodic Table
... Which block spans 14 elemental groups? A. s-block B. p-block C. f-block D. g-block ...
... Which block spans 14 elemental groups? A. s-block B. p-block C. f-block D. g-block ...
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table
... Which block spans 14 elemental groups? A. s-block B. p-block C. f-block D. g-block ...
... Which block spans 14 elemental groups? A. s-block B. p-block C. f-block D. g-block ...
Chapter 8 2013
... Unpaired electrons in orbitals gives rise to paramagnetism and is attracted to a magnetic field. Diamagnetic species contain all paired electrons and is “repelled” by the magnetic field. • Diamagnetic atoms or ions: ...
... Unpaired electrons in orbitals gives rise to paramagnetism and is attracted to a magnetic field. Diamagnetic species contain all paired electrons and is “repelled” by the magnetic field. • Diamagnetic atoms or ions: ...
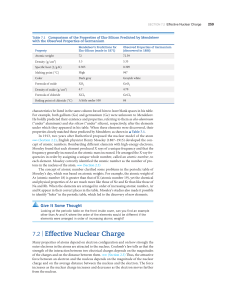
7.2 | Effective Nuclear Charge
... (“under” aluminum) and eka-silicon (“under” silicon), respectively, after the elements under which they appeared in his table. When these elements were discovered, their properties closely matched those predicted by Mendeleev, as shown in ▲ Table 7.1. In 1913, two years after Rutherford proposed the ...
... (“under” aluminum) and eka-silicon (“under” silicon), respectively, after the elements under which they appeared in his table. When these elements were discovered, their properties closely matched those predicted by Mendeleev, as shown in ▲ Table 7.1. In 1913, two years after Rutherford proposed the ...
Chem 103, Section F0F Lecture 9 - Electron Configuratioin Lecture 9
... Lecture 9 - Trends in Atomic Size There are different ways to measure size, we will use the following definitions: • For nonmetals, which typically form covalent bonds with other nonmetals - 1/2 the distance between one one atom and the neighbor it is bonded to. ...
... Lecture 9 - Trends in Atomic Size There are different ways to measure size, we will use the following definitions: • For nonmetals, which typically form covalent bonds with other nonmetals - 1/2 the distance between one one atom and the neighbor it is bonded to. ...
CHAPTER 2
... • Bohr’s model of the atom when applied to atoms with more than one electron failed to explain their line spectra • One major change from Bohr’s model is that electrons do not move in orbits • Atomic orbitals - regions in space with a high probability of finding an electron • Electrons move rapidly ...
... • Bohr’s model of the atom when applied to atoms with more than one electron failed to explain their line spectra • One major change from Bohr’s model is that electrons do not move in orbits • Atomic orbitals - regions in space with a high probability of finding an electron • Electrons move rapidly ...
Graphing Periodic Trends
... Graph #2: Atomic Radii vs Atomic Number 1. Open excel spreadsheet titled Atomic radius 2. Column A, going down, should have the numbers 1-20, 31-38, and 49-54. There are 34 numbers in total and these represent the atomic number of the elements from the periodic table. 3. In column B, going down, ty ...
... Graph #2: Atomic Radii vs Atomic Number 1. Open excel spreadsheet titled Atomic radius 2. Column A, going down, should have the numbers 1-20, 31-38, and 49-54. There are 34 numbers in total and these represent the atomic number of the elements from the periodic table. 3. In column B, going down, ty ...
Chapter 6.3 Periodic Trends
... a. gain electrons to form cations. b. gain electrons to form anions. c. lose electrons to form anions. d. lose electrons to form cations. ...
... a. gain electrons to form cations. b. gain electrons to form anions. c. lose electrons to form anions. d. lose electrons to form cations. ...
Families and Periods of the Periodic Table - CK
... or to lanthanides and actinides. The elements in these groups behave differently and do not obey the same rules as the Group 1A – 8A elements in terms of valence electrons and valence electron energy levels. You may have noticed that the first row has not been mentioned at all. In all of the example ...
... or to lanthanides and actinides. The elements in these groups behave differently and do not obey the same rules as the Group 1A – 8A elements in terms of valence electrons and valence electron energy levels. You may have noticed that the first row has not been mentioned at all. In all of the example ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.