Chapter 8 PPT - Richsingiser.com
... molecules, but they are very reactive. • The reactivity decreases as you go down the group. Their chemistry is dominated by the formation of X- ions. • The interhalogens are compounds formed from different halogens, like IF3 and BrCl. ...
... molecules, but they are very reactive. • The reactivity decreases as you go down the group. Their chemistry is dominated by the formation of X- ions. • The interhalogens are compounds formed from different halogens, like IF3 and BrCl. ...
ionization energy
... molecules, but they are very reactive. • The reactivity decreases as you go down the group. Their chemistry is dominated by the formation of X- ions. • The interhalogens are compounds formed from different halogens, like IF3 and BrCl. ...
... molecules, but they are very reactive. • The reactivity decreases as you go down the group. Their chemistry is dominated by the formation of X- ions. • The interhalogens are compounds formed from different halogens, like IF3 and BrCl. ...
Chemical Matter: Elements and Their Classification
... electron with n = 2, therefore, “feels” an effective nuclear charge only of a little more than 1+, because it can penetrate only to a limited extent within the boundary of the 1s orbital. Now, if the outside electron is located in the 2s orbital it penetrates the 1s shield to a greater extent that i ...
... electron with n = 2, therefore, “feels” an effective nuclear charge only of a little more than 1+, because it can penetrate only to a limited extent within the boundary of the 1s orbital. Now, if the outside electron is located in the 2s orbital it penetrates the 1s shield to a greater extent that i ...
What is an electron?
... proposed the idea that electrons can be found around the nucleus in different energy levels or shells. One cannot pinpoint the location of an electron, only about where it is in a specific energy level or shell ...
... proposed the idea that electrons can be found around the nucleus in different energy levels or shells. One cannot pinpoint the location of an electron, only about where it is in a specific energy level or shell ...
Periodic Trends
... since they are the best electron givers. • The most reactive nonmetals are the smallest ones, the best electron takers. ...
... since they are the best electron givers. • The most reactive nonmetals are the smallest ones, the best electron takers. ...
Chem Ch 5 Release Test
... d. vary unpredictably. ____ 98. As you move left to right from gallium through bromine, atomic radii a. generally increase. c. do not change. b. generally decrease. d. vary unpredictably. ____ 99. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom ____ as you move left to right from potassium th ...
... d. vary unpredictably. ____ 98. As you move left to right from gallium through bromine, atomic radii a. generally increase. c. do not change. b. generally decrease. d. vary unpredictably. ____ 99. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom ____ as you move left to right from potassium th ...
94 Lecture Notes 5th Series: Inorganic Chemistry THE MAIN
... The reaction above is a redox reaction. Write down the balanced ½-reactions for the reduction and the oxidation taking place. How many electrons are being transferred from Na to water? The Group 2 elements are known as the alkaline earth metals. All the elements in groups 1 and 2 are metals and all ...
... The reaction above is a redox reaction. Write down the balanced ½-reactions for the reduction and the oxidation taking place. How many electrons are being transferred from Na to water? The Group 2 elements are known as the alkaline earth metals. All the elements in groups 1 and 2 are metals and all ...
Periodic Trends (Section 6.3).
... AOD C.3.1 Define atomic radii, ionization energy, electronegativity, and energy levels. AOD C.3.2 Recognize periodic trends of elements, including the number of valence electrons, atomic size, and reactivity. ...
... AOD C.3.1 Define atomic radii, ionization energy, electronegativity, and energy levels. AOD C.3.2 Recognize periodic trends of elements, including the number of valence electrons, atomic size, and reactivity. ...
The Periodic Table
... The softness, low density and low melting points are the result of weaker metallic bonding due to only one valence electron in this group. ...
... The softness, low density and low melting points are the result of weaker metallic bonding due to only one valence electron in this group. ...
PeriodicTableA
... as well as s electrons, allowing for multiple oxidation states. Most d Block elements have a +2 oxidation State which corresponds to the loss of the two s electrons. This is especially true on the right side of the d block, but less true on the left. ---- For example Sc+2 does not exist, and Ti+2 is ...
... as well as s electrons, allowing for multiple oxidation states. Most d Block elements have a +2 oxidation State which corresponds to the loss of the two s electrons. This is especially true on the right side of the d block, but less true on the left. ---- For example Sc+2 does not exist, and Ti+2 is ...
Periodic Table - Red Deer Public
... as well as s electrons, allowing for multiple oxidation states. Most d Block elements have a +2 oxidation State which corresponds to the loss of the two s electrons. This is especially true on the right side of the d block, but less true on the left. ---- For example Sc+2 does not exist, and Ti+2 is ...
... as well as s electrons, allowing for multiple oxidation states. Most d Block elements have a +2 oxidation State which corresponds to the loss of the two s electrons. This is especially true on the right side of the d block, but less true on the left. ---- For example Sc+2 does not exist, and Ti+2 is ...
Notes 1
... 3. Sizes of Atoms and Ions • Consider a collection of argon atoms in the gas phase. • When they undergo collisions, they ricochet apart because electron clouds cannot penetrate each other to a significant extent. • The apparent radius is determined by the closest distances separating the nuclei ...
... 3. Sizes of Atoms and Ions • Consider a collection of argon atoms in the gas phase. • When they undergo collisions, they ricochet apart because electron clouds cannot penetrate each other to a significant extent. • The apparent radius is determined by the closest distances separating the nuclei ...
Essentials of Biology Sylvia S. Mader
... • Atoms differ in their electronegativity, or their affinity for electrons in a covalent bond. • The unequal sharing of electrons in a molecule such as water makes the molecule ...
... • Atoms differ in their electronegativity, or their affinity for electrons in a covalent bond. • The unequal sharing of electrons in a molecule such as water makes the molecule ...
What is the PERIODIC TABLE?
... linear accelerator at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Germany. It created the calcium-ions used in new tests that produced element 117. For now, number 117 is the most massive element confirmed to exist! Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807 ...
... linear accelerator at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Germany. It created the calcium-ions used in new tests that produced element 117. For now, number 117 is the most massive element confirmed to exist! Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807 ...
Chapter 6
... • Atoms get smaller as you go bottom to top on the periodic table because as you travel up a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you travel left to right across the periodic table because the number of protons in the nucleus increases. • As the number of pr ...
... • Atoms get smaller as you go bottom to top on the periodic table because as you travel up a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you travel left to right across the periodic table because the number of protons in the nucleus increases. • As the number of pr ...
periodic table
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
CHEMICAL PERIODICITY
... • Good conductors of electricity and have a high luster • Less reactive than alkali and alkali-earth metal • Some (e.g. platinum and gold) are so unreactive that they do not form compounds easily. • Some are found as free element. ...
... • Good conductors of electricity and have a high luster • Less reactive than alkali and alkali-earth metal • Some (e.g. platinum and gold) are so unreactive that they do not form compounds easily. • Some are found as free element. ...
Periodic Table
... Electrons with low ionization energies have low electronegativities because their nuclei do not exert a strong attractive force on electrons. Elements with high ionization energies have high electronegativities due to the strong pull exerted on electrons by the nucleus. In a group, the electronegati ...
... Electrons with low ionization energies have low electronegativities because their nuclei do not exert a strong attractive force on electrons. Elements with high ionization energies have high electronegativities due to the strong pull exerted on electrons by the nucleus. In a group, the electronegati ...
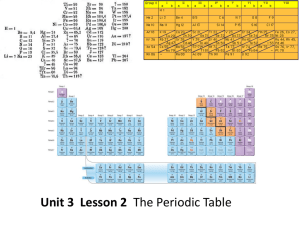
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table Essential Question: How are
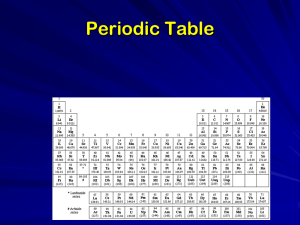
... • Each square contains an element’s chemical name, atomic number, chemical symbol, and average atomic mass. • The atomic number is placed at the top of each square. • The chemical symbol is an abbreviation for the element’s name. • The first letter of the chemical symbol is always capitalized, and a ...
... • Each square contains an element’s chemical name, atomic number, chemical symbol, and average atomic mass. • The atomic number is placed at the top of each square. • The chemical symbol is an abbreviation for the element’s name. • The first letter of the chemical symbol is always capitalized, and a ...
Page 8: Review 1
... List the early attempts of classification of the elements. Match scientists and their contributions to the development of the P.T. State the modern periodic law. Distinguish groups and periods in the P.T. Define chemical stability using the octet rule. Use the periodic table to predict electron conf ...
... List the early attempts of classification of the elements. Match scientists and their contributions to the development of the P.T. State the modern periodic law. Distinguish groups and periods in the P.T. Define chemical stability using the octet rule. Use the periodic table to predict electron conf ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Subtle Trends in 1st I.E.: How can subtle deviations („peaks‟) from the general trend across any row be rationalized for the group II, III and group V, VI elements? Task: Draw out ground state orbital „box‟ diagrams for Be and B, as well as N and O. What differences do you notice between the two di ...
... Subtle Trends in 1st I.E.: How can subtle deviations („peaks‟) from the general trend across any row be rationalized for the group II, III and group V, VI elements? Task: Draw out ground state orbital „box‟ diagrams for Be and B, as well as N and O. What differences do you notice between the two di ...
Practice Packet Unit: 5 Periodic Table
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
periodic trends
... it repeats every so often Because many physical and chemical properties are influenced by the outer shell configuration of an atom, it isn’t surprising that such properties also exhibit periodicity... • atomic radius It is much more important to • ionic radius know and understand each • ionisation e ...
... it repeats every so often Because many physical and chemical properties are influenced by the outer shell configuration of an atom, it isn’t surprising that such properties also exhibit periodicity... • atomic radius It is much more important to • ionic radius know and understand each • ionisation e ...
Document
... The Periodic Table is arranged according to the Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. The properties that will be examined in this lesson are: atomic radius AND first ...
... The Periodic Table is arranged according to the Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. The properties that will be examined in this lesson are: atomic radius AND first ...
Chemistry Periodic Trends in Atomic Radii Graphing Exercise 11
... **Turn to page 175 in your book and look at the quick lab at the top of the page. You will be using Create a Graph to construct 3 graphs. You will need the periodic table you have in your SIS as well. Here is what you will include in this assignment…… 1. Construct a graph comparing the atomic radii ...
... **Turn to page 175 in your book and look at the quick lab at the top of the page. You will be using Create a Graph to construct 3 graphs. You will need the periodic table you have in your SIS as well. Here is what you will include in this assignment…… 1. Construct a graph comparing the atomic radii ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.