Periodic Table - Derry Area School District
... periodic table. – The total number of valence electrons for an atom equals its group number. Page 55 ...
... periodic table. – The total number of valence electrons for an atom equals its group number. Page 55 ...
CHAPTER 8
... right. A larger effective nuclear charge means a more tightly held outer electron, and hence a higher first ionization energy. Thus, in the third period, sodium has the lowest and neon has the highest first ionization energy. ...
... right. A larger effective nuclear charge means a more tightly held outer electron, and hence a higher first ionization energy. Thus, in the third period, sodium has the lowest and neon has the highest first ionization energy. ...
CHAPTER 8 THE PERIODIC TABLE
... right. A larger effective nuclear charge means a more tightly held outer electron, and hence a higher first ionization energy. Thus, in the third period, sodium has the lowest and neon has the highest first ionization energy. ...
... right. A larger effective nuclear charge means a more tightly held outer electron, and hence a higher first ionization energy. Thus, in the third period, sodium has the lowest and neon has the highest first ionization energy. ...
Element Project - Dover Bay
... group 1, period 1, which is just down the street. Hydrogen has two siblings isotopes, deuterium and tritium, who has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. He also has a neighbor, the Alkali Metals who lives in the same street. Their names are Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidi ...
... group 1, period 1, which is just down the street. Hydrogen has two siblings isotopes, deuterium and tritium, who has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. He also has a neighbor, the Alkali Metals who lives in the same street. Their names are Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidi ...
Unit 05 - Periodicity - Lincoln Park High School
... nuclear charge of the ion is more than that of a neutral atom. Positive ions are always smaller than neutral atoms. In a similar fashion, negative ions are formed when an atom gains electrons. The relative hold of the nucleus is less in a negative ion than it is for a neutral atom. Therefore, negati ...
... nuclear charge of the ion is more than that of a neutral atom. Positive ions are always smaller than neutral atoms. In a similar fashion, negative ions are formed when an atom gains electrons. The relative hold of the nucleus is less in a negative ion than it is for a neutral atom. Therefore, negati ...
School of Elements 1. - mt
... 1. Atomic size is defined as the distance between the centre of the nucleus of an atom to its outermost shell. 2. Across a period, the nuclear charge increases. Nuclear charge is the positive charge on the nucleus of an atom. Also, across the period electrons are added to the same shell. So, electro ...
... 1. Atomic size is defined as the distance between the centre of the nucleus of an atom to its outermost shell. 2. Across a period, the nuclear charge increases. Nuclear charge is the positive charge on the nucleus of an atom. Also, across the period electrons are added to the same shell. So, electro ...
Section 11.4 Electron Configurations and Atomic Properties Orbital
... • Valence electrons – electrons in the outermost (highest) principal energy level of an atom • Core electrons – inner electrons ...
... • Valence electrons – electrons in the outermost (highest) principal energy level of an atom • Core electrons – inner electrons ...
ppt - northcampus.net
... the nucleus and repelled by one another. This results in shielding, where an electron is partially shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus by the other electrons. Although all electrons shield one another to some extent, the most effective are the core electrons. As a result, the valu ...
... the nucleus and repelled by one another. This results in shielding, where an electron is partially shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus by the other electrons. Although all electrons shield one another to some extent, the most effective are the core electrons. As a result, the valu ...
Periodic Table and Electrons
... The names of groups and periods on the periodic chart are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases. Metalloids have properties of metals and nonmetals. They are located between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Some are used in semiconductors. Peri ...
... The names of groups and periods on the periodic chart are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases. Metalloids have properties of metals and nonmetals. They are located between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Some are used in semiconductors. Peri ...
Chemistry Part - teko classes bhopal
... Most carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity. The boiling and melting points of the carbon compounds are low. Forces of attraction between these molecules of organic compounds are not very strong/ As these compound are largely non conductors of electricity hence the bonding in these comp ...
... Most carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity. The boiling and melting points of the carbon compounds are low. Forces of attraction between these molecules of organic compounds are not very strong/ As these compound are largely non conductors of electricity hence the bonding in these comp ...
Review Atomic Structure
... move to higher number groups. Group 18 has the highest 1st ionization energy. Ionization energy decreases as you move down the periodic table. ...
... move to higher number groups. Group 18 has the highest 1st ionization energy. Ionization energy decreases as you move down the periodic table. ...
Periodic Table (Wiki)
... nonmetallic; and the monatomic noble gases, which are nonmetallic and almost completely inert. Specialized groupings such as the refractory metals and the noble metals, which are subsets (in this example) of the transition metals, are also known[23] and occasionally denoted.[24] Placing the elements ...
... nonmetallic; and the monatomic noble gases, which are nonmetallic and almost completely inert. Specialized groupings such as the refractory metals and the noble metals, which are subsets (in this example) of the transition metals, are also known[23] and occasionally denoted.[24] Placing the elements ...
ATOMIC ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS AND PERIODICITY
... • Z* increases across a period owing to incomplete shielding by inner electrons. • Estimate Z* by --> [ Z - ( # inner electrons) ] • Charge felt by 2s e- in Li Z* = 3 - 2 = 1 ...
... • Z* increases across a period owing to incomplete shielding by inner electrons. • Estimate Z* by --> [ Z - ( # inner electrons) ] • Charge felt by 2s e- in Li Z* = 3 - 2 = 1 ...
8/29/12 The Science of Matter Objective: Understand the
... When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties Elements are arranged based on similar properties Elements are arranged based on increasing atomic number Atomic number is the number of protons Atom mass is the num ...
... When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties Elements are arranged based on similar properties Elements are arranged based on increasing atomic number Atomic number is the number of protons Atom mass is the num ...
The Periodic Table
... similar chemical properties. • Elements are also organized horizontally in rows, or periods. • The periodic table is divided into four blocks, the s, p, d, and f blocks. The name of each block is determined by the electron sublevel being filled in that block. ...
... similar chemical properties. • Elements are also organized horizontally in rows, or periods. • The periodic table is divided into four blocks, the s, p, d, and f blocks. The name of each block is determined by the electron sublevel being filled in that block. ...
Unit 4 Notes: Periodic Table Notes
... Most are radioactive and manmade Melting points vary, but usually higher than alkaline earth metals. Reactivity varies greatly Used for nuclear power/weapons, radiation therapy, fire alarms. Group 13: Boron Group Group 14: Carbon Group Group 15: Nitrogen Group Group 16: Oxygen Group ...
... Most are radioactive and manmade Melting points vary, but usually higher than alkaline earth metals. Reactivity varies greatly Used for nuclear power/weapons, radiation therapy, fire alarms. Group 13: Boron Group Group 14: Carbon Group Group 15: Nitrogen Group Group 16: Oxygen Group ...
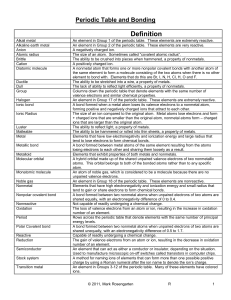
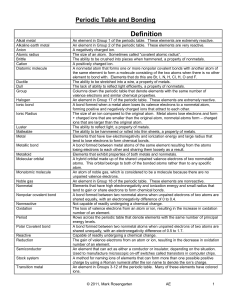
Unit 6: Periodic Table and Bonding
... An element in Group 17 of the periodic table. These elements are extremely reactive. A bond formed when a metal atom loses its valence electrons to a nonmetal atom, forming positive and negatively charged ions that attract to each other. The size of an ion compared to the original atom. Metal atoms ...
... An element in Group 17 of the periodic table. These elements are extremely reactive. A bond formed when a metal atom loses its valence electrons to a nonmetal atom, forming positive and negatively charged ions that attract to each other. The size of an ion compared to the original atom. Metal atoms ...
Unit 6: Periodic Table and Bonding
... An element in Group 17 of the periodic table. These elements are extremely reactive. A bond formed when a metal atom loses its valence electrons to a nonmetal atom, forming positive and negatively charged ions that attract to each other. The size of an ion compared to the original atom. Metal atoms ...
... An element in Group 17 of the periodic table. These elements are extremely reactive. A bond formed when a metal atom loses its valence electrons to a nonmetal atom, forming positive and negatively charged ions that attract to each other. The size of an ion compared to the original atom. Metal atoms ...
Unit 04 Introduction to Atomic Theory
... All atoms of element X are identical. All atoms of element X are different than atoms of any other element. Atoms can chemically combine together in whole number ratios. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms ...
... All atoms of element X are identical. All atoms of element X are different than atoms of any other element. Atoms can chemically combine together in whole number ratios. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms ...
Periodicity Group Project
... The worksheet and or presentation should include questions that compare the following: H and Cs; S and F; Li. Si, and Te; Na and Cl. Worksheet should include drawings showing relative atomic radius and require students to write the Noble gas configurations. ...
... The worksheet and or presentation should include questions that compare the following: H and Cs; S and F; Li. Si, and Te; Na and Cl. Worksheet should include drawings showing relative atomic radius and require students to write the Noble gas configurations. ...
AR IE Graphing - GuerinChemistry
... The last section considered neutral atoms in their ground state. Chemists have found that, by supplying sufficient energy, they can remove the most loosely held electron in the atom. The atom is thereby made into a positive ion. Such ion is called a cation. The energy required for this process is re ...
... The last section considered neutral atoms in their ground state. Chemists have found that, by supplying sufficient energy, they can remove the most loosely held electron in the atom. The atom is thereby made into a positive ion. Such ion is called a cation. The energy required for this process is re ...
Periodic Trends Notes
... If you examine the table, you'll see that the ionization at which the large jump in energy occurs is related to the atom's number of valence electrons. The jump in ionization energy shows that atoms hold onto their inner core electrons much more strongly than they hold onto their valence ele ...
... If you examine the table, you'll see that the ionization at which the large jump in energy occurs is related to the atom's number of valence electrons. The jump in ionization energy shows that atoms hold onto their inner core electrons much more strongly than they hold onto their valence ele ...
Chapter 3
... Elements in the last family, the noble gases, have either two or eight valence electrons. Their most important properties are their extreme stability and lack of reactivity. A full energy level is responsible for this unique stability. The Octet Rule Noble gases are no-nreactive because they all hav ...
... Elements in the last family, the noble gases, have either two or eight valence electrons. Their most important properties are their extreme stability and lack of reactivity. A full energy level is responsible for this unique stability. The Octet Rule Noble gases are no-nreactive because they all hav ...
Learning Activities – Description of the learning activities that will
... Understand that matter is made of atoms and that atoms are made of subatomic particles. Understand atomic structure, including: most space occupied by electrons nucleus made of protons and neutrons isotopes of an element masses of proton and neutron 2000 times greater than mass of electron ...
... Understand that matter is made of atoms and that atoms are made of subatomic particles. Understand atomic structure, including: most space occupied by electrons nucleus made of protons and neutrons isotopes of an element masses of proton and neutron 2000 times greater than mass of electron ...
35 The data table below shows elements Xx, Yy, and
... 1 One electron is removed from both a Na atom and a K atom, producing two ions. Using principles of atomic structure, explain why the Na ion is much smaller than the K ion. Discuss both ions in your answer. 2 Which of the following Group 2 elements has the lowest ionization energy? (1) Be (2) Mg (3) ...
... 1 One electron is removed from both a Na atom and a K atom, producing two ions. Using principles of atomic structure, explain why the Na ion is much smaller than the K ion. Discuss both ions in your answer. 2 Which of the following Group 2 elements has the lowest ionization energy? (1) Be (2) Mg (3) ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.