Dielectric Materials at Microwave Frequencies
... influenced by complex permittivity of the medium it propagates through, the material can be characterized by monitoring the reflected and transmitted waves as well. Some of these high frequency techniques are summarized below [1–5]. Resonant cavity method — Measurement techniques employing lumped ca ...
... influenced by complex permittivity of the medium it propagates through, the material can be characterized by monitoring the reflected and transmitted waves as well. Some of these high frequency techniques are summarized below [1–5]. Resonant cavity method — Measurement techniques employing lumped ca ...
PHYS 1442-004, Dr. Brandt
... • Heinrich Hertz first generated and detected EM waves experimentally in 1887 using a spark gap apparatus – Charge was rushed back and forth in a short period of time, generating waves with frequency about 109Hz (these are called radio waves) – He detected using a loop of wire in which an emf was pr ...
... • Heinrich Hertz first generated and detected EM waves experimentally in 1887 using a spark gap apparatus – Charge was rushed back and forth in a short period of time, generating waves with frequency about 109Hz (these are called radio waves) – He detected using a loop of wire in which an emf was pr ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... • Heinrich Hertz first generated and detected EM waves experimentally in 1887 using a spark gap apparatus – Charge was rushed back and forth in a short period of time, generating waves with frequency about 109Hz (these are called radio waves) – He detected using a loop of wire in which an emf was pr ...
... • Heinrich Hertz first generated and detected EM waves experimentally in 1887 using a spark gap apparatus – Charge was rushed back and forth in a short period of time, generating waves with frequency about 109Hz (these are called radio waves) – He detected using a loop of wire in which an emf was pr ...
CS412 Computer Networks - Winona State University
... (a) Three examples of a light ray from inside a silica fiber impinging on the air/silica boundary at different angles. (b) Light trapped by total internal reflection. ...
... (a) Three examples of a light ray from inside a silica fiber impinging on the air/silica boundary at different angles. (b) Light trapped by total internal reflection. ...
What Are Electromagnetic Waves?
... One way of measuring the energy of an Electromagnetic wave is by measuring its frequency. Frequency refers to the number of waves a vibration creates during a period of time – like counting how frequently cars pass through an intersection in a given time. In general, the higher the frequency, or num ...
... One way of measuring the energy of an Electromagnetic wave is by measuring its frequency. Frequency refers to the number of waves a vibration creates during a period of time – like counting how frequently cars pass through an intersection in a given time. In general, the higher the frequency, or num ...
07110059, 07110100 & 07110067
... (WLANs), current technology is unable to supply data rates comparable to wired standards like gigabit Ethernet and high-defi nition multimedia interface ...
... (WLANs), current technology is unable to supply data rates comparable to wired standards like gigabit Ethernet and high-defi nition multimedia interface ...
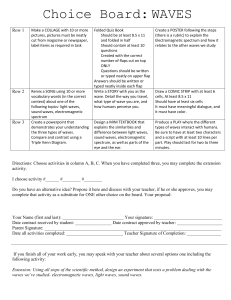
Waves Choice Board
... If you finish all of your work early, you may speak with your teacher about several options one including the following activity: Extension: Using all steps of the scientific method, design an experiment that tests a problem dealing with the waves we’ve studied- electromagnetic waves, light waves, s ...
... If you finish all of your work early, you may speak with your teacher about several options one including the following activity: Extension: Using all steps of the scientific method, design an experiment that tests a problem dealing with the waves we’ve studied- electromagnetic waves, light waves, s ...
dtet5 - advance communication systems
... (A) Fill in the blanks ( each question carry 2 marks) In cellular phones _________ way speech communication is possible _________ machine is a combination of copier / Scanners telephone system and printer. Error signals generated form the sensors are fed to a _________ encoder block For radiation of ...
... (A) Fill in the blanks ( each question carry 2 marks) In cellular phones _________ way speech communication is possible _________ machine is a combination of copier / Scanners telephone system and printer. Error signals generated form the sensors are fed to a _________ encoder block For radiation of ...
Amateur radio
... when penetrating buildings but glass windows are more transparent to radio waves ...
... when penetrating buildings but glass windows are more transparent to radio waves ...
• Maxwell`s equations and electromagnetic waves • sinusoidal
... Maxwell’s equations • After Ampere and Faraday came James Clark Maxwell. He penned a set of four equations that draw Gauss, Ampere, and Faraday’s laws together in a comprehensive description of the behavior of electromagnetic waves. • Don’t hate Maxwell for these equations. Aren’t they elegant? ...
... Maxwell’s equations • After Ampere and Faraday came James Clark Maxwell. He penned a set of four equations that draw Gauss, Ampere, and Faraday’s laws together in a comprehensive description of the behavior of electromagnetic waves. • Don’t hate Maxwell for these equations. Aren’t they elegant? ...
Waveguide (electromagnetism)

In electromagnetics and communications engineering, the term waveguide may refer to any linear structure that conveys electromagnetic waves between its endpoints. However, the original and most common meaning is a hollow metal pipe used to carry radio waves. This type of waveguide is used as a transmission line mostly at microwave frequencies, for such purposes as connecting microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas, in equipment such as microwave ovens, radar sets, satellite communications, and microwave radio links.A dielectric waveguide employs a solid dielectric rod rather than a hollow pipe. An optical fibre is a dielectric guide designed to work at optical frequencies. Transmission lines such as microstrip, coplanar waveguide, stripline or coaxial cable may also be considered to be waveguides.The electromagnetic waves in a (metal-pipe) waveguide may be imagined as travelling down the guide in a zig-zag path, being repeatedly reflected between opposite walls of the guide. For the particular case of rectangular waveguide, it is possible to base an exact analysis on this view. Propagation in a dielectric waveguide may be viewed in the same way, with the waves confined to the dielectric by total internal reflection at its surface. Some structures, such as non-radiative dielectric waveguides and the Goubau line, use both metal walls and dielectric surfaces to confine the wave.







![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008780767_1-2748e7688a1700a94f5fe801abdd55c3-300x300.png)