High power X and C band magnetrons for linac system Handling
... input section of ceramic and terminals includes the lead wires. Waveguide connecting ...
... input section of ceramic and terminals includes the lead wires. Waveguide connecting ...
Tutorial 4 – Experimental Techniques
... Studying several organic crystalline compounds, Cole and Cole found that the centers of the experimental arcs were displaced below the real axis, the experimental data thus having the shape of a depressed arc. ...
... Studying several organic crystalline compounds, Cole and Cole found that the centers of the experimental arcs were displaced below the real axis, the experimental data thus having the shape of a depressed arc. ...
Lecture 1
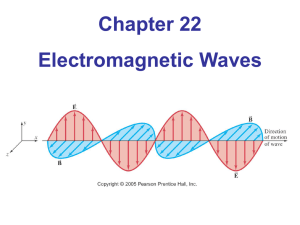
... 2. They are transverse waves. Since the Electric-field and Magnetic-field are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation, they are also called "plane waves" 3. The direction of propagation for EM wave points in the direction of the cross product ...
... 2. They are transverse waves. Since the Electric-field and Magnetic-field are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation, they are also called "plane waves" 3. The direction of propagation for EM wave points in the direction of the cross product ...
Electromagnetics - University of Idaho
... • As devices get smaller and smaller, and frequencies get higher and higher, circuit theory is less able to adequately describe the performance or to predict the operation of circuits. • At very high frequencies, transmission line and guided wave theory must be used - high speed electronics, micro/n ...
... • As devices get smaller and smaller, and frequencies get higher and higher, circuit theory is less able to adequately describe the performance or to predict the operation of circuits. • At very high frequencies, transmission line and guided wave theory must be used - high speed electronics, micro/n ...
Slide 1
... are created in the same space they can propagate on their own. These propagating fields are called electromagnetic waves. ...
... are created in the same space they can propagate on their own. These propagating fields are called electromagnetic waves. ...
PHAS2201 - Electricity and magnetism
... Faraday also introduced the concept of field lines. The unit of capacitance, the farad is named after him. Maxwell’s equations (1860s) James Clerk Maxwell completes his formulation of the field equations of electromagnetism, now known as Maxwell’s equations. Hertz’s oscillating dipole experiment (18 ...
... Faraday also introduced the concept of field lines. The unit of capacitance, the farad is named after him. Maxwell’s equations (1860s) James Clerk Maxwell completes his formulation of the field equations of electromagnetism, now known as Maxwell’s equations. Hertz’s oscillating dipole experiment (18 ...
A MathCAD Program to Calculate the RF Waves Coupled from a
... This number is estimated, actual length should be surveyed from the drawings or installation site. This number also ignores the all WR650 bends effect (either H or E type). I just treat them as a straight section of WR650 waveguide here. Total reduced height waveguide length from the H-bend Sweep to ...
... This number is estimated, actual length should be surveyed from the drawings or installation site. This number also ignores the all WR650 bends effect (either H or E type). I just treat them as a straight section of WR650 waveguide here. Total reduced height waveguide length from the H-bend Sweep to ...
A negatively charged rod is brought near two conducting balls X and Y
... ‘Right hand screw rule’ to draw a diagram to show the magnetic field around the two wires and indicate on the diagram the forces on the two wires. ...
... ‘Right hand screw rule’ to draw a diagram to show the magnetic field around the two wires and indicate on the diagram the forces on the two wires. ...
Waveguide (electromagnetism)

In electromagnetics and communications engineering, the term waveguide may refer to any linear structure that conveys electromagnetic waves between its endpoints. However, the original and most common meaning is a hollow metal pipe used to carry radio waves. This type of waveguide is used as a transmission line mostly at microwave frequencies, for such purposes as connecting microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas, in equipment such as microwave ovens, radar sets, satellite communications, and microwave radio links.A dielectric waveguide employs a solid dielectric rod rather than a hollow pipe. An optical fibre is a dielectric guide designed to work at optical frequencies. Transmission lines such as microstrip, coplanar waveguide, stripline or coaxial cable may also be considered to be waveguides.The electromagnetic waves in a (metal-pipe) waveguide may be imagined as travelling down the guide in a zig-zag path, being repeatedly reflected between opposite walls of the guide. For the particular case of rectangular waveguide, it is possible to base an exact analysis on this view. Propagation in a dielectric waveguide may be viewed in the same way, with the waves confined to the dielectric by total internal reflection at its surface. Some structures, such as non-radiative dielectric waveguides and the Goubau line, use both metal walls and dielectric surfaces to confine the wave.