Snímek 1
... central route processing (careful perceiving, thinking about the content) peripheral route processing (other factors than content) age, race, religion, income, marital status… ...
... central route processing (careful perceiving, thinking about the content) peripheral route processing (other factors than content) age, race, religion, income, marital status… ...
History and Approaches
... • Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior (e.g., deindividuation, group polarization). • Explain how individuals respond to expectations of others, including groupthink, conformity, and obedience to authority. • Predict the impact of the presence of others on individ ...
... • Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior (e.g., deindividuation, group polarization). • Explain how individuals respond to expectations of others, including groupthink, conformity, and obedience to authority. • Predict the impact of the presence of others on individ ...
Parallel Constraint Satisfaction Processes www.AssignmentPoint
... dynamic aspects that vary with different contexts. The concept of neural network models uses the Gestalt principle of totality to explain social, emotional and cognitive tendencies. In a feedback or parallel constraint satisfaction network, activation passes around symmetrically connected nodes unt ...
... dynamic aspects that vary with different contexts. The concept of neural network models uses the Gestalt principle of totality to explain social, emotional and cognitive tendencies. In a feedback or parallel constraint satisfaction network, activation passes around symmetrically connected nodes unt ...
These are my Unit goals for Social Psychology
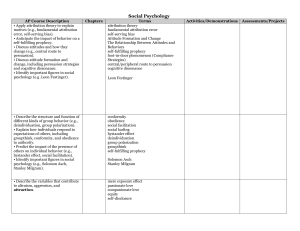
... Social Psychology So this is what I want you to know for this Unit: • Apply attribution theory and self-fulfilling prophesy to explain motives: ...
... Social Psychology So this is what I want you to know for this Unit: • Apply attribution theory and self-fulfilling prophesy to explain motives: ...
STGUIDE2
... to this bias? What purposes does this bias serve for ourself? 7) What are observer biases? 8) Define and explain the Fundamental Attribution Error. How does perceptual salience tie-in? 9) What is Overattribution? 10) Explain the Ultimate Attibution Error. 11) What is a Defensive Attribution? Why do ...
... to this bias? What purposes does this bias serve for ourself? 7) What are observer biases? 8) Define and explain the Fundamental Attribution Error. How does perceptual salience tie-in? 9) What is Overattribution? 10) Explain the Ultimate Attibution Error. 11) What is a Defensive Attribution? Why do ...
Bolt ModEP7e LG43.149-150
... 3. Define attitude, and explain how attitudes and actions affect each other. Attitudes are feelings, often based on our beliefs that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events. For example, we may feel dislike for a person because we believe he or she is mean, and, a ...
... 3. Define attitude, and explain how attitudes and actions affect each other. Attitudes are feelings, often based on our beliefs that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events. For example, we may feel dislike for a person because we believe he or she is mean, and, a ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Tendency for people in group to exert less effort when pooling efforts toward common goal than when individually accountable ...
... Tendency for people in group to exert less effort when pooling efforts toward common goal than when individually accountable ...
Organizational Behavior
... hence the discomfort They will seek a stable state in which there is a minimum of dissonance ...
... hence the discomfort They will seek a stable state in which there is a minimum of dissonance ...
Chapter 13: Social Psychology
... Asch Conformity Experiment Asch’s Results Overall, subjects conformed on about 35% of the trials Two factors influence the likelihood a person will conform: characteristics of the situation characteristics of the individual ...
... Asch Conformity Experiment Asch’s Results Overall, subjects conformed on about 35% of the trials Two factors influence the likelihood a person will conform: characteristics of the situation characteristics of the individual ...
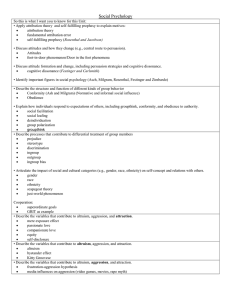
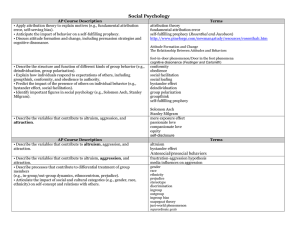
These are the AP Unit goals for social psychology
... http://www.pineforge.com/newman4study/resources/rosenthal1.htm Attitude Formation and Change The Relationship Between Attitudes and Behaviors foot-in-door phenomenon/Door in the foot phenomena cognitive dissonance (Festinger and Carlsmith) ...
... http://www.pineforge.com/newman4study/resources/rosenthal1.htm Attitude Formation and Change The Relationship Between Attitudes and Behaviors foot-in-door phenomenon/Door in the foot phenomena cognitive dissonance (Festinger and Carlsmith) ...
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY social perception and attitudes
... achievement tend to attribute success to internal, stable, controllable factors such as ability, while they contribute failure to either internal, unstable, controllable factors such as effort, or external, uncontrollable factors such as task difficulty. For example, students who experience repeated ...
... achievement tend to attribute success to internal, stable, controllable factors such as ability, while they contribute failure to either internal, unstable, controllable factors such as effort, or external, uncontrollable factors such as task difficulty. For example, students who experience repeated ...
Intro Psych Jan28
... were in their forties. I moved into a male body, and my partner, who is an Older Member in the Level Above Human, took a female body. (We called these bodies "vehicles," for they simply served as physical vehicular tools for us to wear while on a task among humans. They had been tagged and set aside ...
... were in their forties. I moved into a male body, and my partner, who is an Older Member in the Level Above Human, took a female body. (We called these bodies "vehicles," for they simply served as physical vehicular tools for us to wear while on a task among humans. They had been tagged and set aside ...
Textbook PowerPoint
... Social psychology is the scientific study of the ways in which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of one individual are influenced by the real, imagined, or inferred behavior or characteristics of other people. ...
... Social psychology is the scientific study of the ways in which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of one individual are influenced by the real, imagined, or inferred behavior or characteristics of other people. ...
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
... only got 25 cents to try this product, so it couldn’t have been the money that attracted me. I must really like this product after all.” The trick is to induce the behavior that goes against the attitude while leaving people feeling personally responsible for the dissonant act. That way they are mor ...
... only got 25 cents to try this product, so it couldn’t have been the money that attracted me. I must really like this product after all.” The trick is to induce the behavior that goes against the attitude while leaving people feeling personally responsible for the dissonant act. That way they are mor ...
Document
... Does the Hawthorne effect exist today in modern healthcare organizations? (Give an example.) Yes….it exists everywhere!! The Hawthorne effect is the act of modifying your behavior in response simply to being watched, and not by any experimental condition. Employees modify their behavior (sit up st ...
... Does the Hawthorne effect exist today in modern healthcare organizations? (Give an example.) Yes….it exists everywhere!! The Hawthorne effect is the act of modifying your behavior in response simply to being watched, and not by any experimental condition. Employees modify their behavior (sit up st ...
chapter 17 - Cengage Learning
... content). The peripheral route is more likely when a person is busy thinking about something else. 2. Cognitive Dissonance Theory. Cognitive dissonance theory holds that when attitudes and behaviors are inconsistent (or “dissonant”), people feel uneasy and are motivated to make them consistent. One ...
... content). The peripheral route is more likely when a person is busy thinking about something else. 2. Cognitive Dissonance Theory. Cognitive dissonance theory holds that when attitudes and behaviors are inconsistent (or “dissonant”), people feel uneasy and are motivated to make them consistent. One ...
Chapter 13 - Social Psychology
... Conformity: a change in behavior or attitudes brought about ...
... Conformity: a change in behavior or attitudes brought about ...
Chapter 14
... Validity effect (a.k.a., mere exposure effect) Central: slow & difficult Face to face communication is thought to be more effective ...
... Validity effect (a.k.a., mere exposure effect) Central: slow & difficult Face to face communication is thought to be more effective ...