Ubiquitin regulates dissociation of DNA repair factors from chromatin
... during the last decade. Dynamic modification of proteins with ubiquitin after DNA damage has been shown to play important roles in virtually all DNA repair pathways [1]. In this regard, protein ubiquitylation has most frequently been associated with the recruitment of DNA repair factors – many conta ...
... during the last decade. Dynamic modification of proteins with ubiquitin after DNA damage has been shown to play important roles in virtually all DNA repair pathways [1]. In this regard, protein ubiquitylation has most frequently been associated with the recruitment of DNA repair factors – many conta ...
Day 2: Protein Sequence Analysis
... End of the output the percentage likelihood of the subcellular localization. ...
... End of the output the percentage likelihood of the subcellular localization. ...
Protein Folding File
... What are the two main structural motifs present in secondary folding of amino acid chains? What type of bonding stabilizes alpha helices and beta sheets? In addition to H-bonding, what type of bonding leads to stronger covalent bonds between amino acids? After secondary structures are formed, what i ...
... What are the two main structural motifs present in secondary folding of amino acid chains? What type of bonding stabilizes alpha helices and beta sheets? In addition to H-bonding, what type of bonding leads to stronger covalent bonds between amino acids? After secondary structures are formed, what i ...
Slide 1
... • PQS says “dimeric complex”, meaning a protein dimer complexed to DNA (still 4 chains). Published ...
... • PQS says “dimeric complex”, meaning a protein dimer complexed to DNA (still 4 chains). Published ...
SOLUGEL Protein Gummies Leaflet
... Great taste with more than 20% collagen protein in each gummy Triple your gummies’ protein content with SOLUGEL®! The traditional gummy bear contains around 6g of protein per 100g, entirely from its gelatin content. With SOLUGEL®, it is now possible to create a gummy rich in collagen protein that l ...
... Great taste with more than 20% collagen protein in each gummy Triple your gummies’ protein content with SOLUGEL®! The traditional gummy bear contains around 6g of protein per 100g, entirely from its gelatin content. With SOLUGEL®, it is now possible to create a gummy rich in collagen protein that l ...
John Torri Basic Nutrition Special Topic: Protein November 13 2014
... every day. Amino acids are the building blocks for protein. There are two types of amino acids, essential, and non-essential. Essential amino acids are those that are “essential” in the diet. In other words, our bodies cannot create them through our own metabolism. The main essential amino acids are ...
... every day. Amino acids are the building blocks for protein. There are two types of amino acids, essential, and non-essential. Essential amino acids are those that are “essential” in the diet. In other words, our bodies cannot create them through our own metabolism. The main essential amino acids are ...
Teaching Notes
... 1. All proteins have specific shapes that are best suited for their function(s) 2. Strategic locations of amino acid residues, with different physical and chemical properties (side-chains), enable proteins to perform a variety of different functions in the cell. 3. Small globular proteins (made of o ...
... 1. All proteins have specific shapes that are best suited for their function(s) 2. Strategic locations of amino acid residues, with different physical and chemical properties (side-chains), enable proteins to perform a variety of different functions in the cell. 3. Small globular proteins (made of o ...
Soybean Meal - International Feed
... Soybean Meal is the standard to which other protein sources are compared, and is a by-product of soybean oil extraction. Protein, fiber, and fat levels all vary with the process by which the oil is extracted. Soybean Meal is a highly palatable source of protein, and used often as the dominant source ...
... Soybean Meal is the standard to which other protein sources are compared, and is a by-product of soybean oil extraction. Protein, fiber, and fat levels all vary with the process by which the oil is extracted. Soybean Meal is a highly palatable source of protein, and used often as the dominant source ...
ECS 189K - UC Davis
... Detecting knots in proteins Think of the main-chain of a protein as being a long entangled string. The question is: does that string form a knot? (i.e. if you were to hold the two extremities of the string and pull, would it result in the formation of a knot, or would the string become linear?) Some ...
... Detecting knots in proteins Think of the main-chain of a protein as being a long entangled string. The question is: does that string form a knot? (i.e. if you were to hold the two extremities of the string and pull, would it result in the formation of a knot, or would the string become linear?) Some ...
1984 BS, Seoul National University, Korea
... be post-translationally created by ATE1-encoded Arg-tRNA transferases (R-transferases) that transfer the amino acid L-Arg from Arg-tRNAArg to the N-termini. Recognins that recognize the N-terminal Arg residue of N-end rule substrates include the UBR box of a family of proteins, called UBR box protei ...
... be post-translationally created by ATE1-encoded Arg-tRNA transferases (R-transferases) that transfer the amino acid L-Arg from Arg-tRNAArg to the N-termini. Recognins that recognize the N-terminal Arg residue of N-end rule substrates include the UBR box of a family of proteins, called UBR box protei ...
30_General pathways of amino acids transformation
... Mechanism of the binding of ubiquitin to target protein E1 - ubiquitin-activating enzyme (attachment of ubiquitin to a sulfhydryl group of E1; ATP-driven reaction) E2 - ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (ubiquitin is shuttled to a sulfhydryl group of E2) E3 - ubiquitin-protein ligase (transfer of ubiqui ...
... Mechanism of the binding of ubiquitin to target protein E1 - ubiquitin-activating enzyme (attachment of ubiquitin to a sulfhydryl group of E1; ATP-driven reaction) E2 - ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (ubiquitin is shuttled to a sulfhydryl group of E2) E3 - ubiquitin-protein ligase (transfer of ubiqui ...
A Series of Ubiquitin Binding Factors Connects CDC48/p97 to
... Proteolysis is pivotal for cellular and developmental regulation. Due to its irreversible nature, proteolysis is ideally suited for regulating unidirectional pathways such as cell cycle progression or differentiation. In eukaryotes, selective proteolysis is largely mediated by the ubiquitin/ proteas ...
... Proteolysis is pivotal for cellular and developmental regulation. Due to its irreversible nature, proteolysis is ideally suited for regulating unidirectional pathways such as cell cycle progression or differentiation. In eukaryotes, selective proteolysis is largely mediated by the ubiquitin/ proteas ...
Abstract: The backbone chain of a protein (called its fold) can be
... English (Translation provided by R. Dilão and R. Mondaini) ...
... English (Translation provided by R. Dilão and R. Mondaini) ...
Chapter 5 - Richsingiser.com
... – Invariant residue – identical aa among homologues – Conserved residue – similar (class) aa among homologues – Hypervariable residue – no similarity among homologues ...
... – Invariant residue – identical aa among homologues – Conserved residue – similar (class) aa among homologues – Hypervariable residue – no similarity among homologues ...
Protein Structure
... Proteins are made out of C, H, O and N What are the monomers/building blocks for proteins? • Amino Acids! There are 20 different types. They are connected by Peptide Bonds to form Proteins Proteins are also called Polypeptides ...
... Proteins are made out of C, H, O and N What are the monomers/building blocks for proteins? • Amino Acids! There are 20 different types. They are connected by Peptide Bonds to form Proteins Proteins are also called Polypeptides ...
Gene Section UBE3A (ubiquitin protein ligase E3A) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... lesion of the anogenital tract (most notably, cervical cancer) have the ability to bind to E6AP. The E6/E6AP complex binds to the p53 tumor suppressor, thereby targeting p53 for ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. It is commonly assumed that this (p53 degradation and, thus, inactivation) rep ...
... lesion of the anogenital tract (most notably, cervical cancer) have the ability to bind to E6AP. The E6/E6AP complex binds to the p53 tumor suppressor, thereby targeting p53 for ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. It is commonly assumed that this (p53 degradation and, thus, inactivation) rep ...
2016 N1 Week 4
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
Amino Acids - Clydebank High School
... They speed up the rate of reactions in living organisms. Enzymes are PROTEINS. They are very specific. They usually only catalyse 1 type of reaction. When enzymes are at the wrong temperature or pH – they are denatured ( destroyed). They work at optimum conditions – pH and T. ...
... They speed up the rate of reactions in living organisms. Enzymes are PROTEINS. They are very specific. They usually only catalyse 1 type of reaction. When enzymes are at the wrong temperature or pH – they are denatured ( destroyed). They work at optimum conditions – pH and T. ...
Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English
... acids are then used by your cells to make new proteins. Chapter 11: Chemistry of Living Systems 357 ...
... acids are then used by your cells to make new proteins. Chapter 11: Chemistry of Living Systems 357 ...
sample-student-2-Pos.. - NuWrite
... •Prp8 has few characteristic domains, but does contain a variant Jab1/MPN domain. •The Jab1/MPN domain is normally found within deubiquitinating enzymes that remove ubiquitin from proteins marked for destruction. •The non-canonical Jab1/MPN domain of Prp8 does not enable enzyme function, but is stil ...
... •Prp8 has few characteristic domains, but does contain a variant Jab1/MPN domain. •The Jab1/MPN domain is normally found within deubiquitinating enzymes that remove ubiquitin from proteins marked for destruction. •The non-canonical Jab1/MPN domain of Prp8 does not enable enzyme function, but is stil ...
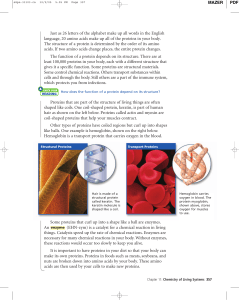
Most Proteins Don`t Exist!
... Proteins fascinate me, they always have. Were it not for structural proteins, catalytic proteins (enzymes), transport proteins, binding proteins, etc., etc., there would be no conscious life. Arguably the only purpose of DNA is to encode the information required to build a protein. There are good ar ...
... Proteins fascinate me, they always have. Were it not for structural proteins, catalytic proteins (enzymes), transport proteins, binding proteins, etc., etc., there would be no conscious life. Arguably the only purpose of DNA is to encode the information required to build a protein. There are good ar ...
Proteins
... 3. R group -different for every AA -determines the properties of AA Joined together by peptide bonds ...
... 3. R group -different for every AA -determines the properties of AA Joined together by peptide bonds ...
Ubiquitin

Ubiquitin is a small (8.5 kDa) regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues (ubiquitously) of eukaryotic organisms. It was discovered in 1975 by Goldstein and further characterized throughout the 1970s and 1980s. There are four genes in the human genome that produce ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A.The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination or ubiquitylation. Ubiquitination can affect proteins in many ways: It can signal for their degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitination is carried out in three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade binds ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bond or to the amino group of the protein's N-terminus via a peptide bond.The protein modifications can be either a single ubiquitin protein (monoubiquitination) or a chain of ubiquitin (polyubiquitination). The ubiquitination bonds are always formed with one of the seven lysine residues from the ubiquitin molecule. These 'linking' lysines are represented by a ""K"" (which is the one-letter amino acid notation of lysine) and a number, referring to its position in the ubiquitin molecule. First, a ubiquitin molecule is bonded by its C-terminus to a specific lysine residue (e.g. K48, K29, K63,...) on the target protein. Poly-ubiquitination occurs when the C-terminus of another ubiquitin, will be linked again to a lysine residue (for example again K48 or K29) on the previously added ubiquitin molecule, forming a chain. This process repeats several times, leading to the addition of several ubiquitins. Only poly-ubiquitination on defined lysines, mostly on K48 and K29, is related to degradation with the proteasome (referred to as the ""molecular kiss of death""), while other polyubiquitinations (e.g. on K63, K11, K6) and monoubiquitinations may regulate processes such as endocytic trafficking, inflammation, translation and DNA repair.Lysine 48-linked chains have been much-studied. They are the forms of chains that signal proteins to the proteasome, which destroys and recycles proteins. This discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004.