notes ch7 Electron Configurations and Chemical Periodicity
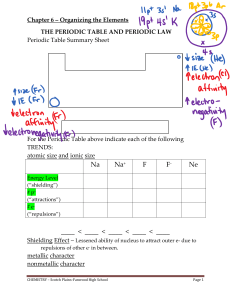
... • Atomic radius is ½ the experimentally determined distance between the centers of the two atoms. • For the main group elements, atomic radius increases going down a group due to the fact that the outermost electrons have a higher n value. • Atomic radius decreases going across a period due to the f ...
... • Atomic radius is ½ the experimentally determined distance between the centers of the two atoms. • For the main group elements, atomic radius increases going down a group due to the fact that the outermost electrons have a higher n value. • Atomic radius decreases going across a period due to the f ...
7-1 Notes: Arranging the Elements
... Elements are classified according to their ____________ as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. The number of ____________ in the outer energy level of an atom helps determine the category in which an element belongs. The __________ line on the periodic table can help you recognize metals, nonmetals, ...
... Elements are classified according to their ____________ as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. The number of ____________ in the outer energy level of an atom helps determine the category in which an element belongs. The __________ line on the periodic table can help you recognize metals, nonmetals, ...
Atomic Radius
... cause of these patterns has to do with something called electron affinity which we will not discuss because if we did, your heads might explode. So lets just describe the trend and leave it at that, ok? ...
... cause of these patterns has to do with something called electron affinity which we will not discuss because if we did, your heads might explode. So lets just describe the trend and leave it at that, ok? ...
Chapter 6 - HCC Learning Web
... subsequently discovered in the next 5 years. • They were originally called the inert gases. • Recently, several compounds of xenon and krypton have been made and the term noble gases or rare gases is currently used. Chapter 6 ...
... subsequently discovered in the next 5 years. • They were originally called the inert gases. • Recently, several compounds of xenon and krypton have been made and the term noble gases or rare gases is currently used. Chapter 6 ...
chemistry 1000 - U of L Class Index
... Most electrons do not ‘feel’ the full positive charge of the nucleus. Other electrons in the atom (particularly those in lower energy orbitals) ‘shield’ some of this charge. The amount of positive charge ‘felt’ by an electron in a given orbital is called the effective nuclear charge (Z eff ). The fo ...
... Most electrons do not ‘feel’ the full positive charge of the nucleus. Other electrons in the atom (particularly those in lower energy orbitals) ‘shield’ some of this charge. The amount of positive charge ‘felt’ by an electron in a given orbital is called the effective nuclear charge (Z eff ). The fo ...
Unit 3.2: The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends Notes
... –2 charge. Oxygen is the most reactive element of this group. ...
... –2 charge. Oxygen is the most reactive element of this group. ...
Chapter 3 Periodic Table
... compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. ...
... compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. ...
File
... 2.C.4 The localized electron bonding model describes and predict molecular geometry using Lewis diagrams and the VSEPR model. 2.D.1 Ionic solids have high melting points, are brittle, and conduct electricity when molten or in solution. 2.D.2 Metallic solids are good conductors of heat and elec ...
... 2.C.4 The localized electron bonding model describes and predict molecular geometry using Lewis diagrams and the VSEPR model. 2.D.1 Ionic solids have high melting points, are brittle, and conduct electricity when molten or in solution. 2.D.2 Metallic solids are good conductors of heat and elec ...
Periodic Trends
... Use the periodic table to write electron configurations Use the periodic table to obtain information about the properties of elements ...
... Use the periodic table to write electron configurations Use the periodic table to obtain information about the properties of elements ...
Mendeleev`s Periodic Table - Scotch Plains
... Nonmetals: to the right of the zig zag line most active nonmetal = F (top right, group 17, not 18) nonmetals have high ionization energies, have high electronegativities, gain electrons, form negative ions when with metals, share electrons with nonmetals, lack luster, are brittle, are poor conductor ...
... Nonmetals: to the right of the zig zag line most active nonmetal = F (top right, group 17, not 18) nonmetals have high ionization energies, have high electronegativities, gain electrons, form negative ions when with metals, share electrons with nonmetals, lack luster, are brittle, are poor conductor ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... [Ne] 3s 23p 5, which has its valence electrons in orbitals of the third energy level. The electron configuration of iron (a transition element) is [Ar]4s 23d 6, which has its valence electrons in orbits of both the third and fourth energy levels. ...
... [Ne] 3s 23p 5, which has its valence electrons in orbitals of the third energy level. The electron configuration of iron (a transition element) is [Ar]4s 23d 6, which has its valence electrons in orbits of both the third and fourth energy levels. ...
Periodic Properties
... across a row in the periodic chart; the most metallic elements are on the left side Metallic character increases from top to bottom in a column in the periodic chart; the most metallic elements will be found at the bottom of the chart. ...
... across a row in the periodic chart; the most metallic elements are on the left side Metallic character increases from top to bottom in a column in the periodic chart; the most metallic elements will be found at the bottom of the chart. ...
Periodic Table 2015
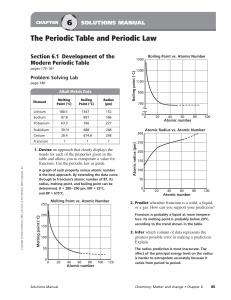
... ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (F I). • 3.2.3 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electronegativities for elements across period 3. • 3.2.4 Compa ...
... ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (F I). • 3.2.3 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electronegativities for elements across period 3. • 3.2.4 Compa ...
Chapter 7 Outline full
... Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of scandium oxide with nitric acid. ...
... Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of scandium oxide with nitric acid. ...
Chapter 7 Outline full
... Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of scandium oxide with nitric acid. ...
... Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of scandium oxide with nitric acid. ...
Chemical Periodicity
... metals High density, strong, malleable, and good conductor of heat. nonmetals Low density, weak, brittle (non-malleable), poor conductor of heat. metalloids or semimetals High density, in between strong and weak, brittle, fair conductors of heat. 2 Who is Dmitri Mendeleev, and what was his con ...
... metals High density, strong, malleable, and good conductor of heat. nonmetals Low density, weak, brittle (non-malleable), poor conductor of heat. metalloids or semimetals High density, in between strong and weak, brittle, fair conductors of heat. 2 Who is Dmitri Mendeleev, and what was his con ...
Section 1 How Are Elements Organized
... • The lanthanides and actinides are sometimes called the f-block of the periodic table. • The actinides are unique in that their nuclear structures are more important than their electron configurations. • Because the nuclei of actinides are unstable and spontaneously break apart, all actinides are r ...
... • The lanthanides and actinides are sometimes called the f-block of the periodic table. • The actinides are unique in that their nuclear structures are more important than their electron configurations. • Because the nuclei of actinides are unstable and spontaneously break apart, all actinides are r ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... their chemical and physical properties – Known as a group – Labeled by a number at the top of the column – Sometimes a group is called a family of elements because they seem to be related – Ex: Group 17 – “Halogen” group • Tend to combine easily with other elements and compounds, especially elements ...
... their chemical and physical properties – Known as a group – Labeled by a number at the top of the column – Sometimes a group is called a family of elements because they seem to be related – Ex: Group 17 – “Halogen” group • Tend to combine easily with other elements and compounds, especially elements ...
What Are Compounds?
... electrons among the bonded atoms in a molecular compound or a polyatomic ion, oxidation numbers are assigned to the atoms composing the compound or ion. • Unlike ionic charges, oxidation numbers do not have an exact physical meaning: rather, they serve as useful “bookkeeping” devices to help keep tr ...
... electrons among the bonded atoms in a molecular compound or a polyatomic ion, oxidation numbers are assigned to the atoms composing the compound or ion. • Unlike ionic charges, oxidation numbers do not have an exact physical meaning: rather, they serve as useful “bookkeeping” devices to help keep tr ...
Periodic Trends 2015 0
... 2. What happens to an electron if you add the appropriate amount of energy? _________________________ 3. What can cause an electron to completely fly off of an atom? ____________________________________ 4. What is it called when an electron flies off of an atom? _____________________________________ ...
... 2. What happens to an electron if you add the appropriate amount of energy? _________________________ 3. What can cause an electron to completely fly off of an atom? ____________________________________ 4. What is it called when an electron flies off of an atom? _____________________________________ ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.