Unit 3 Notes: Periodic Table Notes
... Most are radioactive and manmade Melting points vary, but usually higher than alkaline earth metals. Reactivity varies greatly Used for nuclear power/weapons, radiation therapy, fire alarms. Group 13: Boron Group Group 14: Carbon Group Group 15: Nitrogen Group Group 16: Oxygen Group ...
... Most are radioactive and manmade Melting points vary, but usually higher than alkaline earth metals. Reactivity varies greatly Used for nuclear power/weapons, radiation therapy, fire alarms. Group 13: Boron Group Group 14: Carbon Group Group 15: Nitrogen Group Group 16: Oxygen Group ...
Summary 1 b - Uddingston Grammar School
... 1. The outer electrons are further away from the nucleus. 2. The screening effect of the inner electron shells reduces the nuclear attraction for the outer electrons, despite the increased (positive) nuclear charge. ...
... 1. The outer electrons are further away from the nucleus. 2. The screening effect of the inner electron shells reduces the nuclear attraction for the outer electrons, despite the increased (positive) nuclear charge. ...
Power Point Chapter 5
... • Helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and radon were subsequently discovered in the next 5 years. • They were originally called the inert gases. ...
... • Helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and radon were subsequently discovered in the next 5 years. • They were originally called the inert gases. ...
Chapter 5
... • Helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and radon were subsequently discovered in the next 5 years. • They were originally called the inert gases. ...
... • Helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and radon were subsequently discovered in the next 5 years. • They were originally called the inert gases. ...
Metals - TeacherWeb
... The metals in these groups are nearly as reactive as those on the left side of the table. The most familiar of these metals are aluminum, tin and lead. Aluminum is the lightweight metal used in soda cans, tin is used to coat steel to protect it from corrosion in cans of food. Lead is a shiny, ...
... The metals in these groups are nearly as reactive as those on the left side of the table. The most familiar of these metals are aluminum, tin and lead. Aluminum is the lightweight metal used in soda cans, tin is used to coat steel to protect it from corrosion in cans of food. Lead is a shiny, ...
Chapter 6
... We can use the periodic table to determine which sub-shells should be filled up first. ...
... We can use the periodic table to determine which sub-shells should be filled up first. ...
Increasing Radii
... These groups generally display a wide range of properties which are said to be representative of most elements. ...
... These groups generally display a wide range of properties which are said to be representative of most elements. ...
Unit 3 Activity Exploring Periodic Trends… MORE! Name: Directions
... 1. Obtain a laptop and go to the website: http://www.ptable.com/ 2. Click the blue “properties” tab located at the top of the screen. 3. You will use the interactive tools and this worksheet to continue to learn about the trends (patterns) that exist within the periodic table. 4. You may use Google ...
... 1. Obtain a laptop and go to the website: http://www.ptable.com/ 2. Click the blue “properties” tab located at the top of the screen. 3. You will use the interactive tools and this worksheet to continue to learn about the trends (patterns) that exist within the periodic table. 4. You may use Google ...
Chemistry - Octorara Area School District
... A. Classsified substances (pure vs. mixture) (MOW) B. Introduced the periodic table of the elements, identifying groups and periods.(MOW) B. Differentiate between metal and non-metal.(MOW) B. Listed the noble gases(MOW) C. Students are encouraged to use the answer keys virtuously. D. Studens are rew ...
... A. Classsified substances (pure vs. mixture) (MOW) B. Introduced the periodic table of the elements, identifying groups and periods.(MOW) B. Differentiate between metal and non-metal.(MOW) B. Listed the noble gases(MOW) C. Students are encouraged to use the answer keys virtuously. D. Studens are rew ...
Honors Chemistry
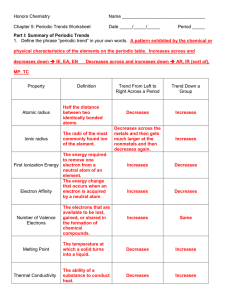
... b. How would this account for the trend you discovered in the first ionization energy? Because of the additional protons, electrons are held more tightly by the nucleus which increases the amount of energy (ionization energy) needed to remove them. c. How would this account for the trend that you di ...
... b. How would this account for the trend you discovered in the first ionization energy? Because of the additional protons, electrons are held more tightly by the nucleus which increases the amount of energy (ionization energy) needed to remove them. c. How would this account for the trend that you di ...
Now
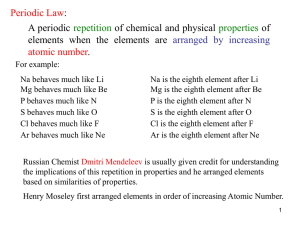
... His periodic table helped to discover new elements like germanium. 1) Mendeleev’s periodic table consists of 7 periods (horizontal) and 9 groups (vertical). 2) Elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic weights. 3) The elements that have similar property were placed in vertical co ...
... His periodic table helped to discover new elements like germanium. 1) Mendeleev’s periodic table consists of 7 periods (horizontal) and 9 groups (vertical). 2) Elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic weights. 3) The elements that have similar property were placed in vertical co ...
Atomic Theory Powerpoint
... Alkaline Earth metals are the elements in group 2 of the Periodic Table. The chemical symbols identify the element names. The alkaline earth metals are silvered colored, soft metals. Elements classified as Alkaline Earth Metals are all found in the Earth’s crust, but not in the elemental form as the ...
... Alkaline Earth metals are the elements in group 2 of the Periodic Table. The chemical symbols identify the element names. The alkaline earth metals are silvered colored, soft metals. Elements classified as Alkaline Earth Metals are all found in the Earth’s crust, but not in the elemental form as the ...
Document
... example, scientists later discovered that atoms are not the most basic unit of matter because they are divisible. As well, the modern periodic table lists the elements in order of their atomic number, not their atomic mass. Of course, it also includes elements that had not been discovered in Mendele ...
... example, scientists later discovered that atoms are not the most basic unit of matter because they are divisible. As well, the modern periodic table lists the elements in order of their atomic number, not their atomic mass. Of course, it also includes elements that had not been discovered in Mendele ...
Chemical Bonds
... we go from left to right across the periodic table. At least it increases until we get to the inert gases. There it drops off to zero because there is no room for additional electrons in the valence energy level. ...
... we go from left to right across the periodic table. At least it increases until we get to the inert gases. There it drops off to zero because there is no room for additional electrons in the valence energy level. ...
Periodic Trends Activity (EChem)
... 2. Make a line graph of the values in group 1. Does Zeff increase, decrease, or remain the same as you move down a group? ______________________________ Knowing the pattern of Zeff is very important! The values of Zeff explain a lot of the other trends you are about to discover. ...
... 2. Make a line graph of the values in group 1. Does Zeff increase, decrease, or remain the same as you move down a group? ______________________________ Knowing the pattern of Zeff is very important! The values of Zeff explain a lot of the other trends you are about to discover. ...
Term 1 Revision Study Guide File
... How many electrons can exist in the first main energy level? How many electrons can exist in the second main energy level? How many electrons can exist in the third main energy level? How many sublevels are there in the first main energy level? What are they? How many sublevels are there in the seco ...
... How many electrons can exist in the first main energy level? How many electrons can exist in the second main energy level? How many electrons can exist in the third main energy level? How many sublevels are there in the first main energy level? What are they? How many sublevels are there in the seco ...
Effective Nuclear Charge
... 2. Make a line graph of the values in group 1. Does Zeff increase, decrease, or remain the same as you move down a group? ______________________________ Knowing the pattern of Zeff is very important! The values of Zeff explain a lot of the other trends you are about to discover. ...
... 2. Make a line graph of the values in group 1. Does Zeff increase, decrease, or remain the same as you move down a group? ______________________________ Knowing the pattern of Zeff is very important! The values of Zeff explain a lot of the other trends you are about to discover. ...
The Organization of the Elements
... number, and therefore organized the table by nuclear charge (or atomic number) rather than atomic weight. Thus Moseley placed argon (atomic number 18) before potassium (atomic number 19) based on their X-ray wavelengths, despite the fact that argon has a greater atomic weight (39.9) than potassium ( ...
... number, and therefore organized the table by nuclear charge (or atomic number) rather than atomic weight. Thus Moseley placed argon (atomic number 18) before potassium (atomic number 19) based on their X-ray wavelengths, despite the fact that argon has a greater atomic weight (39.9) than potassium ( ...
AP CHEMISTRY Periodic Trends Worksheet
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
chapter_07au pt1
... essentially the same, but the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. Periodic Properties of the Elements ...
... essentially the same, but the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. Periodic Properties of the Elements ...
Honors Chemistry
... b. How would this account for the trend you discovered in the first ionization energy? Because of the additional protons, electrons are held more tightly by the nucleus which increases the amount of energy (ionization energy) needed to remove them. c. How would this account for the trend that you di ...
... b. How would this account for the trend you discovered in the first ionization energy? Because of the additional protons, electrons are held more tightly by the nucleus which increases the amount of energy (ionization energy) needed to remove them. c. How would this account for the trend that you di ...
periodic table
... – IA are called alkali metals because the react with water to from an alkaline solution – Group IIA are called the alkaline earth metals because they are reactive, but not as reactive as Group IA. • They are also soft metals like Earth. ...
... – IA are called alkali metals because the react with water to from an alkaline solution – Group IIA are called the alkaline earth metals because they are reactive, but not as reactive as Group IA. • They are also soft metals like Earth. ...
Electrons in Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... A. The 4f sublevel is filled with 14 electrons. The 5d sublevel is partially filled with eight electrons. Therefore, this element is in the d block The element is the transition metal platinum, Pt, which is in Group 10 and has a low reactivity ...
... A. The 4f sublevel is filled with 14 electrons. The 5d sublevel is partially filled with eight electrons. Therefore, this element is in the d block The element is the transition metal platinum, Pt, which is in Group 10 and has a low reactivity ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.