Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... ion is its oxidation number. (sometimes called oxidation state) ...
... ion is its oxidation number. (sometimes called oxidation state) ...
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
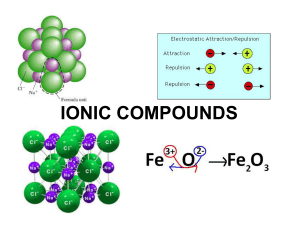
... Ionic Bonds bind oppositely charged ions. The total positive charges of cations =’s the total negative charges or the anions ... so, compounds are neutral. ...
... Ionic Bonds bind oppositely charged ions. The total positive charges of cations =’s the total negative charges or the anions ... so, compounds are neutral. ...
101
... Not all redox reactions give off light, however. How can you recognize a redox reaction, and how can you identify the oxidizing and reducing agents? In section 10.1, you saw net ionic equations with monatomic elements, such as Cu and Zn, and with ions containing a single element, such as Cu2+ and Zn ...
... Not all redox reactions give off light, however. How can you recognize a redox reaction, and how can you identify the oxidizing and reducing agents? In section 10.1, you saw net ionic equations with monatomic elements, such as Cu and Zn, and with ions containing a single element, such as Cu2+ and Zn ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... • A compound is a distinct substance that is composed of atoms of two or more elements. • Compounds are identified by the number and type of each atom in the simplest unit of the compound. – Molecules or ions ...
... • A compound is a distinct substance that is composed of atoms of two or more elements. • Compounds are identified by the number and type of each atom in the simplest unit of the compound. – Molecules or ions ...