Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper.
... 5. Ptolemy tried to describe the motion of the planets by devising a small circle, called a(n) ____, which rotated around the edge of a larger circle. a. epicycle b. foci c. deferent d. equant e. sphere 6. What did the Greek philosopher Philolaus believe about the Universe? a. No parallax seen of n ...
... 5. Ptolemy tried to describe the motion of the planets by devising a small circle, called a(n) ____, which rotated around the edge of a larger circle. a. epicycle b. foci c. deferent d. equant e. sphere 6. What did the Greek philosopher Philolaus believe about the Universe? a. No parallax seen of n ...
Chapters 29-31 Study Guide Answers
... 22.Hippocrates believe that diseases had natural causes and taught his students to observe their patients. 23.Greek astronomers were first to introduce the idea that the Earth moves around the sun. 24.Pythagoras and Euclid wrote about lines, circles , and squares. 25.Todays theaters are like the one ...
... 22.Hippocrates believe that diseases had natural causes and taught his students to observe their patients. 23.Greek astronomers were first to introduce the idea that the Earth moves around the sun. 24.Pythagoras and Euclid wrote about lines, circles , and squares. 25.Todays theaters are like the one ...
Chapter 15 Section 2 Greek Art and Literature
... The Natural Sciences (Input) • He inspired better thinker like Democritus to believe that the universe was made up of atoms • Thales asked questions about the earth that were based on observations of nature ...
... The Natural Sciences (Input) • He inspired better thinker like Democritus to believe that the universe was made up of atoms • Thales asked questions about the earth that were based on observations of nature ...
CVSP 202 PHILOSOPHY Flysheet Fall 2014-2015
... on it, the sun itself does not exist without its rays; (iii) yet, as the rays become more distant from their source and origin, they lose the intensity of their brilliance, and eventually fade away into the darkness of opaque matter. Plotinus focused on the triad: The ONE, Intellect, and World Soul, ...
... on it, the sun itself does not exist without its rays; (iii) yet, as the rays become more distant from their source and origin, they lose the intensity of their brilliance, and eventually fade away into the darkness of opaque matter. Plotinus focused on the triad: The ONE, Intellect, and World Soul, ...
WWII- The Home front
... Academus. This became the location of his school. Aristotle • 384-322 BC • Student of ____________ • Examined the nature of the world and human belief, thought, and knowledge. • Politics: Believed that government’s ________are also ____________to the same ________. • ________theorist of ____________ ...
... Academus. This became the location of his school. Aristotle • 384-322 BC • Student of ____________ • Examined the nature of the world and human belief, thought, and knowledge. • Politics: Believed that government’s ________are also ____________to the same ________. • ________theorist of ____________ ...
first ten slides
... Essential Questions (continued) • Why are the philosophers Rene Descartes and Francis Bacon seen as key to the development of the scientific method even though neither was actually a scientist? • Why are the contributions of Copernicus, Tycho Brahe, Johannes Kepler, Galileo Galilei and Isaac Newton ...
... Essential Questions (continued) • Why are the philosophers Rene Descartes and Francis Bacon seen as key to the development of the scientific method even though neither was actually a scientist? • Why are the contributions of Copernicus, Tycho Brahe, Johannes Kepler, Galileo Galilei and Isaac Newton ...
Greek Achievements - Lake County Schools
... math. • Euclid (YOO-kluhd) was one of these people, and many geometry rules we study today come from his studies. Hypatia (hy-PAY-shuh) was another famous, Greek Mathematician. She devoted her life to teaching her findings to others. ...
... math. • Euclid (YOO-kluhd) was one of these people, and many geometry rules we study today come from his studies. Hypatia (hy-PAY-shuh) was another famous, Greek Mathematician. She devoted her life to teaching her findings to others. ...
Greek Philosophers walkaround
... They traveled from city to city teaching others. They taught how to win an argument and make good political speeches. Sophists did not believe in gods and goddesses and rejected the idea of absolute right and wrong. They also believed what is right for one could be wrong for another. ...
... They traveled from city to city teaching others. They taught how to win an argument and make good political speeches. Sophists did not believe in gods and goddesses and rejected the idea of absolute right and wrong. They also believed what is right for one could be wrong for another. ...
Greek Philosophers
... They traveled from city to city teaching others. They taught how to win an argument and make good political speeches. Sophists did not believe in gods and goddesses and rejected the idea of absolute right and wrong. They also believed what is right for one could be wrong for another. ...
... They traveled from city to city teaching others. They taught how to win an argument and make good political speeches. Sophists did not believe in gods and goddesses and rejected the idea of absolute right and wrong. They also believed what is right for one could be wrong for another. ...
Unit 1: Rise of Democracy
... 1. Athens and Sparta were both Greek city-states; however they were very different. Explain. 2. What process took city-states from monarchy to aristocracy and, in Athens, to democracy? 3. What progress did the Greeks under Pericles make towards a democratic government? 4. How do the ideas of Ancient ...
... 1. Athens and Sparta were both Greek city-states; however they were very different. Explain. 2. What process took city-states from monarchy to aristocracy and, in Athens, to democracy? 3. What progress did the Greeks under Pericles make towards a democratic government? 4. How do the ideas of Ancient ...
The Crisis of Greek Civilization
... In his book, The Republic, Plato applied the theory of Forms to politics, arguing that the perfect political system would emphasize the polis as the center of a person’s identity. In his ideal society, everyone would use their natural skills to fulfill their role in society. Plato’s political ideas ...
... In his book, The Republic, Plato applied the theory of Forms to politics, arguing that the perfect political system would emphasize the polis as the center of a person’s identity. In his ideal society, everyone would use their natural skills to fulfill their role in society. Plato’s political ideas ...
The Glory That Was Greece
... events were caused by the whims of gods. Instead, they used observation and reason to find causes for events. The Greeks called these thinkers philosophers, meaning “lovers of wisdom.” ...
... events were caused by the whims of gods. Instead, they used observation and reason to find causes for events. The Greeks called these thinkers philosophers, meaning “lovers of wisdom.” ...
Chapter 8 Hellenic Culture
... • More opportunities for education • Epicurean school admitted women • Sports were opened to some females ...
... • More opportunities for education • Epicurean school admitted women • Sports were opened to some females ...
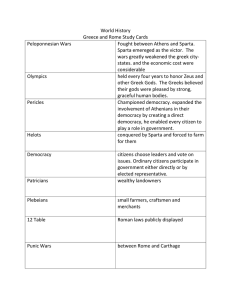
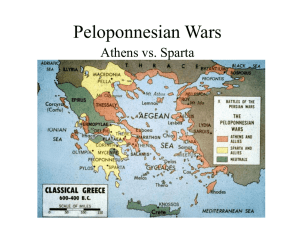
Peloponnesian War
... • Based thinking on 2 assumptions Universe is ordered in a certain way & subject to unchanging laws People can understand laws through logic and reason ...
... • Based thinking on 2 assumptions Universe is ordered in a certain way & subject to unchanging laws People can understand laws through logic and reason ...
Chapter 8 Hellenic Culture
... • Philosophy means “love of wisdom” • Systematic examination of human knowledge, including rules of logic • Ancient Greeks, originators of philosophy with bold ideas and imagination • Three periods: – Pre-Socratic Period: early writings to Socrates 470–399 BCE – Classical Age: from Socrates to 300 B ...
... • Philosophy means “love of wisdom” • Systematic examination of human knowledge, including rules of logic • Ancient Greeks, originators of philosophy with bold ideas and imagination • Three periods: – Pre-Socratic Period: early writings to Socrates 470–399 BCE – Classical Age: from Socrates to 300 B ...
Notes in your spiral/handout sheet over Alexander the Great/Vocab
... 16. A region north of Greece with rough mountains and a cold climate was Egypt Alexandria Macedonia Kuwait 17. Who wrote the book on the basic ideas of geometry? Plato Euclid Socrates Aristotle 18. Who invented clever machines such as the pulley? Archimedes Aristotle Euclid Plato 19. These people o ...
... 16. A region north of Greece with rough mountains and a cold climate was Egypt Alexandria Macedonia Kuwait 17. Who wrote the book on the basic ideas of geometry? Plato Euclid Socrates Aristotle 18. Who invented clever machines such as the pulley? Archimedes Aristotle Euclid Plato 19. These people o ...
Who Am I? (warmUP) Directions: Read each statement and on the
... 7. I also wrote tragedies. I wrote more than 80! But only 7 exist in your world today. My most famous is, The Oresteia. I am ___________________________. 8. I am known as the “father of history.” I described the Persian invasion of Greece. So what if I embellished some of the facts with fable, super ...
... 7. I also wrote tragedies. I wrote more than 80! But only 7 exist in your world today. My most famous is, The Oresteia. I am ___________________________. 8. I am known as the “father of history.” I described the Persian invasion of Greece. So what if I embellished some of the facts with fable, super ...
The Legacies of Ancient Greece What is a legacy?
... Love of wisdom; trying to figure things out through learning and reasoning Socrates ...
... Love of wisdom; trying to figure things out through learning and reasoning Socrates ...
A Short History of Space Science
... Thales One of the earliest Greek astronomers was Thales. He was born around 624 BC. The information we have about Thales is sketchy, but he is thought to have been a merchant and businessman. Because of his occupation Thales probably traveled widely and spent time in Egypt. Thales is considered to h ...
... Thales One of the earliest Greek astronomers was Thales. He was born around 624 BC. The information we have about Thales is sketchy, but he is thought to have been a merchant and businessman. Because of his occupation Thales probably traveled widely and spent time in Egypt. Thales is considered to h ...
characteristics of greek philosophy
... was indicted and exiled; while the earliest of them all, Pythagoras, was expelled from Croton in Italy. Can we imagine the Greeks making such an about turn, as to claim the very teachings which they had at first persecuted and openly rejected? Certainly, they knew they were usurping what they had ne ...
... was indicted and exiled; while the earliest of them all, Pythagoras, was expelled from Croton in Italy. Can we imagine the Greeks making such an about turn, as to claim the very teachings which they had at first persecuted and openly rejected? Certainly, they knew they were usurping what they had ne ...
Greek Philosophers
... and women should have the same education and an equal chance to have the same job. ...
... and women should have the same education and an equal chance to have the same job. ...
History of science in classical antiquity

The history of science in classical antiquity encompasses both those inquiries into the workings of the universe aimed at such practical goals as establishing a reliable calendar or determining how to cure a variety of illnesses and those abstract investigations known as natural philosophy. The ancient peoples who are considered the first scientists may have thought of themselves as natural philosophers, as practitioners of a skilled profession (for example, physicians), or as followers of a religious tradition (for example, temple healers). The encyclopedic works of Aristotle, Archimedes, Hippocrates, Galen, Ptolemy, Euclid, and others spread throughout the world. These works and the important commentaries on them were the wellspring of science.