Electromagnetic Waves Student Worksheet Answer the following
... 4. Which of the following are likely to act as a polarizing filter for radio waves: a picket fence consisting of long, thin slats made out of metal or wood? The polarizing filter would need to be made out of metal in order to prevent radio waves with a particular polarization (or orientation of elec ...
... 4. Which of the following are likely to act as a polarizing filter for radio waves: a picket fence consisting of long, thin slats made out of metal or wood? The polarizing filter would need to be made out of metal in order to prevent radio waves with a particular polarization (or orientation of elec ...
Waves - SFP Online!
... – Transverse waves exhibit simple harmonic motion about a rest position perpendicular to the direction of motion. (EX: waves on a string) – Longitudinal waves exhibit SHM parallel to the direction of motion (EX: sound, slinky) – Surface wave exhibit motion both parallel and perpendicular to the dire ...
... – Transverse waves exhibit simple harmonic motion about a rest position perpendicular to the direction of motion. (EX: waves on a string) – Longitudinal waves exhibit SHM parallel to the direction of motion (EX: sound, slinky) – Surface wave exhibit motion both parallel and perpendicular to the dire ...
Waves Continuous disturbance that transfers energy without any net
... electromagnetic wave and matter wave. ...
... electromagnetic wave and matter wave. ...
Slide 1
... dielectric constant (V = .3/r m/ns); the .3 is because radar-waves are referenced to the speed of light in air or in vacuum (.3 m/ns). Dielectric constants for most dry geologic materials range from 4 (quartz sand) to 7 (shales and carbonates). Water, however, has a dielectric constant of 81 at 20 ...
... dielectric constant (V = .3/r m/ns); the .3 is because radar-waves are referenced to the speed of light in air or in vacuum (.3 m/ns). Dielectric constants for most dry geologic materials range from 4 (quartz sand) to 7 (shales and carbonates). Water, however, has a dielectric constant of 81 at 20 ...
Section 2
... A Cathode Ray Oscilloscope can be used to view waves. The waves are converted into electrical vibrations using various devices such as a microphone. Use an oscilloscope to observe and draw signals that produce ...
... A Cathode Ray Oscilloscope can be used to view waves. The waves are converted into electrical vibrations using various devices such as a microphone. Use an oscilloscope to observe and draw signals that produce ...
Lecture 3: Fiber Modes
... core. This “normalized frequency” determines how many different guided modes a fiber can support. ...
... core. This “normalized frequency” determines how many different guided modes a fiber can support. ...
14 Microwaves
... A TE wave has a characteristic impedance > 120 π. As the cutoff frequency is approached, the impedance approaches infinity. These modes are generated by means of a vertical probe antenna. A TM wave has a characteristic impedance < 120 π. As the cutoff frequency is approached, the impedance approache ...
... A TE wave has a characteristic impedance > 120 π. As the cutoff frequency is approached, the impedance approaches infinity. These modes are generated by means of a vertical probe antenna. A TM wave has a characteristic impedance < 120 π. As the cutoff frequency is approached, the impedance approache ...
EE4302 Fl04 Class Sy..
... Physical properties of materials (types) Electric and magnetic dipoles => ε and µ Collisions and Drag Material related electric and magnetic fields Maxwell’s equations and charge conservation Equivalence between integral and point forms Boundary conditions Section III – Dynamic electromagnetic field ...
... Physical properties of materials (types) Electric and magnetic dipoles => ε and µ Collisions and Drag Material related electric and magnetic fields Maxwell’s equations and charge conservation Equivalence between integral and point forms Boundary conditions Section III – Dynamic electromagnetic field ...
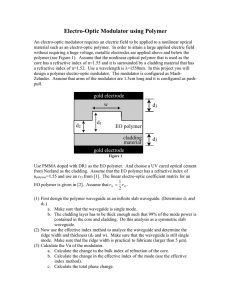
Design Project 4: Modulator
... Electro-Optic Modulator using Polymer An electro-optic modulator requires an electric field to be applied to a nonlinear optical material such as an electro-optic polymer. In order to attain a large applied electric field without requiring a huge voltage, metallic electrodes are applied above and be ...
... Electro-Optic Modulator using Polymer An electro-optic modulator requires an electric field to be applied to a nonlinear optical material such as an electro-optic polymer. In order to attain a large applied electric field without requiring a huge voltage, metallic electrodes are applied above and be ...
Physics 3323 Intermediate Electricity and Magnetism
... Study Hall: An opportunity for you to work together to work through issues in HW that have you stumped. Attendance is optional. I will be available until ~5:15 to help the group should everyone be ...
... Study Hall: An opportunity for you to work together to work through issues in HW that have you stumped. Attendance is optional. I will be available until ~5:15 to help the group should everyone be ...
energy propagation in dielectric and magnetic materials
... will be diminished at the given rate as it propagates in the section of line that is filled by the material. The tabulated or calculated rate does not include any effects of energy reflections at the input or output interfaces between the lossy material and any other materials such as air in adjacen ...
... will be diminished at the given rate as it propagates in the section of line that is filled by the material. The tabulated or calculated rate does not include any effects of energy reflections at the input or output interfaces between the lossy material and any other materials such as air in adjacen ...
Microwaves in Waveguides
... reveal microwave antennas used for telecommunication. You may even have a satellite antenna for TV reception. If you have been caught speeding in an automobile you may have been the "victim" of microwave technology. Microwaves are a part of the electromagnetic spectrum situated between radio frequen ...
... reveal microwave antennas used for telecommunication. You may even have a satellite antenna for TV reception. If you have been caught speeding in an automobile you may have been the "victim" of microwave technology. Microwaves are a part of the electromagnetic spectrum situated between radio frequen ...
Waveguide (electromagnetism)

In electromagnetics and communications engineering, the term waveguide may refer to any linear structure that conveys electromagnetic waves between its endpoints. However, the original and most common meaning is a hollow metal pipe used to carry radio waves. This type of waveguide is used as a transmission line mostly at microwave frequencies, for such purposes as connecting microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas, in equipment such as microwave ovens, radar sets, satellite communications, and microwave radio links.A dielectric waveguide employs a solid dielectric rod rather than a hollow pipe. An optical fibre is a dielectric guide designed to work at optical frequencies. Transmission lines such as microstrip, coplanar waveguide, stripline or coaxial cable may also be considered to be waveguides.The electromagnetic waves in a (metal-pipe) waveguide may be imagined as travelling down the guide in a zig-zag path, being repeatedly reflected between opposite walls of the guide. For the particular case of rectangular waveguide, it is possible to base an exact analysis on this view. Propagation in a dielectric waveguide may be viewed in the same way, with the waves confined to the dielectric by total internal reflection at its surface. Some structures, such as non-radiative dielectric waveguides and the Goubau line, use both metal walls and dielectric surfaces to confine the wave.