Consolodation on the electromagnetic spectrum
... 12.Write out the electromagnetic spectrum in order of wavelength, starting with the longest: __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Visible light __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________ ...
... 12.Write out the electromagnetic spectrum in order of wavelength, starting with the longest: __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Visible light __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________ ...
EE4301 sp06 Class Sy..
... Concept, Nature and sources of vector fields Proof of Divergence and Stokes theorems Point to Integral form Concept of vector and scalar potential Section II – Static electric and magnetic fields Electrostatic fields from point charge sources Magnetostatic fields from ‘point’ current sources Physica ...
... Concept, Nature and sources of vector fields Proof of Divergence and Stokes theorems Point to Integral form Concept of vector and scalar potential Section II – Static electric and magnetic fields Electrostatic fields from point charge sources Magnetostatic fields from ‘point’ current sources Physica ...
â« â«
... • a) An electromagnetic wave is a result of electric and magnetic fields acting together. • b) The speed of electromagnetic waves through a vacuum is ten times the speed of sound in air. • c) Electromagnetic waves are longitudinal. • d) Electromagnetic waves in a vacuum travel with the speed of ...
... • a) An electromagnetic wave is a result of electric and magnetic fields acting together. • b) The speed of electromagnetic waves through a vacuum is ten times the speed of sound in air. • c) Electromagnetic waves are longitudinal. • d) Electromagnetic waves in a vacuum travel with the speed of ...
Domain 4: Waves, Electricity, and Magnetism
... 23. Drew has to make an electromagnet for science class. What materials would he need to collect? Name 2 things that Drew could do to make his electromagnet stronger? What does the passing electrical current through the wire coils do to the iron? Name 3 household items that have electromagnets in t ...
... 23. Drew has to make an electromagnet for science class. What materials would he need to collect? Name 2 things that Drew could do to make his electromagnet stronger? What does the passing electrical current through the wire coils do to the iron? Name 3 household items that have electromagnets in t ...
Lecture 17 - UConn Physics
... • These EM waves can take on any wavelength from angstroms to miles (and beyond). • We give these waves different names depending on the wavelength. ...
... • These EM waves can take on any wavelength from angstroms to miles (and beyond). • We give these waves different names depending on the wavelength. ...
ElectromagneticSpectrumPowerPoint
... forms the electromagnetic spectrum. • The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into different parts. ...
... forms the electromagnetic spectrum. • The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into different parts. ...
Introduction to telecommunication_part 2
... • F1 layer exists at about 180 kM in day time. Its thickness is 20 kM. • F2 layer exists at about 250 to 400 kM. Its height rises with atmospheric temperature. It’s thickness at times can be about 200 kM. • At night, F1 & F2 layers merge. • It is the topmost layer and with reduced degree, remains io ...
... • F1 layer exists at about 180 kM in day time. Its thickness is 20 kM. • F2 layer exists at about 250 to 400 kM. Its height rises with atmospheric temperature. It’s thickness at times can be about 200 kM. • At night, F1 & F2 layers merge. • It is the topmost layer and with reduced degree, remains io ...
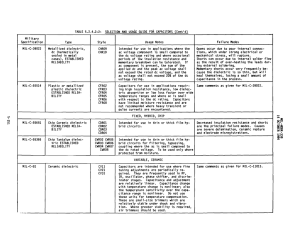
TABLE 5.2.4.2-2: SELECTION AND USAGE GUIDE FOR
... the dc rated voltage. To be used only where protected from moisture. VARIABLE, CERAMIC ...
... the dc rated voltage. To be used only where protected from moisture. VARIABLE, CERAMIC ...
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION LINES
... As we transport energy energy gets lost of the wire à lossy cable ¤ Radiation (the energy radiates out of the wire à the wire is acting as an antenna ¤ Resistance ...
... As we transport energy energy gets lost of the wire à lossy cable ¤ Radiation (the energy radiates out of the wire à the wire is acting as an antenna ¤ Resistance ...
Waves Web quest
... 1. Go to: http://www.ck12.org/book/CK-12-Physical-Science-Concepts-For-MiddleSchool/r6/section/5.23/ A) ...
... 1. Go to: http://www.ck12.org/book/CK-12-Physical-Science-Concepts-For-MiddleSchool/r6/section/5.23/ A) ...
The Doppler Effect and Electromagnetic Waves
... and the symbol c is used to denote its value. This speed is called the speed of light in a vacuum and is c = 3.00 × 108 m/s. In air, electromagnetic waves travel at nearly the same speed as they do in a vacuum, but, in general, they move through a substance such as glass at a speed that is substanti ...
... and the symbol c is used to denote its value. This speed is called the speed of light in a vacuum and is c = 3.00 × 108 m/s. In air, electromagnetic waves travel at nearly the same speed as they do in a vacuum, but, in general, they move through a substance such as glass at a speed that is substanti ...
ECE341 Introduction - UTK-EECS
... This course is about electromagnetics (EM), the foundation of Electrical and Computer Engineering, or, how electricity really works. -- Look into the black boxes. ...
... This course is about electromagnetics (EM), the foundation of Electrical and Computer Engineering, or, how electricity really works. -- Look into the black boxes. ...
Waveguide (electromagnetism)

In electromagnetics and communications engineering, the term waveguide may refer to any linear structure that conveys electromagnetic waves between its endpoints. However, the original and most common meaning is a hollow metal pipe used to carry radio waves. This type of waveguide is used as a transmission line mostly at microwave frequencies, for such purposes as connecting microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas, in equipment such as microwave ovens, radar sets, satellite communications, and microwave radio links.A dielectric waveguide employs a solid dielectric rod rather than a hollow pipe. An optical fibre is a dielectric guide designed to work at optical frequencies. Transmission lines such as microstrip, coplanar waveguide, stripline or coaxial cable may also be considered to be waveguides.The electromagnetic waves in a (metal-pipe) waveguide may be imagined as travelling down the guide in a zig-zag path, being repeatedly reflected between opposite walls of the guide. For the particular case of rectangular waveguide, it is possible to base an exact analysis on this view. Propagation in a dielectric waveguide may be viewed in the same way, with the waves confined to the dielectric by total internal reflection at its surface. Some structures, such as non-radiative dielectric waveguides and the Goubau line, use both metal walls and dielectric surfaces to confine the wave.