Periodicity - ilc.edu.hk
... are great ∵ extent of bond breaking : boiling >> melting Particles are completely separated on boiling For Gp4A elements, the differences between m.p. and b.p. are relatively small ∵ extent of bond breaking : boiling melting ...
... are great ∵ extent of bond breaking : boiling >> melting Particles are completely separated on boiling For Gp4A elements, the differences between m.p. and b.p. are relatively small ∵ extent of bond breaking : boiling melting ...
Bohr Model Practice PP
... (Since electrons are negatively charged, taking away an electron will cause the atom to be positively charged.) ...
... (Since electrons are negatively charged, taking away an electron will cause the atom to be positively charged.) ...
Study guide for periodic table trends. A. By referring to electron
... Define the term first ionization energy and state what is meant by the term periodicity? The minimum energy to remove one electron from a gaseous atom. Or the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms and periodicity is the repeating pattern of physical and chemi ...
... Define the term first ionization energy and state what is meant by the term periodicity? The minimum energy to remove one electron from a gaseous atom. Or the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms and periodicity is the repeating pattern of physical and chemi ...
Periodic Table
... How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? As the number of elements increased, chemists inevitably began to find patterns in their properties. Chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into groups Ex. Chlorine, bromine, and iodine have very similar ...
... How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? As the number of elements increased, chemists inevitably began to find patterns in their properties. Chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into groups Ex. Chlorine, bromine, and iodine have very similar ...
Periodic Table
... How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? As the number of elements increased, chemists inevitably began to find patterns in their properties. Chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into groups Ex. Chlorine, bromine, and iodine have very similar ...
... How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? As the number of elements increased, chemists inevitably began to find patterns in their properties. Chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into groups Ex. Chlorine, bromine, and iodine have very similar ...
Chemistry
... Chemists use the Periodic Table to help them understand the reactions of the elements. John Newlands was one of the first chemists to see repeating patterns in the properties and reactions of the elements. ...
... Chemists use the Periodic Table to help them understand the reactions of the elements. John Newlands was one of the first chemists to see repeating patterns in the properties and reactions of the elements. ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... bond radius. Measure the distance between the nuclei of 2 atoms bonded together and divide by two. ...
... bond radius. Measure the distance between the nuclei of 2 atoms bonded together and divide by two. ...
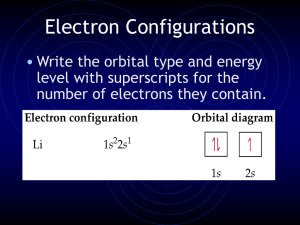
Electron Configurations
... Electron Configurations • Need to Know: • Period numbers of periodic table are the energy levels (n) of the orbitals • Regions of periodic table where certain “clouds” exist. ...
... Electron Configurations • Need to Know: • Period numbers of periodic table are the energy levels (n) of the orbitals • Regions of periodic table where certain “clouds” exist. ...
Trends of the Periodic Table
... Why? Elements on the right of the chart want to take others atom's electron (not given them up) because they are close to achieving the octet. The means it will require more energy to remove the outer most electron. Elements on the left of the chart would prefer to give up their electrons so it is e ...
... Why? Elements on the right of the chart want to take others atom's electron (not given them up) because they are close to achieving the octet. The means it will require more energy to remove the outer most electron. Elements on the left of the chart would prefer to give up their electrons so it is e ...
“Periodic Properties of the Element: Trends in the Periodic Table” By
... The properties of the elements exhibit trends. These trends can be predicted using the periodic table and can be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements. Elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve stable octet formation. Stable octets are see ...
... The properties of the elements exhibit trends. These trends can be predicted using the periodic table and can be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements. Elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve stable octet formation. Stable octets are see ...
Final Review Questions - Lakeland Regional High School
... ____ 24. As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table ____. a. ionization energy increases c. electronegativity decreases b. atomic radii increase d. atomic mass decreases ____ 25. Of the following elements, which one has the smallest first ionization energy? a. boro ...
... ____ 24. As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table ____. a. ionization energy increases c. electronegativity decreases b. atomic radii increase d. atomic mass decreases ____ 25. Of the following elements, which one has the smallest first ionization energy? a. boro ...
UNIT VIII - St John Brebeuf
... each ORBITAL holds 2 eonly dealing with s and p orbitals so the maximum number of electrons in a shell is: _______________ only UNPAIRED electrons take part in bonding! ...
... each ORBITAL holds 2 eonly dealing with s and p orbitals so the maximum number of electrons in a shell is: _______________ only UNPAIRED electrons take part in bonding! ...
Discovering and understanding patterns in the PT Periodic Trends
... across the period the atomic radius decreases and since the electrons are closer to the nucleus, they are held very tightly and require large amounts of ionization energy in order to remove an electron. The tendency for atoms with high electronegativity is to hold very tightly to the electrons withi ...
... across the period the atomic radius decreases and since the electrons are closer to the nucleus, they are held very tightly and require large amounts of ionization energy in order to remove an electron. The tendency for atoms with high electronegativity is to hold very tightly to the electrons withi ...
H Unit 4: Periodic Table
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
The Periodic Table - Newburyport High School
... to the nucleus and can hold on to the e- tighter. –ALSO…………………. ...
... to the nucleus and can hold on to the e- tighter. –ALSO…………………. ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. The octet rule is useful for predicting what types of ions an element is likely ...
... The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. The octet rule is useful for predicting what types of ions an element is likely ...
Chapter 13 Homework
... in the quantum or wave model of the atom, an atomic orbital is a region in space with high probability of finding an electron, and each atomic orbital can hold two electrons. in the quantum or wave theory, the location of an electron is designated by its principle quantum number (energy level) a ...
... in the quantum or wave model of the atom, an atomic orbital is a region in space with high probability of finding an electron, and each atomic orbital can hold two electrons. in the quantum or wave theory, the location of an electron is designated by its principle quantum number (energy level) a ...
The Structure of the Atom
... A great deal of practical chemical knowledge was accumulated from their D. search for methods of separating metals from ores. E. Raison bun or plum pudding model. F. Earliest suggestion that matter was composed of atoms. G. Particles that have the same electronic configuration. H. Subatomic particle ...
... A great deal of practical chemical knowledge was accumulated from their D. search for methods of separating metals from ores. E. Raison bun or plum pudding model. F. Earliest suggestion that matter was composed of atoms. G. Particles that have the same electronic configuration. H. Subatomic particle ...
unit-8-ppt-3-metalsnon-metalsie-and-size-of-atom
... each ORBITAL holds 2 eonly dealing with s and p orbitals so the maximum number of electrons in a shell is: _______________ only UNPAIRED electrons take part in bonding! ...
... each ORBITAL holds 2 eonly dealing with s and p orbitals so the maximum number of electrons in a shell is: _______________ only UNPAIRED electrons take part in bonding! ...
File
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... The Modern Periodic Table • Three main types of elements: – _________: shiny, solids at room temperature, good conductors, ductile, malleable. • Alkali Metals (group 1), Alkaline Earth Metals (group 2), transition metals (groups 3-12), and inner transition metals. ...
... The Modern Periodic Table • Three main types of elements: – _________: shiny, solids at room temperature, good conductors, ductile, malleable. • Alkali Metals (group 1), Alkaline Earth Metals (group 2), transition metals (groups 3-12), and inner transition metals. ...
L to R
... • A measure ability to attract electrons • L to R, more protons more pulling from nucleus easier to attract another electron increase in electronegativity • T to B, more electron shells farther ...
... • A measure ability to attract electrons • L to R, more protons more pulling from nucleus easier to attract another electron increase in electronegativity • T to B, more electron shells farther ...
Document
... Thomson’s Cathode-ray Results • Calculated mass-to-charge ratio (using math and known field strengths) and energy of ray particles • Mass-to-charge ratio for cathode rays was over 1000 times smaller than that of a charged hydrogen atom (a proton), suggesting – either cathode rays carried huge charg ...
... Thomson’s Cathode-ray Results • Calculated mass-to-charge ratio (using math and known field strengths) and energy of ray particles • Mass-to-charge ratio for cathode rays was over 1000 times smaller than that of a charged hydrogen atom (a proton), suggesting – either cathode rays carried huge charg ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.