Polyatomic Ions Writing Formulas / Naming Compounds
... between two non-metals that have similar electronegativities. ...
... between two non-metals that have similar electronegativities. ...
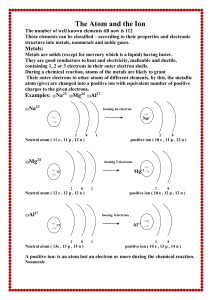
Notes on Atomic Structure atoms
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply ch ...
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply ch ...
Lecture 14_withfigures
... for more covalent M-O bonds of the non-metals → Acid Amphoteric Hydroxides also exist Alkoxides The basic formula of an alkoxide is OR- where R is an organic group such as an alkyl group. They are very reactive in water and hydrolyze quickly… OR- + H2O OH- + ROH (forms an alcohol) ...
... for more covalent M-O bonds of the non-metals → Acid Amphoteric Hydroxides also exist Alkoxides The basic formula of an alkoxide is OR- where R is an organic group such as an alkyl group. They are very reactive in water and hydrolyze quickly… OR- + H2O OH- + ROH (forms an alcohol) ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... Remember: positive charges must = negative charges Ex.1: What is the formula for magnesium phosphide? Magnesium is Mg2+ Phosphorous is P3– Lowest common multiple of 2 and 3 is 6 3 Mg2+ ions & 2 P3– ions (6 +ve’s & 6 –ve’s) ...
... Remember: positive charges must = negative charges Ex.1: What is the formula for magnesium phosphide? Magnesium is Mg2+ Phosphorous is P3– Lowest common multiple of 2 and 3 is 6 3 Mg2+ ions & 2 P3– ions (6 +ve’s & 6 –ve’s) ...
17.The d-Block Elements.General properties
... Color: The complexes of the d-block metal ions are usually colored, except, very often, those of d0 and d10 metal ions. The colors are due to: a) electronic transitions of d-electrons within the d subshell. These are known as d→d transitions. d0 and d10 metal ions do not show these transitions. b) e ...
... Color: The complexes of the d-block metal ions are usually colored, except, very often, those of d0 and d10 metal ions. The colors are due to: a) electronic transitions of d-electrons within the d subshell. These are known as d→d transitions. d0 and d10 metal ions do not show these transitions. b) e ...
Electronic Structures and Chemical Bonding of Minerals and
... When electrons are completely transferred between atoms to yield cations and anions, the atoms will be held together by ionic bonds. If atoms have similar electronegativities, they adopt closed-shell configurations by sharing electrons with each other; the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. ...
... When electrons are completely transferred between atoms to yield cations and anions, the atoms will be held together by ionic bonds. If atoms have similar electronegativities, they adopt closed-shell configurations by sharing electrons with each other; the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. ...
Redox Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Oxidation and reduction reaction = redox rxn Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons = transfer of electrons Those 2 reactions are occurring simultaneously ...
... Oxidation and reduction reaction = redox rxn Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons = transfer of electrons Those 2 reactions are occurring simultaneously ...
Chemistry 332 Basic Inorganic Chemistry II
... Ni reacts with CO (leaving the impurities behind), to form Ni(CO)4. The Ni(CO)4 is passed through a tower filled with nickel pellets at a high velocity and 400 K. Pure Ni plates out on the pellets. * A commercial process for the manufacture of Na2CO3. NH3 and CO2 are passed into a sat’d NaCl(aq) sol ...
... Ni reacts with CO (leaving the impurities behind), to form Ni(CO)4. The Ni(CO)4 is passed through a tower filled with nickel pellets at a high velocity and 400 K. Pure Ni plates out on the pellets. * A commercial process for the manufacture of Na2CO3. NH3 and CO2 are passed into a sat’d NaCl(aq) sol ...
ch 5 notes
... water; not electrolytic; not as hard as ionic compounds Distillation : process which uses the differences between ionic and covalent compounds to separate them from one another…remember the apparatus? (p. 171) Molecular Elements: when atoms of the same elements bond together to form a molecule…NOT c ...
... water; not electrolytic; not as hard as ionic compounds Distillation : process which uses the differences between ionic and covalent compounds to separate them from one another…remember the apparatus? (p. 171) Molecular Elements: when atoms of the same elements bond together to form a molecule…NOT c ...