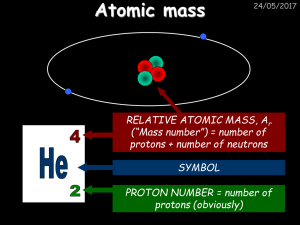
Atomic mass - drseemaljelani
... reaction, it is not always possible to obtain the calculated amount of product. Because: • The reaction may not totally finish – it may be reversible • Some of the product may be lost when it is separated from the reaction mixture – filtered • Some of the reactants may react in different ways to the ...
... reaction, it is not always possible to obtain the calculated amount of product. Because: • The reaction may not totally finish – it may be reversible • Some of the product may be lost when it is separated from the reaction mixture – filtered • Some of the reactants may react in different ways to the ...
Chapter 6
... Can you figure out what is missing in the following chemical reactions? 1. Aluminum resists corrosion (rust) because it reacts with a gas in the air to form a protective coating of aluminum oxide. Aluminum + ____________ → aluminum oxide ...
... Can you figure out what is missing in the following chemical reactions? 1. Aluminum resists corrosion (rust) because it reacts with a gas in the air to form a protective coating of aluminum oxide. Aluminum + ____________ → aluminum oxide ...
Chem A Week 2 Matter Notes
... A.Solids– are ____________ matter They have a definite shape and volume matter B. Liquids – are ___________ They take the shape of their container, volume but still have a definite ________________. ...
... A.Solids– are ____________ matter They have a definite shape and volume matter B. Liquids – are ___________ They take the shape of their container, volume but still have a definite ________________. ...
Hydrogen Models 1
... one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucle ...
... one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucle ...
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM 1998 - University of Waterloo
... middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed ...
... middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed ...
Atomic structure
... ELECTRONS can be gained or lost, making IONS. Lose an electron, become positive ion (ie. Na+1) Gain an electron, become negative ion (ie. Cl-1) IONS like to bond together, because OPPOSITES attract! ...
... ELECTRONS can be gained or lost, making IONS. Lose an electron, become positive ion (ie. Na+1) Gain an electron, become negative ion (ie. Cl-1) IONS like to bond together, because OPPOSITES attract! ...
- International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and
... This study is conducted to provide a new solution for the problem of electricity in the world represented mainly in the full dependence on fossil fuel resources which causes a huge damage to the environment besides its increasing high cost and non-renew ability. The development of a new method for h ...
... This study is conducted to provide a new solution for the problem of electricity in the world represented mainly in the full dependence on fossil fuel resources which causes a huge damage to the environment besides its increasing high cost and non-renew ability. The development of a new method for h ...
Hydrogen as a Renewable Energy Source from the Biophotolysis of
... Hydrogen production using biological methods is based on biophotolysis of water by algae and cyanobacteria, photodecomposition of organic compounds by photosynthetic bacteria, fermentative hydrogen production from organic compounds and hybrid systems using photosynthetic and fermentative bacteria (D ...
... Hydrogen production using biological methods is based on biophotolysis of water by algae and cyanobacteria, photodecomposition of organic compounds by photosynthetic bacteria, fermentative hydrogen production from organic compounds and hybrid systems using photosynthetic and fermentative bacteria (D ...
2015 AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 40. Penicillin, the first of a number of antibiotics, was discovered accidentally by the Scottish bacteriologist Alexander Fleming in 1928. He was never able to isolate it as a pure compound. This and similar antibiotics have saved millions of lives that might have been lost to infections. Penicill ...
... 40. Penicillin, the first of a number of antibiotics, was discovered accidentally by the Scottish bacteriologist Alexander Fleming in 1928. He was never able to isolate it as a pure compound. This and similar antibiotics have saved millions of lives that might have been lost to infections. Penicill ...
Chemical Equations
... Reaction Types: Synthesis or Composition • Synthesis are, at this introductory level, almost always the reverse of a decomposition reaction. That means that two pieces join together to produce one, a more complex compounds. These pieces can be elements or simpler compounds. • A + B ---> AB Reaction ...
... Reaction Types: Synthesis or Composition • Synthesis are, at this introductory level, almost always the reverse of a decomposition reaction. That means that two pieces join together to produce one, a more complex compounds. These pieces can be elements or simpler compounds. • A + B ---> AB Reaction ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... - for elements with atomic numbers between 1 and 20, the number of neutrons to protons are about the same. - Those elements between 20 and 83 require an increasingly larger ratio of neutrons to protons. - Elements beyond 83 naturally encounter nuclear decay. - However, not only does an isotope of an ...
... - for elements with atomic numbers between 1 and 20, the number of neutrons to protons are about the same. - Those elements between 20 and 83 require an increasingly larger ratio of neutrons to protons. - Elements beyond 83 naturally encounter nuclear decay. - However, not only does an isotope of an ...
Reactions of common metals and properties of
... Atoms of the alkali metals are easily excited; even the flame of a Bunsen burner can excite their valence electrons. As the electrons jump back to lower energy levels, they give characteristic colours to the flame; lithium imparts a red colour, sodium a yellow colour, and potassium a lilac colour. T ...
... Atoms of the alkali metals are easily excited; even the flame of a Bunsen burner can excite their valence electrons. As the electrons jump back to lower energy levels, they give characteristic colours to the flame; lithium imparts a red colour, sodium a yellow colour, and potassium a lilac colour. T ...
Atoms and Elements - Steven Lin`s Websites
... • Ion: A charged atom. Not neutral. There is either more electrons than protons or more protons than electrons. This does not change the element because the same amount of protons exist. – Hydrogen with one proton and one electron is neutral but is not stable. A stable Hydrogen will have two electro ...
... • Ion: A charged atom. Not neutral. There is either more electrons than protons or more protons than electrons. This does not change the element because the same amount of protons exist. – Hydrogen with one proton and one electron is neutral but is not stable. A stable Hydrogen will have two electro ...
Chapter 8
... • Identify the names of reactants and products, and write a word equation. • Write a formula equation by substituting correct formulas for the names of the reactants and the products. • Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. • Count atoms on both sides to be sure ...
... • Identify the names of reactants and products, and write a word equation. • Write a formula equation by substituting correct formulas for the names of the reactants and the products. • Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. • Count atoms on both sides to be sure ...
Equilibrium Constant- Keq
... 2. Nitrogen dioxide gas (4.6 mol/L) is produced from nitrogen monoxide gas (1.3 mol/L) and oxygen gas (1.8 mol/L). What is the equilibrium constant of this reaction? Are reactants or products favored? 3. Sulfur dioxide gas (0.141 mol/L) and oxygen gas (0.25 mol/L) are produced when sulfur trioxide g ...
... 2. Nitrogen dioxide gas (4.6 mol/L) is produced from nitrogen monoxide gas (1.3 mol/L) and oxygen gas (1.8 mol/L). What is the equilibrium constant of this reaction? Are reactants or products favored? 3. Sulfur dioxide gas (0.141 mol/L) and oxygen gas (0.25 mol/L) are produced when sulfur trioxide g ...
Word and Skeleton Equations Practice (ws Fall 2010)
... 2. Solid sodium metal reacts with liquid water to form an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. 3. Solid potassium chlorate breaks down to form solid potassium chloride and oxygen gas. 4. Solid copper reacts with oxygen gas to form solid copper(II) oxide. 5. When aqueous solutions o ...
... 2. Solid sodium metal reacts with liquid water to form an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. 3. Solid potassium chlorate breaks down to form solid potassium chloride and oxygen gas. 4. Solid copper reacts with oxygen gas to form solid copper(II) oxide. 5. When aqueous solutions o ...
Microbiology with Diseases Taxonomy
... cell, whereas synthesis reactions utilize component monomers to build larger molecules. The chemistry of the cell would basically be impossible without hydrogen bonds. Water, which is required by all cellular reactions, would not have its unique properties of cohesiveness and polarity without hydrog ...
... cell, whereas synthesis reactions utilize component monomers to build larger molecules. The chemistry of the cell would basically be impossible without hydrogen bonds. Water, which is required by all cellular reactions, would not have its unique properties of cohesiveness and polarity without hydrog ...
Empirical is the
... one, then divide the others by that number to find the ratios between the other ones: [ 1.121 g N ( 1 mole of N/ 14.00 g) = 0.008 moles N] { Carbon mole is 0.004 moles C- so there are 2 N for every 1 C}) 72. A compound containing only sulfur and nitrogen is 69.6% S, by mass; the molar mass is 184 g/ ...
... one, then divide the others by that number to find the ratios between the other ones: [ 1.121 g N ( 1 mole of N/ 14.00 g) = 0.008 moles N] { Carbon mole is 0.004 moles C- so there are 2 N for every 1 C}) 72. A compound containing only sulfur and nitrogen is 69.6% S, by mass; the molar mass is 184 g/ ...
M220 Lecture 11 - Napa Valley College
... Respiration is any energy yielding oxidation in which the terminal hydrogen acceptor is an inorganic compound. Gaseous oxygen is not necessarily involved. 1. Aerobic Respiration-any energy yielding oxidation in which the terminal hydrogen acceptor is the inorganic compound oxygen. (Highest energy yi ...
... Respiration is any energy yielding oxidation in which the terminal hydrogen acceptor is an inorganic compound. Gaseous oxygen is not necessarily involved. 1. Aerobic Respiration-any energy yielding oxidation in which the terminal hydrogen acceptor is the inorganic compound oxygen. (Highest energy yi ...
Atom Reading Passage and Questions File
... Atoms form the building blocks of the simplest substances, the chemical elements. Familiar elements include hydrogen, helium, sodium, chlorine, iron, lead, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. The smallest unit into which an element may be divided while keeping all of the characteristics of that element is ...
... Atoms form the building blocks of the simplest substances, the chemical elements. Familiar elements include hydrogen, helium, sodium, chlorine, iron, lead, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. The smallest unit into which an element may be divided while keeping all of the characteristics of that element is ...
(p. 522)
... A.These substances have distinct stoichiometric formulas like ionic hydrides. B.Hydrogen forms bonds with the metals by donating its electron to the valence band of the metal. C.Hydrogen molecules and atoms occupy holes within the crystal structure of the metal. D.These substances are useful catalys ...
... A.These substances have distinct stoichiometric formulas like ionic hydrides. B.Hydrogen forms bonds with the metals by donating its electron to the valence band of the metal. C.Hydrogen molecules and atoms occupy holes within the crystal structure of the metal. D.These substances are useful catalys ...
Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are one of the
... Atoms form the building blocks of the simplest substances, the chemical elements. Familiar elements include hydrogen, helium, sodium, chlorine, iron, lead, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. The smallest unit into which an element may be divided while keeping all of the characteristics of that element is ...
... Atoms form the building blocks of the simplest substances, the chemical elements. Familiar elements include hydrogen, helium, sodium, chlorine, iron, lead, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. The smallest unit into which an element may be divided while keeping all of the characteristics of that element is ...
Targets of Opportunity
... Bhopal, India. The aftermath was apocalyptic. Between 7,000 and 10,000 people died in the three days after the explosion and 15,000 more have died since. ...
... Bhopal, India. The aftermath was apocalyptic. Between 7,000 and 10,000 people died in the three days after the explosion and 15,000 more have died since. ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... 1. Before the experiment conducted by Ernest Rutherford, how did many scientists envision the structure of an atom? Answer: Scientists were aware that atoms contained charged particles. Many believed that the positive charges and mass were evenly distributed throughout the atom. 2. What was the hypo ...
... 1. Before the experiment conducted by Ernest Rutherford, how did many scientists envision the structure of an atom? Answer: Scientists were aware that atoms contained charged particles. Many believed that the positive charges and mass were evenly distributed throughout the atom. 2. What was the hypo ...
Hydrogen

Hydrogen is a chemical element with chemical symbol H and atomic number 1. With an atomic weight of 7000100794000000000♠1.00794 u, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass. Non-remnant stars are mainly composed of hydrogen in its plasma state. The most common isotope of hydrogen, termed protium (name rarely used, symbol 1H), has one proton and no neutrons.The universal emergence of atomic hydrogen first occurred during the recombination epoch. At standard temperature and pressure, hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, nonmetallic, highly combustible diatomic gas with the molecular formula H2. Since hydrogen readily forms covalent compounds with most non-metallic elements, most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as in the form of water or organic compounds. Hydrogen plays a particularly important role in acid–base reactions as many acid-base reactions involve the exchange of protons between soluble molecules. In ionic compounds, hydrogen can take the form of a negative charge (i.e., anion) when it is known as a hydride, or as a positively charged (i.e., cation) species denoted by the symbol H+. The hydrogen cation is written as though composed of a bare proton, but in reality, hydrogen cations in ionic compounds are always more complex species than that would suggest. As the only neutral atom for which the Schrödinger equation can be solved analytically, study of the energetics and bonding of the hydrogen atom has played a key role in the development of quantum mechanics.Hydrogen gas was first artificially produced in the early 16th century, via the mixing of metals with acids. In 1766–81, Henry Cavendish was the first to recognize that hydrogen gas was a discrete substance, and that it produces water when burned, a property which later gave it its name: in Greek, hydrogen means ""water-former"".Industrial production is mainly from the steam reforming of natural gas, and less often from more energy-intensive hydrogen production methods like the electrolysis of water. Most hydrogen is employed near its production site, with the two largest uses being fossil fuel processing (e.g., hydrocracking) and ammonia production, mostly for the fertilizer market. Hydrogen is a concern in metallurgy as it can embrittle many metals, complicating the design of pipelines and storage tanks.