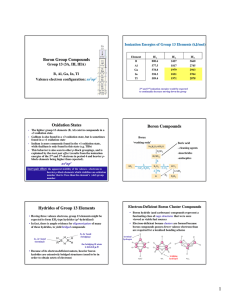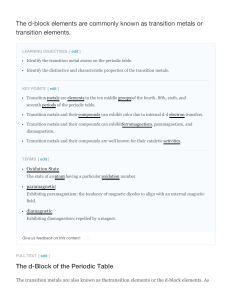
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
... If an element has 3 valence electrons, it will ( lose / gain ) 3 electrons to become a ( + / - ) 3 ion. If an element has 7 valence electrons, it will ( lose / gain ) __ electrons to become a ( + / - ) __ ion. Using your periodic table, find the number of protons and electrons in the following ions: ...
... If an element has 3 valence electrons, it will ( lose / gain ) 3 electrons to become a ( + / - ) 3 ion. If an element has 7 valence electrons, it will ( lose / gain ) __ electrons to become a ( + / - ) __ ion. Using your periodic table, find the number of protons and electrons in the following ions: ...
Chapter 4 Student Notes
... A redox equation is balanced if: it is balanced for atoms on each side. the total electrons lost and gained are equal. the reducing agent: the oxidizing agent: Our equation now looks like this: ...
... A redox equation is balanced if: it is balanced for atoms on each side. the total electrons lost and gained are equal. the reducing agent: the oxidizing agent: Our equation now looks like this: ...
Oregon State University, Summer 2009 Chemistry 121 Midterm
... a. A combustion reaction is one in which a compound reacts with oxygen to make carbon monoxide and water. b. The Law of Conservation of Matter (Mass) states that the total mass of substances in a chemical reaction does not change. c. In a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of all types remains c ...
... a. A combustion reaction is one in which a compound reacts with oxygen to make carbon monoxide and water. b. The Law of Conservation of Matter (Mass) states that the total mass of substances in a chemical reaction does not change. c. In a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of all types remains c ...
Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Nicotinamide Cobalt (II) Complexes
... Nicotinamide (NA) is one form of niacin. A deficiency of this vitamin leads to loss of copper from the body, known as pellagra disease. Victims of pellagra show unusually high serum and urinary copper levels (1). The nicotinic acid derivative N,N-diethylnicotinamide (DENA) is an important respirator ...
... Nicotinamide (NA) is one form of niacin. A deficiency of this vitamin leads to loss of copper from the body, known as pellagra disease. Victims of pellagra show unusually high serum and urinary copper levels (1). The nicotinic acid derivative N,N-diethylnicotinamide (DENA) is an important respirator ...
formula writing and nomenclature of inorganic - Parkway C-2
... share electrons in forming a chemical bond. The number of electrons that an atom loses, gains, or shares when it bonds with another atom is known as the oxidation number of the atom. Elements which lose electrons in a chemical reaction, or which have electrons which are shared with another element d ...
... share electrons in forming a chemical bond. The number of electrons that an atom loses, gains, or shares when it bonds with another atom is known as the oxidation number of the atom. Elements which lose electrons in a chemical reaction, or which have electrons which are shared with another element d ...
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... How did we find out the structure of the atom if it is so small? ...
... How did we find out the structure of the atom if it is so small? ...
File
... – The ending of the nonmetal is changed to end in -ide – When a metal can have various oxidation states the oxidation state is give by roman numerals in parenthesis after the name of the metal. ...
... – The ending of the nonmetal is changed to end in -ide – When a metal can have various oxidation states the oxidation state is give by roman numerals in parenthesis after the name of the metal. ...
Classifying Chemical Reactions by What Atoms Do
... The titration of 10.00 mL of HCl solution of unknown concentration requires 12.54 mL of 0.100 M NaOH solution to reach the end point. What is the concentration of the unknown HCl solution? ...
... The titration of 10.00 mL of HCl solution of unknown concentration requires 12.54 mL of 0.100 M NaOH solution to reach the end point. What is the concentration of the unknown HCl solution? ...
ch14
... valence level. • H is similar to the other Group 4A elements in terms of – ionization energy, ...
... valence level. • H is similar to the other Group 4A elements in terms of – ionization energy, ...