Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... The atomic symbols in “B.” represent isotopes of carbon with 6 protons each, but one has 6 neutrons and the other has 8. C. ...
... The atomic symbols in “B.” represent isotopes of carbon with 6 protons each, but one has 6 neutrons and the other has 8. C. ...
Review guide for Chemistry`s First Semester Exam Unit 1 Thinking
... Know the value for the density of water 8. Write the value of density for pure water Know what makes one substance more dense than a different substance 9. If you have 1 kg of lead and 1 kg of cotton, which takes up more space? 10. If you have a volume of 10 cm3 of lead and another volume of 10 cm3 ...
... Know the value for the density of water 8. Write the value of density for pure water Know what makes one substance more dense than a different substance 9. If you have 1 kg of lead and 1 kg of cotton, which takes up more space? 10. If you have a volume of 10 cm3 of lead and another volume of 10 cm3 ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... The s-, p-, d-, and f-Block Elements • The shape of the periodic table becomes clear if it is divided into blocks representing the atom’s energy sublevel being filled with valence electrons. ...
... The s-, p-, d-, and f-Block Elements • The shape of the periodic table becomes clear if it is divided into blocks representing the atom’s energy sublevel being filled with valence electrons. ...
Inorganic and Physical Chemistry - university of nairobi staff profiles
... Which of the following properties are intensive and which are extensive? (a) length, (b) volume, (c) temperature, (d) mass. 4. Give an example of an element and a compound. How do elements and compounds differ? 5. Classify each of the following substances as an element or a compound: (a) hydrogen, ( ...
... Which of the following properties are intensive and which are extensive? (a) length, (b) volume, (c) temperature, (d) mass. 4. Give an example of an element and a compound. How do elements and compounds differ? 5. Classify each of the following substances as an element or a compound: (a) hydrogen, ( ...
Periodic Trends - Ector County ISD.
... What term is used to describe an atom's tendency to attract electrons (selfish of electrons) to itself when it is chemically combined with another element? electronegativity Really greedy because they are so close to having 8 valence electrons. ...
... What term is used to describe an atom's tendency to attract electrons (selfish of electrons) to itself when it is chemically combined with another element? electronegativity Really greedy because they are so close to having 8 valence electrons. ...
Periodic Trends
... What term is used to describe an atom's tendency to attract electrons (selfish of electrons) to itself when it is chemically combined with another element? electronegativity Really greedy because they are so close to having 8 valence electrons. ...
... What term is used to describe an atom's tendency to attract electrons (selfish of electrons) to itself when it is chemically combined with another element? electronegativity Really greedy because they are so close to having 8 valence electrons. ...
Lesson 3 - St John Brebeuf
... Valence: The number of unpaired valence electrons on the atom (COMBINING CAPACITY) each ORBITAL holds 2 eonly dealing with s and p orbitals so the maximum number of electrons in a shell is: 2 _______________ e- (s) + 6 e- (p) = 8 e only UNPAIRED electrons take part in bonding! ...
... Valence: The number of unpaired valence electrons on the atom (COMBINING CAPACITY) each ORBITAL holds 2 eonly dealing with s and p orbitals so the maximum number of electrons in a shell is: 2 _______________ e- (s) + 6 e- (p) = 8 e only UNPAIRED electrons take part in bonding! ...
Summary of things you need to know from this first quarter. The
... 1. Each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms 2. The atoms of a given element are identical 3. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms 4. Chemical reactions involve reorganizations of the a ...
... 1. Each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms 2. The atoms of a given element are identical 3. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms 4. Chemical reactions involve reorganizations of the a ...
File - Chemical Engineering
... the metalloids. Metals are to the left of the line and non-metals to the right. The layout of the periodic table demonstrates recurring ("periodic") chemical properties. Elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number (i.e., the number of protons in the atomic nucleus). Rows are arranged so ...
... the metalloids. Metals are to the left of the line and non-metals to the right. The layout of the periodic table demonstrates recurring ("periodic") chemical properties. Elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number (i.e., the number of protons in the atomic nucleus). Rows are arranged so ...
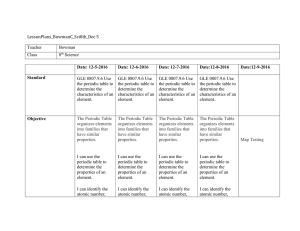
LessonPlans_BowmanC_Sci8th_Dec 5 Teacher Bowman Class 8th
... atomic mass, number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of an element using the periodic table. ...
... atomic mass, number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of an element using the periodic table. ...
History of Periodic Table
... weight • Example - halogen triad composed of chlorine, bromine, and iodine ...
... weight • Example - halogen triad composed of chlorine, bromine, and iodine ...
Electrons - TCS Moodle 2
... • Must go in order (Aufbau principle) • 2 electrons per orbital, maximum (Pauli Ex.) • We need electron configurations so that we can determine the number of electrons in the outermost energy level These are called valence electrons • The number of valence electrons determines how many and what this ...
... • Must go in order (Aufbau principle) • 2 electrons per orbital, maximum (Pauli Ex.) • We need electron configurations so that we can determine the number of electrons in the outermost energy level These are called valence electrons • The number of valence electrons determines how many and what this ...
File
... Metals: Left side of table to “zig zag” Nonmetals: Right side of table to “zig zag” + hydrogen Periods: Rows across →, numbered 1, 2, 3, … down left side (number = outer energy level) Groups: Columns down ↓, numbered 1 – 8 across top (number = valence e-) Families: Names Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth ...
... Metals: Left side of table to “zig zag” Nonmetals: Right side of table to “zig zag” + hydrogen Periods: Rows across →, numbered 1, 2, 3, … down left side (number = outer energy level) Groups: Columns down ↓, numbered 1 – 8 across top (number = valence e-) Families: Names Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth ...
Part B: Periodic Trends
... 14. What is the symbol of the element with the highest ionization energy? _______ 15. What element has the lowest electronegativity? _______ 16. Who was given credit for first developing the periodic table of the elements? ______________ 17. The energy that is required to remove an electron from it ...
... 14. What is the symbol of the element with the highest ionization energy? _______ 15. What element has the lowest electronegativity? _______ 16. Who was given credit for first developing the periodic table of the elements? ______________ 17. The energy that is required to remove an electron from it ...
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry Directions: Use your notes
... you are unsure of an answer you can email me [email protected] or chat on Remind. Scientific Theories Dalton theorized that atoms were the smallest particle and could not be divided. Atoms can bond with one another in whole number ratios to form compounds but cannot be created or destroye ...
... you are unsure of an answer you can email me [email protected] or chat on Remind. Scientific Theories Dalton theorized that atoms were the smallest particle and could not be divided. Atoms can bond with one another in whole number ratios to form compounds but cannot be created or destroye ...
File
... •It dips down after filling “s’ orbital and after 1 electron is put in each “p” orbital ...
... •It dips down after filling “s’ orbital and after 1 electron is put in each “p” orbital ...
Periodic Table - Mrs. Sousa`s Science Site
... Valence electrons are those in the outer energy level – they are used for bonding and come from the s & p orbital space Noble Gases (group #18) all have 8 valence electrons. Exception to the octet rule: He (helium) has 2 valence electrons ...
... Valence electrons are those in the outer energy level – they are used for bonding and come from the s & p orbital space Noble Gases (group #18) all have 8 valence electrons. Exception to the octet rule: He (helium) has 2 valence electrons ...
Chapter 8 Electron Configurations and Periodicity
... Contents and Concepts Electronic Structure of Atoms In the previous chapter, you learned that we characterize an atomic orbital by four quantum numbers: n, l, ml, and ms. In the first section, we look further at electron spin; then we discuss how electrons are distributed among the possible orbital ...
... Contents and Concepts Electronic Structure of Atoms In the previous chapter, you learned that we characterize an atomic orbital by four quantum numbers: n, l, ml, and ms. In the first section, we look further at electron spin; then we discuss how electrons are distributed among the possible orbital ...
Slide 1
... atomic number! Therefore, atomic number will increase as you move from left to right across a period and as you move from top to bottom down a group. We also know that the atomic number is exactly equal to the number of protons so the trend for protons will be the same In a neutral atom, the num ...
... atomic number! Therefore, atomic number will increase as you move from left to right across a period and as you move from top to bottom down a group. We also know that the atomic number is exactly equal to the number of protons so the trend for protons will be the same In a neutral atom, the num ...
Atoms and The Periodic Table
... Atoms and The Periodic Table Aristotle and Democritus In the fourth century BC two models were presented by Greek philosophers to explain the nature of matter. Aristotle, perhaps the most important philosopher and naturalists that ever lived, explained that all matter was composed of four earth elem ...
... Atoms and The Periodic Table Aristotle and Democritus In the fourth century BC two models were presented by Greek philosophers to explain the nature of matter. Aristotle, perhaps the most important philosopher and naturalists that ever lived, explained that all matter was composed of four earth elem ...
Midterm Review
... a. tightly packed protons. b. tightly packed neutrons. c. tightly packed protons and neutrons. d. loosely connected protons and electrons. ____ 72. Protons and neutrons strongly attract when they a. are moving fast. c. are at high energies. b. are very close together. d. have opposite charges. ____ ...
... a. tightly packed protons. b. tightly packed neutrons. c. tightly packed protons and neutrons. d. loosely connected protons and electrons. ____ 72. Protons and neutrons strongly attract when they a. are moving fast. c. are at high energies. b. are very close together. d. have opposite charges. ____ ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.