Isotopes and the Electron Configuration of the Blocks in the Periodic
... also opens and closes Period 9, being located in Group 1 of this Period. This scheme of calculation is applicable to all Tables of Elements containing more than 118 elements. The necessity of our study, presented herein, and the suggested version of the Table which limits by element No.155, is due t ...
... also opens and closes Period 9, being located in Group 1 of this Period. This scheme of calculation is applicable to all Tables of Elements containing more than 118 elements. The necessity of our study, presented herein, and the suggested version of the Table which limits by element No.155, is due t ...
TCSS Physical Science Unit 2 – Atomic Structure Information
... Periodic Table PowerPoint – Multi-day PowerPoint for the trends on the periodic table vocabulary and periodic table graphic organizer. Trends on the Periodic Table Vocabulary – Graphic organizer for the students to fill out when the teacher uses the Periodic Table Notes PowerPoint (slides 14-29) Val ...
... Periodic Table PowerPoint – Multi-day PowerPoint for the trends on the periodic table vocabulary and periodic table graphic organizer. Trends on the Periodic Table Vocabulary – Graphic organizer for the students to fill out when the teacher uses the Periodic Table Notes PowerPoint (slides 14-29) Val ...
Trends in Atomic Radii – Visualization Activity
... 1. How do the atomic radii change as you go from left to right across a period? ...
... 1. How do the atomic radii change as you go from left to right across a period? ...
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) – Part 2
... undiscovered elements and he predicted their properties. Later elements were discovered with properties he predicted! 3. Problems with his table – a few elements did not fit – the atomic mass arrangement did not match with other similar properties. 4. Recognition – Mendeleev never received the Nobel ...
... undiscovered elements and he predicted their properties. Later elements were discovered with properties he predicted! 3. Problems with his table – a few elements did not fit – the atomic mass arrangement did not match with other similar properties. 4. Recognition – Mendeleev never received the Nobel ...
CHEM 1405 CHAPTER 5
... Periodic Table of Elements The periodic Table is a systematic arrangement of elements in the order of increasing atomic numbers. Classification of the Elements In the modern Periodic table, the classification of elements is based on Moseley’s Periodic law, which states that the physical and chemical ...
... Periodic Table of Elements The periodic Table is a systematic arrangement of elements in the order of increasing atomic numbers. Classification of the Elements In the modern Periodic table, the classification of elements is based on Moseley’s Periodic law, which states that the physical and chemical ...
Chapter 5- The Periodic Law
... 1. Consists of all elements in groups 13-18, except Helium. 2. Along with the s-block are called the main-group elements 3. Properties vary greatly because some p-block elements are metals, some are non-metals and some are metalloids 4. The elements of Group 17 are known as the halogens. A. React wi ...
... 1. Consists of all elements in groups 13-18, except Helium. 2. Along with the s-block are called the main-group elements 3. Properties vary greatly because some p-block elements are metals, some are non-metals and some are metalloids 4. The elements of Group 17 are known as the halogens. A. React wi ...
EXPERIMENT 4 – The Periodic Table
... For this part of the experiment you will make a graph of a periodic property vs. atomic number. The property chosen is atomic radius, given in pm (1 pm = 10–12 m). The atomic radius, r, is related to the volume of the atom by the formula of a sphere, V = 4/3 π r3. In Table 1 below, the atomic radii ...
... For this part of the experiment you will make a graph of a periodic property vs. atomic number. The property chosen is atomic radius, given in pm (1 pm = 10–12 m). The atomic radius, r, is related to the volume of the atom by the formula of a sphere, V = 4/3 π r3. In Table 1 below, the atomic radii ...
Unit 3 `Atoms and the Periodic Table` Study Guide
... Periodic Table (of elements) – a table that visually organizes the similarities between all known elements. Products – the results of a chemical reaction Proton – a subatomic particle identical with the nucleus of the hydrogen atom; found with neutrons in all atomic nuclei; carries a positive charge ...
... Periodic Table (of elements) – a table that visually organizes the similarities between all known elements. Products – the results of a chemical reaction Proton – a subatomic particle identical with the nucleus of the hydrogen atom; found with neutrons in all atomic nuclei; carries a positive charge ...
EXPERIMENT 4 – The Periodic Table
... For this part of the experiment you will make a graph of a periodic property vs. atomic number. The property chosen is atomic radius, given in pm (1 pm = 10–12 m). The atomic radius, r, is related to the volume of the atom by the formula of a sphere, V = 4/3 π r3. In Table 1 below, the atomic radii ...
... For this part of the experiment you will make a graph of a periodic property vs. atomic number. The property chosen is atomic radius, given in pm (1 pm = 10–12 m). The atomic radius, r, is related to the volume of the atom by the formula of a sphere, V = 4/3 π r3. In Table 1 below, the atomic radii ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... • Late 1790s: Lavoisier compiled a list of the 23 known elements • 1870: 70 known elements • 1864: John Newlands proposed an organizational scheme for the elements – When elements are arranged by increasing atomic mass their properties repeat every eight element. – Named this periodic property the l ...
... • Late 1790s: Lavoisier compiled a list of the 23 known elements • 1870: 70 known elements • 1864: John Newlands proposed an organizational scheme for the elements – When elements are arranged by increasing atomic mass their properties repeat every eight element. – Named this periodic property the l ...
Lesson 1 - Scientist in Residence
... Atoms consist of a nucleus containing a number of protons, which have a positive charge and neutrons, which have no charge, and surrounded by a cloud of electrons, which have a negative charge equal in magnitude to the proton charge. There is usually one electron per proton. Elements are defined by ...
... Atoms consist of a nucleus containing a number of protons, which have a positive charge and neutrons, which have no charge, and surrounded by a cloud of electrons, which have a negative charge equal in magnitude to the proton charge. There is usually one electron per proton. Elements are defined by ...
Periodic Table Trends - Magoffin County Schools
... • As you move left to right, the atomic radius gets SMALLER, so atoms hold on to their electrons more tightly and are more reactive. • As you move down a group, the atomic radius gets LARGER, so atoms have a weaker hold on their electrons and are less reactive. ...
... • As you move left to right, the atomic radius gets SMALLER, so atoms hold on to their electrons more tightly and are more reactive. • As you move down a group, the atomic radius gets LARGER, so atoms have a weaker hold on their electrons and are less reactive. ...
The Periodic Table
... – An element is identified by its chemical symbol. – The number above the symbol is the atomic number – The number below the symbol is the rounded atomic weight of the element. – A row is called a period – A column is called a group ...
... – An element is identified by its chemical symbol. – The number above the symbol is the atomic number – The number below the symbol is the rounded atomic weight of the element. – A row is called a period – A column is called a group ...
The Periodic Table
... – An element is identified by its chemical symbol. – The number above the symbol is the atomic number – The number below the symbol is the rounded atomic weight of the element. – A row is called a period – A column is called a group ...
... – An element is identified by its chemical symbol. – The number above the symbol is the atomic number – The number below the symbol is the rounded atomic weight of the element. – A row is called a period – A column is called a group ...
Chapter 5
... • Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. • Repeating patterns are referred to as periodic. • Mendeleev created a table in which elements with similar properties were g ...
... • Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. • Repeating patterns are referred to as periodic. • Mendeleev created a table in which elements with similar properties were g ...
Periodic Table
... • In 1829, the German chemist J. W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. ...
... • In 1829, the German chemist J. W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. ...
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts & Connections 4th Edition
... • In 1829, the German chemist J. W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. ...
... • In 1829, the German chemist J. W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... 3. Record the element’s properties from the list provided in part 1 of Table 1. 4. Note that you can select various periodic trends for the element and period. These trends appear as graphs on the right side of the screen. 5. Observe the graph for atomic radius (pm). Describe the relationship betwee ...
... 3. Record the element’s properties from the list provided in part 1 of Table 1. 4. Note that you can select various periodic trends for the element and period. These trends appear as graphs on the right side of the screen. 5. Observe the graph for atomic radius (pm). Describe the relationship betwee ...
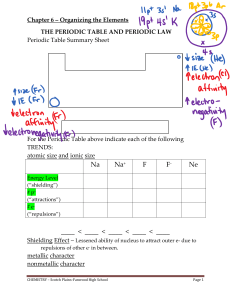
Mendeleev`s Periodic Table - Scotch Plains
... Compare and Contrast Organizing information in a table helps you compare and contrast several topics at one time. For example, you might compare and contrast different groups of elements. As you read, ask yourself, “How are they similar? How are they different?” As you read Lesson 6.1, use the compa ...
... Compare and Contrast Organizing information in a table helps you compare and contrast several topics at one time. For example, you might compare and contrast different groups of elements. As you read, ask yourself, “How are they similar? How are they different?” As you read Lesson 6.1, use the compa ...
Unit 3.2 Periodic Table Test
... An electron has the same mass as a proton. An electron has much more mass than a neutron. An electron has about the same mass as a neutron. An electron has much less mass than a proton. An electron has much less mass than a neutron. A proton has more mass than ...
... An electron has the same mass as a proton. An electron has much more mass than a neutron. An electron has about the same mass as a neutron. An electron has much less mass than a proton. An electron has much less mass than a neutron. A proton has more mass than ...
chapter-5-periodic-classification-of-elements
... similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respectively. 16. Write any one of the strength of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table. Answer: One of the strengths of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table was that, when Noble gases like helium (He), neon (Ne) and argon (Ar) were discovered, they could be placed i ...
... similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respectively. 16. Write any one of the strength of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table. Answer: One of the strengths of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table was that, when Noble gases like helium (He), neon (Ne) and argon (Ar) were discovered, they could be placed i ...
6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table Objectives: 1
... 4. Characterize metals, nonmetals and metalloids. History of the Periodic Table’s Development th 18 Century – 23 elements th 19 Century – 70 elements John Newlands – English Chemist (1837-1898) 1864 – Newlands arranged elements by atomic mass and noticed that their properties repeated every ...
... 4. Characterize metals, nonmetals and metalloids. History of the Periodic Table’s Development th 18 Century – 23 elements th 19 Century – 70 elements John Newlands – English Chemist (1837-1898) 1864 – Newlands arranged elements by atomic mass and noticed that their properties repeated every ...
Homework Packet - Chemistry from AZ
... vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and therefore have similar chemical properties. Note there are some variations in the transition metals. Group 1 Alkali Metals: hydrogen is NOT a member; good conduc ...
... vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and therefore have similar chemical properties. Note there are some variations in the transition metals. Group 1 Alkali Metals: hydrogen is NOT a member; good conduc ...
Matching - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ____ 13. Which of the following elements is in the same period as magnesium? a. carbon c. nitrogen b. phosphorus d. oxygen ____ 14. Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass and used the arrangement to predict the properties of missing elements? a. Henry Moseley c. John Dalton b. Antoine La ...
... ____ 13. Which of the following elements is in the same period as magnesium? a. carbon c. nitrogen b. phosphorus d. oxygen ____ 14. Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass and used the arrangement to predict the properties of missing elements? a. Henry Moseley c. John Dalton b. Antoine La ...
Dmitri Mendeleev

Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev (/ˌmɛndəlˈeɪəf/; Russian: Дми́трий Ива́нович Менделе́ев; IPA: [ˈdmʲitrʲɪj ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ mʲɪndʲɪˈlʲejɪf]; 8 February 1834 – 2 February 1907 O.S. 27 January 1834 – 20 January 1907) was a Russian chemist and inventor. He formulated the Periodic Law, created his own version of the periodic table of elements, and used it to correct the properties of some already discovered elements and also to predict the properties of eight elements yet to be discovered.