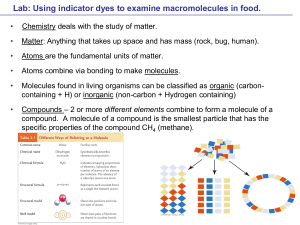
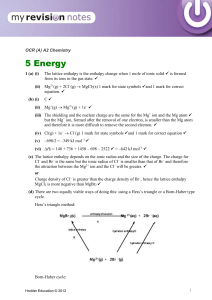
Elementary my dear Watson review
... from the atomic number and you will get the number of neutrons found in the nucleus of the atom, intermingled with the protons. ...
... from the atomic number and you will get the number of neutrons found in the nucleus of the atom, intermingled with the protons. ...
Introduction to Chemical Equations
... • You may NOT change any subscripts in any of the reactant’s or product’s formulas ...
... • You may NOT change any subscripts in any of the reactant’s or product’s formulas ...
Date Hour
... Aqueous solution (a metal salt dissolved in water or an acid or base). The word solution is your clue that you are to use the subscript (aq). ...
... Aqueous solution (a metal salt dissolved in water or an acid or base). The word solution is your clue that you are to use the subscript (aq). ...
Chemistry Unit Test Review
... Students added liver to hydrogen peroxide. The mass of the substance after the reaction took place was less than the mass before. What might have accounted for the mass being different after? ...
... Students added liver to hydrogen peroxide. The mass of the substance after the reaction took place was less than the mass before. What might have accounted for the mass being different after? ...
Acids and Bases and Aqueous Equilibria
... "We are inclined to think of substances as possessing acid or basic properties, without having a particular solvent in mind. It seems to me that with complete generality we may say that a basic substance is one which has a lone pair of electrons which may be used to complete the stable group of anot ...
... "We are inclined to think of substances as possessing acid or basic properties, without having a particular solvent in mind. It seems to me that with complete generality we may say that a basic substance is one which has a lone pair of electrons which may be used to complete the stable group of anot ...
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Outline I. Molar Mass and
... 20. Sodium metal and water react to form hydrogen and sodium hydroxide. If 5.98 g of sodium react with water to form 0.26 g of hydrogen and 10.40 g of sodium hydroxide, what mass of water was consumed in the reaction? a. 10.66 g b. 4.68 g c. 10.14 g d. 5.98 g 21. What is the chemical formula for str ...
... 20. Sodium metal and water react to form hydrogen and sodium hydroxide. If 5.98 g of sodium react with water to form 0.26 g of hydrogen and 10.40 g of sodium hydroxide, what mass of water was consumed in the reaction? a. 10.66 g b. 4.68 g c. 10.14 g d. 5.98 g 21. What is the chemical formula for str ...
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with
... partners, which can be interpreted as a kind of valence. These covalent features are more significant when acceptors bind hydrogens from more electronegative donors. The partially covalent nature of a hydrogen bond raises the questions: "To which molecule or atom does the hydrogen nucleus belong?" a ...
... partners, which can be interpreted as a kind of valence. These covalent features are more significant when acceptors bind hydrogens from more electronegative donors. The partially covalent nature of a hydrogen bond raises the questions: "To which molecule or atom does the hydrogen nucleus belong?" a ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... molecules of ATP must be hydrolyzed to start the process 30 molecules of NADH are produced 6 molecules of FADH2 are produced 18 molecules of ATP are produced via substrate phosphorylation (12 in glycolysis and 6 in Krebs) 18 molecules of water are produced in ETS 18 molecules of CO2 are re ...
... molecules of ATP must be hydrolyzed to start the process 30 molecules of NADH are produced 6 molecules of FADH2 are produced 18 molecules of ATP are produced via substrate phosphorylation (12 in glycolysis and 6 in Krebs) 18 molecules of water are produced in ETS 18 molecules of CO2 are re ...
Exam practice answers 5
... (f) Add silver nitrate to each and observe the colour of the precipitate. MgCl2 would give a white solid and MgBr2 would give a cream solid. If dilute ammonia, NH3, is added the white precipitate dissolves. The cream precipitate will only dissolve in concentrated NH3. There are other ways of d ...
... (f) Add silver nitrate to each and observe the colour of the precipitate. MgCl2 would give a white solid and MgBr2 would give a cream solid. If dilute ammonia, NH3, is added the white precipitate dissolves. The cream precipitate will only dissolve in concentrated NH3. There are other ways of d ...
Tutorial - Brock physics
... orbital quantum number `. This rule is called a selection rule and states that ∆` = ±1. In other words, when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, the value of ` can only increase or decrease by one. The value of ` may not remain the same or increase or decrease by more than one. Acc ...
... orbital quantum number `. This rule is called a selection rule and states that ∆` = ±1. In other words, when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, the value of ` can only increase or decrease by one. The value of ` may not remain the same or increase or decrease by more than one. Acc ...
Chemistry of Life biochemistry CHS
... ex: magnesium is a cofactor that is essential for the proper functioning of chlorophyll ...
... ex: magnesium is a cofactor that is essential for the proper functioning of chlorophyll ...
Hydrogen Chemistry of Basalt Aquifers -- Treiman et
... water. This was only inferred from isotopic measurements and several assumptions about isotope equilibrium and exchange. Direct experimental measurements of rock-water interaction with materials from this site are required in order to prove the source of hydrogen in this system. It is also important ...
... water. This was only inferred from isotopic measurements and several assumptions about isotope equilibrium and exchange. Direct experimental measurements of rock-water interaction with materials from this site are required in order to prove the source of hydrogen in this system. It is also important ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: SIMPLE ADDITION REACTIONS
... 1. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reactions involving hydrogen cyanide in which H and CN add on across the carbon-oxygen double bond. a) Why isn’t hydrogen cyanide itself normally used in these reactions? b) Give a mixture which can be used instead of starting with hydrogen cyanide itself. c ...
... 1. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reactions involving hydrogen cyanide in which H and CN add on across the carbon-oxygen double bond. a) Why isn’t hydrogen cyanide itself normally used in these reactions? b) Give a mixture which can be used instead of starting with hydrogen cyanide itself. c ...
Hydrogen Atom
... single negatively-charged electron circling a single positively-charged nucleus of the hydrogen atom. The nucleus of hydrogen consists of only a single proton (in the case of hydrogen-1 or protium; see box at right), or it may also include one or more neutrons (giving deuterium, tritium, and other i ...
... single negatively-charged electron circling a single positively-charged nucleus of the hydrogen atom. The nucleus of hydrogen consists of only a single proton (in the case of hydrogen-1 or protium; see box at right), or it may also include one or more neutrons (giving deuterium, tritium, and other i ...
Unit Test: Atomic Structure
... Neils Bohr Ernest Rutherford Antoine Lavoisier Joseph Priestly 2. Be able to define: Atom Atomic mass unit Isotope Nucleus Electron Proton Neutron Atomic Number Mass Number Average Atomic Mass Nuclear Atom 3. Be able to identify the following in a given atom: Number of protons Number of electrons -i ...
... Neils Bohr Ernest Rutherford Antoine Lavoisier Joseph Priestly 2. Be able to define: Atom Atomic mass unit Isotope Nucleus Electron Proton Neutron Atomic Number Mass Number Average Atomic Mass Nuclear Atom 3. Be able to identify the following in a given atom: Number of protons Number of electrons -i ...
PowerPoint Overview for Introduction
... and cell structures, regulating the body's pH, carrying charge, and driving chemical reactions. ...
... and cell structures, regulating the body's pH, carrying charge, and driving chemical reactions. ...
The Biology of
... What do proteins do? • Carry out molecular function – Antibodies, enzymes, signals, etc – Proteins = Nature’s “nanomachines” ...
... What do proteins do? • Carry out molecular function – Antibodies, enzymes, signals, etc – Proteins = Nature’s “nanomachines” ...
100610 chem a GALL
... number of one because it has one proton. Hydrogen only SOMETIMES has a neutron... The average mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.0079 amu. ...
... number of one because it has one proton. Hydrogen only SOMETIMES has a neutron... The average mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.0079 amu. ...
Atoms
... 1, then it has 0 neutrons. It will have 1 proton to account for its mass number. An atom can lose or gain electrons to alter its charge and it can have different numbers of neutrons to change its mass, but the number of protons is always equal to its atomic number. On the other hand if Hydrogen has ...
... 1, then it has 0 neutrons. It will have 1 proton to account for its mass number. An atom can lose or gain electrons to alter its charge and it can have different numbers of neutrons to change its mass, but the number of protons is always equal to its atomic number. On the other hand if Hydrogen has ...
chapter 22 guided notes: the evidence for evolution
... B. Covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms of two adjacent water molecules C. Hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule D. Covalent bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule E. ...
... B. Covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms of two adjacent water molecules C. Hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule D. Covalent bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule E. ...
Hydrogen

Hydrogen is a chemical element with chemical symbol H and atomic number 1. With an atomic weight of 7000100794000000000♠1.00794 u, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass. Non-remnant stars are mainly composed of hydrogen in its plasma state. The most common isotope of hydrogen, termed protium (name rarely used, symbol 1H), has one proton and no neutrons.The universal emergence of atomic hydrogen first occurred during the recombination epoch. At standard temperature and pressure, hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, nonmetallic, highly combustible diatomic gas with the molecular formula H2. Since hydrogen readily forms covalent compounds with most non-metallic elements, most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as in the form of water or organic compounds. Hydrogen plays a particularly important role in acid–base reactions as many acid-base reactions involve the exchange of protons between soluble molecules. In ionic compounds, hydrogen can take the form of a negative charge (i.e., anion) when it is known as a hydride, or as a positively charged (i.e., cation) species denoted by the symbol H+. The hydrogen cation is written as though composed of a bare proton, but in reality, hydrogen cations in ionic compounds are always more complex species than that would suggest. As the only neutral atom for which the Schrödinger equation can be solved analytically, study of the energetics and bonding of the hydrogen atom has played a key role in the development of quantum mechanics.Hydrogen gas was first artificially produced in the early 16th century, via the mixing of metals with acids. In 1766–81, Henry Cavendish was the first to recognize that hydrogen gas was a discrete substance, and that it produces water when burned, a property which later gave it its name: in Greek, hydrogen means ""water-former"".Industrial production is mainly from the steam reforming of natural gas, and less often from more energy-intensive hydrogen production methods like the electrolysis of water. Most hydrogen is employed near its production site, with the two largest uses being fossil fuel processing (e.g., hydrocracking) and ammonia production, mostly for the fertilizer market. Hydrogen is a concern in metallurgy as it can embrittle many metals, complicating the design of pipelines and storage tanks.