Chapter 8
... y What is the periodic trend for ionization energy? y What is the difference between 1st and successive ionization energies? y ...
... y What is the periodic trend for ionization energy? y What is the difference between 1st and successive ionization energies? y ...
Dmitri Mendeleev
... On these cards, Mendeleev wrote information such as the elements' melting points, densities, colors, atomic masses and bonding powers. Mendeleev noticed that patterns appeared when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. As he laid out cards, each element had properties simila ...
... On these cards, Mendeleev wrote information such as the elements' melting points, densities, colors, atomic masses and bonding powers. Mendeleev noticed that patterns appeared when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. As he laid out cards, each element had properties simila ...
Part I
... Semiconductors: 0 ~ ≤ Eg ≤ ~ 3 eV Metals & Semimetals: Eg = 0 eV Insulators: Eg ≥ 3 eV • An Exception is Diamond: Eg = ~ 6 eV. Diamond is usually an insulator, but it can be doped & used as a semiconductor! • Also, sometimes there is confusing terminology like: ...
... Semiconductors: 0 ~ ≤ Eg ≤ ~ 3 eV Metals & Semimetals: Eg = 0 eV Insulators: Eg ≥ 3 eV • An Exception is Diamond: Eg = ~ 6 eV. Diamond is usually an insulator, but it can be doped & used as a semiconductor! • Also, sometimes there is confusing terminology like: ...
Electron Configurations and Periodic Properties Name
... Electron Configurations and Periodic Properties Name:___________________ Guided Inquiry Period:____ Objective: You have learned how the atoms are arranged and how to determine the electron configurations for atoms. Now we need to look at the relationship between electron configurations and periodic ...
... Electron Configurations and Periodic Properties Name:___________________ Guided Inquiry Period:____ Objective: You have learned how the atoms are arranged and how to determine the electron configurations for atoms. Now we need to look at the relationship between electron configurations and periodic ...
The Upper Limit of the Periodic Table of Elements Points out to the
... Herein we present an analysis of the internal constitution of the “short” and “long” forms of the Periodic Table of Elements. As a result, we conclude that the second (long) version is more correct. We also suggest a long version of the Table consisting of 8 periods and 18 groups, with the last (hea ...
... Herein we present an analysis of the internal constitution of the “short” and “long” forms of the Periodic Table of Elements. As a result, we conclude that the second (long) version is more correct. We also suggest a long version of the Table consisting of 8 periods and 18 groups, with the last (hea ...
As化学汉英双解讲义
... Candidates should be able to: (f) *describe the number and relative energies of the s, p and d orbitals for the principal quantum numbers 1, 2 and 3 and also the 4s and 4p orbitals. (g) *describe the shapes of s and p orbitals (h) state the electronic configuration of atoms and ions given the proton ...
... Candidates should be able to: (f) *describe the number and relative energies of the s, p and d orbitals for the principal quantum numbers 1, 2 and 3 and also the 4s and 4p orbitals. (g) *describe the shapes of s and p orbitals (h) state the electronic configuration of atoms and ions given the proton ...
No Slide Title
... of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic (repeating) pattern. patterns on the periodic table are called periodic trends ...
... of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic (repeating) pattern. patterns on the periodic table are called periodic trends ...
C3 Homework Booklet File
... Label each of the group of the periodic table below. You may colour each group a different colour to show where they are. ...
... Label each of the group of the periodic table below. You may colour each group a different colour to show where they are. ...
Primeasia University
... 1. Principal Quantum Number (n): This quantum number denotes the energy level or the principal shell to which an electron belongs. It is denoted by “n”. It can have only integral value from 1 to , but 1 to 7 has so far been established. The letters K, L, M…… are also used to designate the values ...
... 1. Principal Quantum Number (n): This quantum number denotes the energy level or the principal shell to which an electron belongs. It is denoted by “n”. It can have only integral value from 1 to , but 1 to 7 has so far been established. The letters K, L, M…… are also used to designate the values ...
A “periodic table” is an arrangement of elements in
... arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties The periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element to another ...
... arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties The periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element to another ...
Electron Arrangements - Madison Public Schools
... Orbitals can hold a maximum of two electrons; two electrons in one orbital must have opposite spins. • Hund’s Rule Electrons fill equal energy orbitals one at a time until each is occupied by one electron; Electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin. ...
... Orbitals can hold a maximum of two electrons; two electrons in one orbital must have opposite spins. • Hund’s Rule Electrons fill equal energy orbitals one at a time until each is occupied by one electron; Electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin. ...
electrons - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • Fluorine (F) : 9 protons, 9 electrons (10 neutrons, only natural isotope) – Group 17: gain 1 electron – F- (fluoride): 9 protons, 10 electrons ……. – If we changed number of protons, element changes • Alchemy ...
... • Fluorine (F) : 9 protons, 9 electrons (10 neutrons, only natural isotope) – Group 17: gain 1 electron – F- (fluoride): 9 protons, 10 electrons ……. – If we changed number of protons, element changes • Alchemy ...
Chapter 1 - WebAssign
... If a test supports a hypothesis, another experiment is devised to further test the hypothesis. If a test does not support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis is changed or even discarded depending upon how badly it fails the test. After a hypothesis has been supported by many independent observers, it ...
... If a test supports a hypothesis, another experiment is devised to further test the hypothesis. If a test does not support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis is changed or even discarded depending upon how badly it fails the test. After a hypothesis has been supported by many independent observers, it ...
05-Notes - HCC Learning Web
... S-block elements: Groups IA and IIA fill s-sublevels (first 2 groups = 2 s-electrons). P-block elements: Groups IIIA to VIIIA fill the p-sublevels (last 6 groups = 6 p-electrons). D-block elements: Groups IIIB to IIB fill the d-sublevels (middle 10 groups = 10 d-electrons). f-block of elements: Inne ...
... S-block elements: Groups IA and IIA fill s-sublevels (first 2 groups = 2 s-electrons). P-block elements: Groups IIIA to VIIIA fill the p-sublevels (last 6 groups = 6 p-electrons). D-block elements: Groups IIIB to IIB fill the d-sublevels (middle 10 groups = 10 d-electrons). f-block of elements: Inne ...
Chapter_5_Notes_Periodic
... S-block elements: Groups IA and IIA fill s-sublevels (first 2 groups = 2 s-electrons). P-block elements: Groups IIIA to VIIIA fill the p-sublevels (last 6 groups = 6 p-electrons). D-block elements: Groups IIIB to IIB fill the d-sublevels (middle 10 groups = 10 d-electrons). f-block of elements: Inne ...
... S-block elements: Groups IA and IIA fill s-sublevels (first 2 groups = 2 s-electrons). P-block elements: Groups IIIA to VIIIA fill the p-sublevels (last 6 groups = 6 p-electrons). D-block elements: Groups IIIB to IIB fill the d-sublevels (middle 10 groups = 10 d-electrons). f-block of elements: Inne ...
chapter 6 - HCC Learning Web
... S-block elements: Groups IA and IIA fill s-sublevels (first 2 groups = 2 s-electrons). P-block elements: Groups IIIA to VIIIA fill the p-sublevels (last 6 groups = 6 p-electrons). D-block elements: Groups IIIB to IIB fill the d-sublevels (middle 10 groups = 10 d-electrons). f-block of elements: Inne ...
... S-block elements: Groups IA and IIA fill s-sublevels (first 2 groups = 2 s-electrons). P-block elements: Groups IIIA to VIIIA fill the p-sublevels (last 6 groups = 6 p-electrons). D-block elements: Groups IIIB to IIB fill the d-sublevels (middle 10 groups = 10 d-electrons). f-block of elements: Inne ...
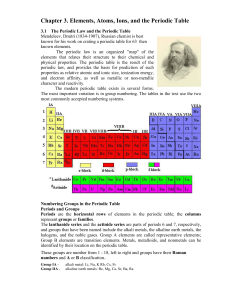
Chapter 3
... The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table The periodic law is an organized "map" of the elements that relates their structure to their chemical and physical properties. The periodic table is the result of the periodic law, and provides the basis for prediction of such properties as relative atomic and ...
... The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table The periodic law is an organized "map" of the elements that relates their structure to their chemical and physical properties. The periodic table is the result of the periodic law, and provides the basis for prediction of such properties as relative atomic and ...
Chapter 1 Classnotes CHEM
... Most nonmetals are gases at room temperature: N, O, F and Cl. Others are solid at room temperature: C, P, Se, S & I. Br (bromine) is liquid at room temperature. Metalloids have properties of both metals and non metals. They are ALL solid at room temperature. They are semiconductors of electricity wh ...
... Most nonmetals are gases at room temperature: N, O, F and Cl. Others are solid at room temperature: C, P, Se, S & I. Br (bromine) is liquid at room temperature. Metalloids have properties of both metals and non metals. They are ALL solid at room temperature. They are semiconductors of electricity wh ...
Periodic Table Trends - Waterford Public Schools
... photon) to overcome the effective nuclear charge in a gaseous atom or ion, it can leave the atom completely and become ionized or charged 0 This is because the number of protons and electrons is no longer equal ...
... photon) to overcome the effective nuclear charge in a gaseous atom or ion, it can leave the atom completely and become ionized or charged 0 This is because the number of protons and electrons is no longer equal ...
The Periodic Table and The Periodic Law
... Noble gases are ignored. Fluorine has the largest E.N. Francium the smallest E.N. ...
... Noble gases are ignored. Fluorine has the largest E.N. Francium the smallest E.N. ...
Writing Electron Configurations - highamc
... • Helium is He 1s2 symbolizing there are 2 electrons in the s sublevel. • Lithium is 1s22s1 symbolizing that there are 2 electrons in the 1 s sublevel and 1 electron in the 2 s level. • Fluorine is written as 1s22s22p5 • Why do you think that there are only 2 electrons in the s sublevel, but there ...
... • Helium is He 1s2 symbolizing there are 2 electrons in the s sublevel. • Lithium is 1s22s1 symbolizing that there are 2 electrons in the 1 s sublevel and 1 electron in the 2 s level. • Fluorine is written as 1s22s22p5 • Why do you think that there are only 2 electrons in the s sublevel, but there ...
Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
... making it easier to gain an electron, thus the electronegativity _________________________. • Reactivity is defined as the ability for an atom to react/combine with other atoms. o With reactivity we must look at the metals and non-metals as two separate groups. • Metal Reactivity- metals want to los ...
... making it easier to gain an electron, thus the electronegativity _________________________. • Reactivity is defined as the ability for an atom to react/combine with other atoms. o With reactivity we must look at the metals and non-metals as two separate groups. • Metal Reactivity- metals want to los ...
Chapter_6_Notes_Periodic
... when they are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. He is known as the architect of the modern periodic table, showing systematic arrangement of the elements. He arranged the elements by increasing atomic masses and began a new row with an element that repeated the properties of a previous el ...
... when they are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. He is known as the architect of the modern periodic table, showing systematic arrangement of the elements. He arranged the elements by increasing atomic masses and began a new row with an element that repeated the properties of a previous el ...
SCH 3U - Norbraten
... a) From your observations, what physical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? b) From your observations, what chemical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? 3. Is the solution that is produced when a metal reacts with water acidic or basic? 4. ...
... a) From your observations, what physical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? b) From your observations, what chemical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? 3. Is the solution that is produced when a metal reacts with water acidic or basic? 4. ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.