Chapter 2
... • Table salt (sodium chloride or NaCl) is a compound with equal numbers of chlorine and sodium atoms. • While pure sodium is a metal and chlorine is a gas, their combination forms an edible compound, an emergent property. ...
... • Table salt (sodium chloride or NaCl) is a compound with equal numbers of chlorine and sodium atoms. • While pure sodium is a metal and chlorine is a gas, their combination forms an edible compound, an emergent property. ...
3 molecules
... Valence Electrons in Ionic Compounds • The A-group (representative) elements follow the OCTET RULE; they obtain an inert gas valence (outer) shell that contains 8 electrons • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e. ...
... Valence Electrons in Ionic Compounds • The A-group (representative) elements follow the OCTET RULE; they obtain an inert gas valence (outer) shell that contains 8 electrons • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e. ...
Chapter 5 - U of L Class Index
... elements in compounds are replaced by other elements. If only one compound has an element replaced, it is a single replacement reaction. If two compounds have elements replaced, then it is a double replacement reaction. e.g. Fe2O3 + 3C AgNO3 + NaCl ...
... elements in compounds are replaced by other elements. If only one compound has an element replaced, it is a single replacement reaction. If two compounds have elements replaced, then it is a double replacement reaction. e.g. Fe2O3 + 3C AgNO3 + NaCl ...
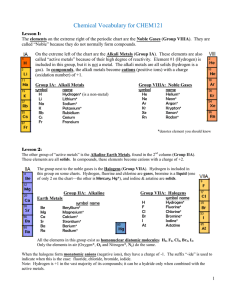
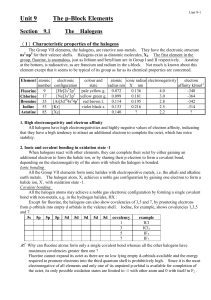
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... 1. High electronegativity and electron affinity All halogens have high electronegativities and highly negative values of electron affinity, indicating that they have a high tendency to attract an additional electron to complete the octet, which has extra stability. 2. Ionic and covalent bonding in o ...
... 1. High electronegativity and electron affinity All halogens have high electronegativities and highly negative values of electron affinity, indicating that they have a high tendency to attract an additional electron to complete the octet, which has extra stability. 2. Ionic and covalent bonding in o ...
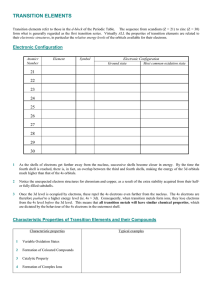
The Transition Metals
... Each metal contributes the same number of electrons as its group number. ...
... Each metal contributes the same number of electrons as its group number. ...
Column A
... a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal numbers in a neutral ato ...
... a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal numbers in a neutral ato ...
Chemistry of d And f block Elements Transition Metals Including
... The first ionisation enthalpies of Cr and Cu are low. This is because the removal of one electron does not change their d configuration. Similarly first ionisation enthalpy of Zn is high because after the removal of one electron there is no change in the d configuration Zn → Zn+ + e- 3d104s2 3d104s1 ...
... The first ionisation enthalpies of Cr and Cu are low. This is because the removal of one electron does not change their d configuration. Similarly first ionisation enthalpy of Zn is high because after the removal of one electron there is no change in the d configuration Zn → Zn+ + e- 3d104s2 3d104s1 ...
5_slides_olefin_complexes_VIPEr
... Created by Margaret L. Scheuermann, Princeton University; Abby R. O’Connor, The College of New Jersey, [email protected]. Copyright Scheuermann and O’Connor, 2014. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercialShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this licens ...
... Created by Margaret L. Scheuermann, Princeton University; Abby R. O’Connor, The College of New Jersey, [email protected]. Copyright Scheuermann and O’Connor, 2014. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercialShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this licens ...
Notes
... (Don’t worry! There’s an easier way to calculate it without having to memorize the formula!) ...
... (Don’t worry! There’s an easier way to calculate it without having to memorize the formula!) ...
PPT - George Mason University
... They lack a Stoichiometric formula because metal can incorporate a variable amount of hydrogen, depending upon temperature and pressure ...
... They lack a Stoichiometric formula because metal can incorporate a variable amount of hydrogen, depending upon temperature and pressure ...