Enzyme Biosinthess
... Several proteases present in the eukaryotic cytosol two Ca2+ activated proteases calpains an ATP-dependent protease proteasome Four structural features are currently thought to be determinants of turnover rate : 1. Ubiquitination ...
... Several proteases present in the eukaryotic cytosol two Ca2+ activated proteases calpains an ATP-dependent protease proteasome Four structural features are currently thought to be determinants of turnover rate : 1. Ubiquitination ...
Peptide Bonds
... 2. Planar to allow delocalisation 3. Restricted Rotation about the amide bond 4. Rotation of Groups (R and R’) attached to the amide bond is relatively free ...
... 2. Planar to allow delocalisation 3. Restricted Rotation about the amide bond 4. Rotation of Groups (R and R’) attached to the amide bond is relatively free ...
PTM
... 1. Dealing with the N-terminal residue In bacteria, the N-terminal residue of the newlysynthesized protein is modified to remove the formyl group. The N-terminal methionine may also be ...
... 1. Dealing with the N-terminal residue In bacteria, the N-terminal residue of the newlysynthesized protein is modified to remove the formyl group. The N-terminal methionine may also be ...
Polypeptide: alpha-helix and beta
... Fibrous proteins are stringy, tough, and usually insoluble in water. Many fibrous proteins are involved with the structural parts of an organism. Alpha-keratin, the protein in hooves and fingernails and reptile scales, has an alpha-helix structure. Silk fibers of insects and spiders are fibrous prot ...
... Fibrous proteins are stringy, tough, and usually insoluble in water. Many fibrous proteins are involved with the structural parts of an organism. Alpha-keratin, the protein in hooves and fingernails and reptile scales, has an alpha-helix structure. Silk fibers of insects and spiders are fibrous prot ...
Essential amino acids
... Biosynthesis of nonessential amino acids TCA cycle member + amino acid α-keto acid + nonessential amino acid A source of energy (10%) ( CO2+H2O ) Glucogenesis and ketogenesis ...
... Biosynthesis of nonessential amino acids TCA cycle member + amino acid α-keto acid + nonessential amino acid A source of energy (10%) ( CO2+H2O ) Glucogenesis and ketogenesis ...
Episode 23 0 Proetin: Structure and Function
... 4. The video estimates that 100 billion proteins may exist. How can so many proteins form from just a few molecules? When amino acids are joined in different orders, different proteins result. 5. What is the name of the bond that results in the formation of proteins? Peptide bond 6. What are the nam ...
... 4. The video estimates that 100 billion proteins may exist. How can so many proteins form from just a few molecules? When amino acids are joined in different orders, different proteins result. 5. What is the name of the bond that results in the formation of proteins? Peptide bond 6. What are the nam ...
RCT Chapter 7
... – Interact with a variety of receptors from neighboring cells and regulate cell growth ...
... – Interact with a variety of receptors from neighboring cells and regulate cell growth ...
Protein Reading Questions Due Monday File
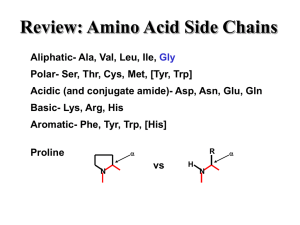
... 8. Explain the properties of the amino acid groups below, based on their R-group: a. Nonpolar side chains/Hydrophobic: b. Polar side chains/ Hydrophilic: c. Electrically charged side chains/Hydrophilic: 9. What are the bonds between amino acids in a polypeptide called AND what type of bond is it? ...
... 8. Explain the properties of the amino acid groups below, based on their R-group: a. Nonpolar side chains/Hydrophobic: b. Polar side chains/ Hydrophilic: c. Electrically charged side chains/Hydrophilic: 9. What are the bonds between amino acids in a polypeptide called AND what type of bond is it? ...
D6- Bulletin Board Powerful Protein
... • There are 9 essential amino acids that our bodies can’t make, so we need to get them from our food. • If a protein food has all 9 essential amino acids, it is called a complete protein. If it doesn’t, it is called an incomplete protein. • You can eat incomplete protein foods together to make sure ...
... • There are 9 essential amino acids that our bodies can’t make, so we need to get them from our food. • If a protein food has all 9 essential amino acids, it is called a complete protein. If it doesn’t, it is called an incomplete protein. • You can eat incomplete protein foods together to make sure ...
Center for Structural Biology
... Review: Heirarchy of Structure Primary- sequence Secondary- local Supersecondary (motifs)- intermediate Domains- independent folding units Tertiary- organization of a complete chain Quaternary- organization of multiple chains ...
... Review: Heirarchy of Structure Primary- sequence Secondary- local Supersecondary (motifs)- intermediate Domains- independent folding units Tertiary- organization of a complete chain Quaternary- organization of multiple chains ...
The Cold Never Bothered Me Anyway Measuring the Forces at Work
... identified in many organisms from various environments. This protein binds to nucleic acids when there is a drop in temperature and is thought to help maintain protein production. It has a highly conserved structure but small differences in the amino acid sequence of extremophilic Cold Shock protein ...
... identified in many organisms from various environments. This protein binds to nucleic acids when there is a drop in temperature and is thought to help maintain protein production. It has a highly conserved structure but small differences in the amino acid sequence of extremophilic Cold Shock protein ...
37151
... down flight path centered bw two rods •For given voltage, only certain m/z ions will reach detector ...
... down flight path centered bw two rods •For given voltage, only certain m/z ions will reach detector ...
Transient intracellular expression of chicken UCH-L3 and
... S1 Fig. Sequence alignment analysis of UCH-L3 and UCH-L5. The deduced amino acid sequences of UCH-L3 and UCH-L5 proteins cloned from HD11 cells were compared with sequences of UCH-L3 and UCH-L5 proteins from human, cow, mouse, rat, and chicken obtained from the GenBank database (http://www.ncbi.nlm. ...
... S1 Fig. Sequence alignment analysis of UCH-L3 and UCH-L5. The deduced amino acid sequences of UCH-L3 and UCH-L5 proteins cloned from HD11 cells were compared with sequences of UCH-L3 and UCH-L5 proteins from human, cow, mouse, rat, and chicken obtained from the GenBank database (http://www.ncbi.nlm. ...
Proteomics techniques used to identify proteins
... LC/MS/MS analysis and UniProt database search with “rigorous” filtering of the search results allow identification of three 14-3-3 regulatory proteins (zeta, theta, and sigma). ...
... LC/MS/MS analysis and UniProt database search with “rigorous” filtering of the search results allow identification of three 14-3-3 regulatory proteins (zeta, theta, and sigma). ...
Word Doc - Biochemistry
... Proteins are macromolecules (heteropolymers) made up from 20 different Lamino acids, also referred to as residues. Below about 40 residues the term peptide is frequently used. A certain number of residues is necessary to perform a particular biochemical function, and around 40-50 residues appears ...
... Proteins are macromolecules (heteropolymers) made up from 20 different Lamino acids, also referred to as residues. Below about 40 residues the term peptide is frequently used. A certain number of residues is necessary to perform a particular biochemical function, and around 40-50 residues appears ...
Chapter 5 – Proteins and Amino Acids
... 2. Amino Acid Composition 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetarian diets nutritionally sound? B. What should be my main concerns when planning a nutritionally sound vegetarian diet? C. Isn’t protein a problem in ...
... 2. Amino Acid Composition 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetarian diets nutritionally sound? B. What should be my main concerns when planning a nutritionally sound vegetarian diet? C. Isn’t protein a problem in ...
Chapter 6 questions
... 1. Identify the body's working proteins. 2. Identify the body's structural proteins. 3. What do proteins contain that carbohydrates and lipids do not? 4. _______________ are the building blocks of proteins. 5. What is an essential amino acid? How many are there? 6. What are proteins made of? Illustr ...
... 1. Identify the body's working proteins. 2. Identify the body's structural proteins. 3. What do proteins contain that carbohydrates and lipids do not? 4. _______________ are the building blocks of proteins. 5. What is an essential amino acid? How many are there? 6. What are proteins made of? Illustr ...
Protein Function Foldable Activity
... which provides the protective structures of our hair and nails. ...
... which provides the protective structures of our hair and nails. ...
... The Nobel Prize in Chemistry for 2004 is shared between three scientists who have made fundamental discoveries concerning how cells regulate the breakdown of intracellular proteins with extreme specificity as to target, time and space. Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin Rose together discove ...
Chapter 6: Protein 1. Identify the body's working proteins.
... 3. What do proteins contain that carbohydrates and lipids do not? 4. _______________ are the building blocks of proteins. 5. What is an essential amino acid? How many are there? 6. What are proteins made of? Illustrate an example. 7. Globular shaped proteins are __________ proteins and are _________ ...
... 3. What do proteins contain that carbohydrates and lipids do not? 4. _______________ are the building blocks of proteins. 5. What is an essential amino acid? How many are there? 6. What are proteins made of? Illustrate an example. 7. Globular shaped proteins are __________ proteins and are _________ ...
From the Cradle to the grave: molecular chaperones that may
... Chaperone-binding motifs found in Hsp70 and Hsp90 co-chaperones consist of a tandem arrangement of three degenerate 34 amino acid repeats-tetratricopeptide repeats, TPRs The Hsp70/Hsp90 organizing protein Hop contains multiple TPRs which allow it to bind to Hsp70 and Hsp90, and to promote the regula ...
... Chaperone-binding motifs found in Hsp70 and Hsp90 co-chaperones consist of a tandem arrangement of three degenerate 34 amino acid repeats-tetratricopeptide repeats, TPRs The Hsp70/Hsp90 organizing protein Hop contains multiple TPRs which allow it to bind to Hsp70 and Hsp90, and to promote the regula ...
MATERIAL DATA SHEET - Boston Biochem, Inc.
... MATERIAL DATA SHEET Methylated Ubiquitin-13C 15N, human recombinant Cat. # U-720 Isotopically labeled ubiquitin is useful in determining total cellular concentrations of ubiquitin, or determining the ratio of free- to substrate-bound ubiquitin using the protein standard absolute quantification (PSAQ ...
... MATERIAL DATA SHEET Methylated Ubiquitin-13C 15N, human recombinant Cat. # U-720 Isotopically labeled ubiquitin is useful in determining total cellular concentrations of ubiquitin, or determining the ratio of free- to substrate-bound ubiquitin using the protein standard absolute quantification (PSAQ ...
Protein misfolding associated to mild modifications of local cellular pH
... Protein misfolding associated to mild modifications of local cellular pH: Amyloid-like aggregation of human apolipoprotein A-I variants Ramella N., Tricerri M. A., Rimoldi O.J. INIBIOLP-CONICET. Fac. Ciencias Medicas, UNLP. Argentina The native folding of proteins is critical to fulfill their biolog ...
... Protein misfolding associated to mild modifications of local cellular pH: Amyloid-like aggregation of human apolipoprotein A-I variants Ramella N., Tricerri M. A., Rimoldi O.J. INIBIOLP-CONICET. Fac. Ciencias Medicas, UNLP. Argentina The native folding of proteins is critical to fulfill their biolog ...
Ubiquitin

Ubiquitin is a small (8.5 kDa) regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues (ubiquitously) of eukaryotic organisms. It was discovered in 1975 by Goldstein and further characterized throughout the 1970s and 1980s. There are four genes in the human genome that produce ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A.The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination or ubiquitylation. Ubiquitination can affect proteins in many ways: It can signal for their degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitination is carried out in three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade binds ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bond or to the amino group of the protein's N-terminus via a peptide bond.The protein modifications can be either a single ubiquitin protein (monoubiquitination) or a chain of ubiquitin (polyubiquitination). The ubiquitination bonds are always formed with one of the seven lysine residues from the ubiquitin molecule. These 'linking' lysines are represented by a ""K"" (which is the one-letter amino acid notation of lysine) and a number, referring to its position in the ubiquitin molecule. First, a ubiquitin molecule is bonded by its C-terminus to a specific lysine residue (e.g. K48, K29, K63,...) on the target protein. Poly-ubiquitination occurs when the C-terminus of another ubiquitin, will be linked again to a lysine residue (for example again K48 or K29) on the previously added ubiquitin molecule, forming a chain. This process repeats several times, leading to the addition of several ubiquitins. Only poly-ubiquitination on defined lysines, mostly on K48 and K29, is related to degradation with the proteasome (referred to as the ""molecular kiss of death""), while other polyubiquitinations (e.g. on K63, K11, K6) and monoubiquitinations may regulate processes such as endocytic trafficking, inflammation, translation and DNA repair.Lysine 48-linked chains have been much-studied. They are the forms of chains that signal proteins to the proteasome, which destroys and recycles proteins. This discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004.