national unit specification: general information
... sand dunes and farmland. Sampling methods could include: use of quadrats, line transects, sweep nets, pitfall traps and bird ...
... sand dunes and farmland. Sampling methods could include: use of quadrats, line transects, sweep nets, pitfall traps and bird ...
Cover: Its Importance to Wyoming`s Wildlife
... openings in a coniferous forest, for example, provides a sunny area for wildlife to obtain food sources while remaining close to protective cover. A combination of different cover-type patches allows wildlife to meet all their needs without traveling far. Improving horizontal diversity or patchiness ...
... openings in a coniferous forest, for example, provides a sunny area for wildlife to obtain food sources while remaining close to protective cover. A combination of different cover-type patches allows wildlife to meet all their needs without traveling far. Improving horizontal diversity or patchiness ...
Decomposer diversity and identity influence plant
... isopods functioned as key decomposers; although decomposer diversity effects did not solely rely on these two decomposer species, positive plant net biodiversity and complementarity effects only occurred in the absence of isopods and the presence of anecic earthworms. Using a structural equation mod ...
... isopods functioned as key decomposers; although decomposer diversity effects did not solely rely on these two decomposer species, positive plant net biodiversity and complementarity effects only occurred in the absence of isopods and the presence of anecic earthworms. Using a structural equation mod ...
Food webs: reconciling the structure and function of biodiversity
... relatively few species. This is consistent with species removal experiments in BEF studies, which have suggested a small sub-group of species disproportionately influences productivity [9]. Incorporating energy flow Weighted networks allow foodweb metrics to include the strength of trophic interacti ...
... relatively few species. This is consistent with species removal experiments in BEF studies, which have suggested a small sub-group of species disproportionately influences productivity [9]. Incorporating energy flow Weighted networks allow foodweb metrics to include the strength of trophic interacti ...
Invasions and Extinctions Reshape Coastal
... in primary consumer richness, terrestrial systems may experience greater species gain at the producer level. Research on the consequences of these types of changes in the number of species at multiple trophic levels is still relatively new [11], despite a thorough understanding of the consequences o ...
... in primary consumer richness, terrestrial systems may experience greater species gain at the producer level. Research on the consequences of these types of changes in the number of species at multiple trophic levels is still relatively new [11], despite a thorough understanding of the consequences o ...
Introduction to Natural Heritage
... the process of plate tectonics. Over large periods of time continents can dramatically chance location and alter the distribution of species, e.g., Australia and South America were once joined as Gondwanaland. Both are the only places on earth with marsupials. • Climate change: the variation in the ...
... the process of plate tectonics. Over large periods of time continents can dramatically chance location and alter the distribution of species, e.g., Australia and South America were once joined as Gondwanaland. Both are the only places on earth with marsupials. • Climate change: the variation in the ...
The Distribution, Abundance And Ecological Impacts Of Invasive
... Invasive species are a major conservation and management concerns in natural ecosystems and pose a significant threat to many of Africa’s conservation areas. The aim of this study was to asses the impacts of invasive plants species on the biodiversity of Ol-Donyo Sabuk National Park. The objectives ...
... Invasive species are a major conservation and management concerns in natural ecosystems and pose a significant threat to many of Africa’s conservation areas. The aim of this study was to asses the impacts of invasive plants species on the biodiversity of Ol-Donyo Sabuk National Park. The objectives ...
Compromising genetic diversity in the wild: unmonitored large
... releases and potential risks to natural populations are comparable to those for aquatic species. Our primary objectives are to: (i) draw attention to the global extent of mass releases and the urgent need for understanding the consequences for natural ecosystems, (ii) review documented genetic effec ...
... releases and potential risks to natural populations are comparable to those for aquatic species. Our primary objectives are to: (i) draw attention to the global extent of mass releases and the urgent need for understanding the consequences for natural ecosystems, (ii) review documented genetic effec ...
appendix w5 - Department of Water Affairs
... where 0 indicates no importance and 4 indicates very high importance (please refer to the rating guidelines for each separate determinant as discussed in W5.3 below). The median of the determinants is used to assign the Ecological Management Class (EMC) for a floodplain (see Table W5-2). The method ...
... where 0 indicates no importance and 4 indicates very high importance (please refer to the rating guidelines for each separate determinant as discussed in W5.3 below). The median of the determinants is used to assign the Ecological Management Class (EMC) for a floodplain (see Table W5-2). The method ...
Taking fungi into account in biodiversity conservation
... First, fungi constitute a significant part of the total biodiversity, as the boreal zone consists ...
... First, fungi constitute a significant part of the total biodiversity, as the boreal zone consists ...
Environment, Politics and Development Working Paper Series
... intrinsic values of species existence. Placing value judgements on the intrinsic and extrinsic values of species is inherent in our approach to conservation (Carolan, 2008; Trudgill, 2008), yet, the issues of uncertainty should also clearly give us pause. A useful example of dichotomy in our approa ...
... intrinsic values of species existence. Placing value judgements on the intrinsic and extrinsic values of species is inherent in our approach to conservation (Carolan, 2008; Trudgill, 2008), yet, the issues of uncertainty should also clearly give us pause. A useful example of dichotomy in our approa ...
Time course of plant diversity effects on
... a proxy for aboveground competition, for establishment success and its importance in mediating diversity and compositional effects. Our study was conducted in the experimental grassland communities of the Jena Experiment, with plant communities varying in numbers of plant species between 1 and 60 an ...
... a proxy for aboveground competition, for establishment success and its importance in mediating diversity and compositional effects. Our study was conducted in the experimental grassland communities of the Jena Experiment, with plant communities varying in numbers of plant species between 1 and 60 an ...
Alpine Biodiversity in Europe: an Introduction
... elevation, determine climate. The coloured areas of the elevation map below lie over 600 m above sea level (the approximate lower limit of the montane forest zone in central Europe). At the Arctic Circle, however, the same elevation marks the upper limit of tree growth. The treeline in the Alps vari ...
... elevation, determine climate. The coloured areas of the elevation map below lie over 600 m above sea level (the approximate lower limit of the montane forest zone in central Europe). At the Arctic Circle, however, the same elevation marks the upper limit of tree growth. The treeline in the Alps vari ...
Multiple diversity–stability mechanisms enhance population and
... and microbial communities were filtered through a 30lm mesh to remove zooplankton and macroinvertebrates and then allowed to establish for 10 days in the tanks before zooplankton were added. We created a gradient of zooplankton richness using two different approaches. First, we established low zoopla ...
... and microbial communities were filtered through a 30lm mesh to remove zooplankton and macroinvertebrates and then allowed to establish for 10 days in the tanks before zooplankton were added. We created a gradient of zooplankton richness using two different approaches. First, we established low zoopla ...
Food webs: reconciling the structure and function of biodiversity
... relatively few species. This is consistent with species removal experiments in BEF studies, which have suggested a small sub-group of species disproportionately influences productivity [9]. Incorporating energy flow Weighted networks allow foodweb metrics to include the strength of trophic interacti ...
... relatively few species. This is consistent with species removal experiments in BEF studies, which have suggested a small sub-group of species disproportionately influences productivity [9]. Incorporating energy flow Weighted networks allow foodweb metrics to include the strength of trophic interacti ...
2007-2008 - Illinois Natural History Survey
... Collection-based studies remain a core area of research at INHS. Its world-renowned collections both reflect and support the active roles that our scientists continue to play in efforts to improve knowledge of Earth’s biological diversity. The INHS biological collections, assembled by Survey scienti ...
... Collection-based studies remain a core area of research at INHS. Its world-renowned collections both reflect and support the active roles that our scientists continue to play in efforts to improve knowledge of Earth’s biological diversity. The INHS biological collections, assembled by Survey scienti ...
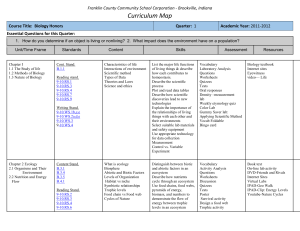
Q1 - FCCSC
... List the limiting factors that cause populations to decrease. Apply limiting factors to a J-shaped curve to change it to an S-Shaped curve. Compare and contrast populations under and above carrying capacity. Describe Density Dependent factors effect on populations Describe Density Independent factor ...
... List the limiting factors that cause populations to decrease. Apply limiting factors to a J-shaped curve to change it to an S-Shaped curve. Compare and contrast populations under and above carrying capacity. Describe Density Dependent factors effect on populations Describe Density Independent factor ...
CO 2
... overexploitation are the major threats to biodiversity • Human alteration of habitats poses the single greatest threat to biodiversity – The loss of tropical rain forests and marine habitats are especially devastating Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... overexploitation are the major threats to biodiversity • Human alteration of habitats poses the single greatest threat to biodiversity – The loss of tropical rain forests and marine habitats are especially devastating Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Rapid loss of genetic variation in a founding
... urbanum, suggesting that the processes that affect genetic diversity in populations located in recently established forests might vary from one system to the next. A different, more direct approach to studying the effects of population turnover on genetic diversity would be to investigate temporal c ...
... urbanum, suggesting that the processes that affect genetic diversity in populations located in recently established forests might vary from one system to the next. A different, more direct approach to studying the effects of population turnover on genetic diversity would be to investigate temporal c ...
The links between biodiversity, ecosystem services and human well
... the debates that have developed around it is shown in Figure 2. The diagram makes a distinction between ecological structures and processes created or generated by living organism and the benefits that people eventually derive. In the real world the links are not as simple and linear as this. Howeve ...
... the debates that have developed around it is shown in Figure 2. The diagram makes a distinction between ecological structures and processes created or generated by living organism and the benefits that people eventually derive. In the real world the links are not as simple and linear as this. Howeve ...
Potential problems of removing one invasive species at a time
... Porter-Whitaker et al., 2012; Meza-Lopez & Siemann, 2015). Interactions between these co-occurring invaders are of superlative interest for wildlife management because managers can often only control or eradicate a single invasive species at a time (Glen et al., 2013). Without prior knowledge of inv ...
... Porter-Whitaker et al., 2012; Meza-Lopez & Siemann, 2015). Interactions between these co-occurring invaders are of superlative interest for wildlife management because managers can often only control or eradicate a single invasive species at a time (Glen et al., 2013). Without prior knowledge of inv ...
A GENERAL HYPOTHESIS OF SPECIES DIVERSITY Many
... capacity, but this relationship is not essential for the model. 3. Changes in certain environmental variables will affect all competing populations in basically the same way; that is, the population growth rates of all may be increased or decreased by changes in such factors as energy or nutrient av ...
... capacity, but this relationship is not essential for the model. 3. Changes in certain environmental variables will affect all competing populations in basically the same way; that is, the population growth rates of all may be increased or decreased by changes in such factors as energy or nutrient av ...
MACRO-INVERTEBRATE FUNCTIONAL GROUPS IN
... ABSTRACT. – Functional group definitions in aquatic ecology vary depending on the type of ecosystem (e.g., marine compared to fresh water ecosystems, stream compared to lake ecosystems). Since the benthic environment functions as the major storage and recycling compartment for virtually all material ...
... ABSTRACT. – Functional group definitions in aquatic ecology vary depending on the type of ecosystem (e.g., marine compared to fresh water ecosystems, stream compared to lake ecosystems). Since the benthic environment functions as the major storage and recycling compartment for virtually all material ...
Intraspecific phytochemical variation shapes community and
... (Fig. 1a), and which all have significant negative effects on herbivores, microbes and fungi (Jeffrey et al., 2014). We collected P. kelleyi, Eois caterpillars and parasitoids from 10 sites in close proximity to Yanayacu Biological Station (00°360 S and 77°530 W) from June to August 2011 and 2012. Y ...
... (Fig. 1a), and which all have significant negative effects on herbivores, microbes and fungi (Jeffrey et al., 2014). We collected P. kelleyi, Eois caterpillars and parasitoids from 10 sites in close proximity to Yanayacu Biological Station (00°360 S and 77°530 W) from June to August 2011 and 2012. Y ...
CONSERVATION AREA MANAGEMENT
... Biological diversity is a key element to healthy, sustainable forests. Biodiversity exists at many levels of biological organization (i.e. genetic, species, communities, ecosystems and landscapes). Biodiversity also occurs at a variety of spatial scales from a few square feet to millions of acres. N ...
... Biological diversity is a key element to healthy, sustainable forests. Biodiversity exists at many levels of biological organization (i.e. genetic, species, communities, ecosystems and landscapes). Biodiversity also occurs at a variety of spatial scales from a few square feet to millions of acres. N ...
Biodiversity
Global Biodiversity is the variety of different types of life found on Earth and the variations within species. It is a measure of the variety of organisms present in different ecosystems. This can refer to genetic variation, ecosystem variation, or species variation (number of species) within an area, biome, or planet. Terrestrial biodiversity tends to be highest near the equator, which seems to be the result of the warm climate and high primary productivity. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth. It is the richest in the tropics. Marine biodiversity tends to be highest along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time but will be likely to slow in the future.The number and variety of plants, animals and other organisms that exist is known as biodiversity. It is an essential component of nature and it ensures the survival of human species by providing food, fuel, shelter, medicines and other resources to mankind. The richness of biodiversity depends on the climatic conditions and area of the region. All species of plants taken together are known as flora and about 70,000 species of plants are known till date. All species of animals taken together are known as fauna which includes birds, mammals, fish, reptiles, insects, crustaceans, molluscs, etc.Rapid environmental changes typically cause mass extinctions. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described. The total amount of related DNA base pairs on Earth is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon).The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland. Since life began on Earth, five major mass extinctions and several minor events have led to large and sudden drops in biodiversity. The Phanerozoic eon (the last 540 million years) marked a rapid growth in biodiversity via the Cambrian explosion—a period during which the majority of multicellular phyla first appeared. The next 400 million years included repeated, massive biodiversity losses classified as mass extinction events. In the Carboniferous, rainforest collapse led to a great loss of plant and animal life. The Permian–Triassic extinction event, 251 million years ago, was the worst; vertebrate recovery took 30 million years. The most recent, the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, occurred 65 million years ago and has often attracted more attention than others because it resulted in the extinction of the dinosaurs.The period since the emergence of humans has displayed an ongoing biodiversity reduction and an accompanying loss of genetic diversity. Named the Holocene extinction, the reduction is caused primarily by human impacts, particularly habitat destruction. Conversely, biodiversity impacts human health in a number of ways, both positively and negatively.The United Nations designated 2011–2020 as the United Nations Decade on Biodiversity.