Phases of HIV infection
... This is a surrogate because most of the viral replication occurs in the lymph nodes rather than in the peripheral blood. The test is a quantitative amplification of the viral RNA using nucleic acid sequencebased amplification (NASBA), reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR), or sim ...
... This is a surrogate because most of the viral replication occurs in the lymph nodes rather than in the peripheral blood. The test is a quantitative amplification of the viral RNA using nucleic acid sequencebased amplification (NASBA), reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR), or sim ...
General Virology I
... nucleotides), single stranded, circular RNAs, these are not packaged, do not appear to code for any proteins, and so far have only been shown to be associated with plant disease. However, there are some suggestions that somewhat similar agents may possibly be involved in some human disease. ...
... nucleotides), single stranded, circular RNAs, these are not packaged, do not appear to code for any proteins, and so far have only been shown to be associated with plant disease. However, there are some suggestions that somewhat similar agents may possibly be involved in some human disease. ...
Conceptualizing disease management by use of resistant cultivars
... environmentally friendly and economically sustainable disease control in modern crop production. It is put at risk by the evolutionary potential of pathogens to overcome disease resistance of crop cultivars. Three different modelling tools have been developed that consider key evolutionary mechanism ...
... environmentally friendly and economically sustainable disease control in modern crop production. It is put at risk by the evolutionary potential of pathogens to overcome disease resistance of crop cultivars. Three different modelling tools have been developed that consider key evolutionary mechanism ...
Genetic algorithm
... generations. In each generation, the fitness of every individual in the population is evaluated, multiple individuals are stochastically selected from the current population (based on their fitness), and modified (recombined and possibly randomly mutated) to form a new population. The new population ...
... generations. In each generation, the fitness of every individual in the population is evaluated, multiple individuals are stochastically selected from the current population (based on their fitness), and modified (recombined and possibly randomly mutated) to form a new population. The new population ...
Monte Carlo Simulations of Biological Systems
... One of the pioneer models for microevolution was proposed by M. Eigen [2] as an attempt to explain the origins of life in Earth. It describes the dynamics of biological macromolecules (that can replicate) under the influence of selection and mutation mechanisms. The macromolecules can be represented ...
... One of the pioneer models for microevolution was proposed by M. Eigen [2] as an attempt to explain the origins of life in Earth. It describes the dynamics of biological macromolecules (that can replicate) under the influence of selection and mutation mechanisms. The macromolecules can be represented ...
Evolution of Host Defense against Multiple Enemy Populations
... et al. (2013) found that prey branching leading to dimorphism is induced when prey are highly sensitive to competition, as this increases the advantage of branching into prey with distinct traits. More generally, it has been found that the evolution of antipredator defense in the prey can promote th ...
... et al. (2013) found that prey branching leading to dimorphism is induced when prey are highly sensitive to competition, as this increases the advantage of branching into prey with distinct traits. More generally, it has been found that the evolution of antipredator defense in the prey can promote th ...
2.7 - mikrobiol unsoed
... iii. RNA Viruses-most have single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) as their genome iv. Plus strand viruses have a genomic RNA with the same sequence as the viral mRNA; the genomic RNA molecules may have other features (5¢ cap, poly-A tail, etc.) common to mRNA and may direct the synthesis of proteins immediatel ...
... iii. RNA Viruses-most have single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) as their genome iv. Plus strand viruses have a genomic RNA with the same sequence as the viral mRNA; the genomic RNA molecules may have other features (5¢ cap, poly-A tail, etc.) common to mRNA and may direct the synthesis of proteins immediatel ...
Title Univers Bold Italic, 36pt Align Left
... swine flu do occur, and cases of human-tohuman spread of swine flu viruses has been documented • Most commonly, human cases of swine flu happen in people who are around pigs but it’s possible for swine flu viruses to spread from person to person also ...
... swine flu do occur, and cases of human-tohuman spread of swine flu viruses has been documented • Most commonly, human cases of swine flu happen in people who are around pigs but it’s possible for swine flu viruses to spread from person to person also ...
chapter_21b
... Rates and types of migration vary, increases effective population size and decreases divergence by encouraging gene flow (and reduces drift), but also creates major changes in allele frequencies; balanced with selection. ...
... Rates and types of migration vary, increases effective population size and decreases divergence by encouraging gene flow (and reduces drift), but also creates major changes in allele frequencies; balanced with selection. ...
Evolutionary Rate Variation at Multiple Levels of Biological
... caused by the same mechanisms that produce rate variation among genes or among lineages within S. vulgaris? Is the extreme divergence of S. noctiflora simply a case of the more modest interspecific variation writ large, or is it the result of an entirely different mechanism? How does selection act o ...
... caused by the same mechanisms that produce rate variation among genes or among lineages within S. vulgaris? Is the extreme divergence of S. noctiflora simply a case of the more modest interspecific variation writ large, or is it the result of an entirely different mechanism? How does selection act o ...
From molecular to genomic epidemiology
... nucleotide substitutions that underlie MLST variation can be interpreted directly in terms of population genetics and evolutionary processes. Because nucleotide polymorphisms evolve slowly in bacteria, MLST is very appropriate to describe the patterns of genetic variation within bacterial species at ...
... nucleotide substitutions that underlie MLST variation can be interpreted directly in terms of population genetics and evolutionary processes. Because nucleotide polymorphisms evolve slowly in bacteria, MLST is very appropriate to describe the patterns of genetic variation within bacterial species at ...
Chapter 2 The role of chance in evolution
... Chapter 2 The role of chance in evolution Objective The Hardy-Weinberg principle serves as a valuable “null hypothesis” for interpreting genetic variation. Each of the assumptions of HW can be (and often in nature, are) relaxed. This allows many insights into what kinds of genetic changes are possib ...
... Chapter 2 The role of chance in evolution Objective The Hardy-Weinberg principle serves as a valuable “null hypothesis” for interpreting genetic variation. Each of the assumptions of HW can be (and often in nature, are) relaxed. This allows many insights into what kinds of genetic changes are possib ...
Some types of evolutionary change seem to occur repeatedly
... gene lead to abnormalities in the larval ectoderm. Expression of wg in the ectoderm (A–D), and cuticular pattern in the ventral (E–H) and dorsal (I–L) ...
... gene lead to abnormalities in the larval ectoderm. Expression of wg in the ectoderm (A–D), and cuticular pattern in the ventral (E–H) and dorsal (I–L) ...
SHORT COMMUNICATION
... various regions of tropical Africa. The picture is not complete without also investigating SIVs from southern African primates. In this study we investigated six animals with HIV}SIV-cross-reactive antibodies : three vervets (Cercopithecus aethiops pygerythrus) from Kenya (IPR806, IPR859, IPR1185), ...
... various regions of tropical Africa. The picture is not complete without also investigating SIVs from southern African primates. In this study we investigated six animals with HIV}SIV-cross-reactive antibodies : three vervets (Cercopithecus aethiops pygerythrus) from Kenya (IPR806, IPR859, IPR1185), ...
E-Halliburton chapter 6
... coefficients and population sizes play roles for the efficiency of this. In very small populations genetic drift can override selection, and more often lead to fixation of harmful mutant alleles. ”Silent”, or synonymous mutations in a codon (3rd codon position) do not change the resultant amino acid ...
... coefficients and population sizes play roles for the efficiency of this. In very small populations genetic drift can override selection, and more often lead to fixation of harmful mutant alleles. ”Silent”, or synonymous mutations in a codon (3rd codon position) do not change the resultant amino acid ...
Articles - American Scientist
... in more detail in the 3D model on the cover of this magazine. The stargate substructure of genetic material and protein coat) viruses. This unprecedented property lacks fibers and is visible as an indentation has an icosahedral core of ~500 nano- and other features of its lifestyle have in the fiber ...
... in more detail in the 3D model on the cover of this magazine. The stargate substructure of genetic material and protein coat) viruses. This unprecedented property lacks fibers and is visible as an indentation has an icosahedral core of ~500 nano- and other features of its lifestyle have in the fiber ...
The Lassa Virus Nucleoprotein Exhibits Conformational Control of
... termed P), which prevents polymerization of N and nonspecific encapsidation of host cellular RNAs in place of the desired viral RNAs. The resulting complex is termed N0-P, in which N0 denotes RNA-free N. However, other negative-strand RNA viruses such as Lassa have surprisingly simple genomes. Lassa ...
... termed P), which prevents polymerization of N and nonspecific encapsidation of host cellular RNAs in place of the desired viral RNAs. The resulting complex is termed N0-P, in which N0 denotes RNA-free N. However, other negative-strand RNA viruses such as Lassa have surprisingly simple genomes. Lassa ...
OSHA Pandemic for Healthcare Workers Whitepaper
... • Airborne transmission, as occurs in tuberculosis, is spread through small infectious particles such as droplet nuclei. These very small airborne droplet nuclei can be readily disseminated by air currents to susceptible individuals. • They can travel significant distances and can penetrate deep int ...
... • Airborne transmission, as occurs in tuberculosis, is spread through small infectious particles such as droplet nuclei. These very small airborne droplet nuclei can be readily disseminated by air currents to susceptible individuals. • They can travel significant distances and can penetrate deep int ...
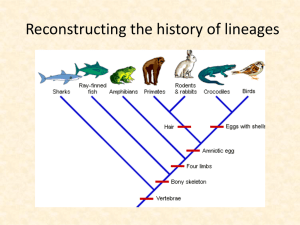
12-History of Lineages
... How can the history of evolution be reconstructed without seeing speciation events? 1) Identification of key characters (heritable parts or attributes of an organism) 2) Transform characters into transformation series 3) Compare these characters to an outgroup 4) Construct a cladogram based on the o ...
... How can the history of evolution be reconstructed without seeing speciation events? 1) Identification of key characters (heritable parts or attributes of an organism) 2) Transform characters into transformation series 3) Compare these characters to an outgroup 4) Construct a cladogram based on the o ...
Australian Influenza - Department of Health
... Note: Viruses tested by the WHO CC are not necessarily a random sample of all those in the community. There may be up to a month delay on reporting of samples. ...
... Note: Viruses tested by the WHO CC are not necessarily a random sample of all those in the community. There may be up to a month delay on reporting of samples. ...
Output Interpretation - UCSF Viral Diagnostics and Discovery Center
... 1. maps unmatched reads directly to all of nr (slower method) ...
... 1. maps unmatched reads directly to all of nr (slower method) ...
Human Cytomegalovirus UL34 Early and late Proteins Are Essential
... 2. Results and Discussion 2.1. Both UL34 Proteins Are Essential for Viral Replication Yu et al. [4] and Dunn et al. [3] identified UL34 as essential for viral replication in their global analyses of the HCMV genome. We extended their results by constructing and studying recombinant viruses using the ...
... 2. Results and Discussion 2.1. Both UL34 Proteins Are Essential for Viral Replication Yu et al. [4] and Dunn et al. [3] identified UL34 as essential for viral replication in their global analyses of the HCMV genome. We extended their results by constructing and studying recombinant viruses using the ...
Frequency-Dependent Selection on a Polygenic Trait
... to affect the equilibrium structure qualitatively. ...
... to affect the equilibrium structure qualitatively. ...
Evolutionary Biology Today
... of degree of similarity. Taxonomy was quite a developed science well before the concept of evolution was widely accepted, and many workers emphasized the need to consider many different characters when assessing similarity, claiming that classification based on one or a few arbitrarily chosen charac ...
... of degree of similarity. Taxonomy was quite a developed science well before the concept of evolution was widely accepted, and many workers emphasized the need to consider many different characters when assessing similarity, claiming that classification based on one or a few arbitrarily chosen charac ...
Viral phylodynamics
Viral phylodynamics is defined as the study of how epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes act and potentially interact to shape viral phylogenies.Since the coining of the term in 2004, research on viral phylodynamics has focused on transmission dynamics in an effort to shed light on how these dynamics impact viral genetic variation. Transmission dynamics can be considered at the level of cells within an infected host, individual hosts within a population, or entire populations of hosts.Many viruses, especially RNA viruses, rapidly accumulate genetic variation because of short generation times and high mutation rates.Patterns of viral genetic variation are therefore heavily influenced by how quickly transmission occurs and by which entities transmit to one another.Patterns of viral genetic variation will also be affected by selection acting on viral phenotypes.Although viruses can differ with respect to many phenotypes, phylodynamic studies have to date tended to focus on a limited number of viral phenotypes.These include virulence phenotypes, phenotypes associated with viral transmissibility, cell or tissue tropism phenotypes, and antigenic phenotypes that can facilitate escape from host immunity.Due to the impact that transmission dynamics and selection can have on viral genetic variation, viral phylogenies can therefore be used to investigate important epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes, such as epidemic spread, spatio-temporal dynamics including metapopulation dynamics, zoonotic transmission, tissue tropism, and antigenic drift.The quantitative investigation of these processes through the consideration of viral phylogenies is the central aim of viral phylodynamics.