Alcohols from Alkenes: Oxymercuration–Demercuration
... form of the starting material reacts in such a way that it gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product. ...
... form of the starting material reacts in such a way that it gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product. ...
Get Reprint - McMaster Chemistry
... alcohol, the proton transfer step is slower than that for complex formation is consistent with the small but clearly primary deuterium kinetic isotope effects that these two alcohols exhibit in their reactions with 1.17 The magnitudes of the Arrhenius activation energies indicate that the transition ...
... alcohol, the proton transfer step is slower than that for complex formation is consistent with the small but clearly primary deuterium kinetic isotope effects that these two alcohols exhibit in their reactions with 1.17 The magnitudes of the Arrhenius activation energies indicate that the transition ...
Chromatography Spectroscopy HW
... Phenol reacts readily with dilute nitric acid at room temperature in a nitration reaction to produce a mixture of products as shown below. OH ...
... Phenol reacts readily with dilute nitric acid at room temperature in a nitration reaction to produce a mixture of products as shown below. OH ...
Arenes HW
... Phenol reacts readily with dilute nitric acid at room temperature in a nitration reaction to produce a mixture of products as shown below. OH ...
... Phenol reacts readily with dilute nitric acid at room temperature in a nitration reaction to produce a mixture of products as shown below. OH ...
Reactions of Alcohols - John Carroll University
... • Ethers can be synthesized by the reaction of alkoxide ions with primary alkyl halides in what is known as the Williamson ether synthesis. • This is an SN2 displacement reaction and as such, works better with primary alkyl halides to facilitate back-side attack. • If a secondary or tertiary alkyl h ...
... • Ethers can be synthesized by the reaction of alkoxide ions with primary alkyl halides in what is known as the Williamson ether synthesis. • This is an SN2 displacement reaction and as such, works better with primary alkyl halides to facilitate back-side attack. • If a secondary or tertiary alkyl h ...
Ch 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I
... ketones to give a wide variety of alcohols • Examples: • Now, we examine a similar reaction that involves the addition of an organozinc reagent • This reaction extends the carbon skeleton of an aldehyde and ketones and yields a β-hydroxy ester ...
... ketones to give a wide variety of alcohols • Examples: • Now, we examine a similar reaction that involves the addition of an organozinc reagent • This reaction extends the carbon skeleton of an aldehyde and ketones and yields a β-hydroxy ester ...
10 bioenergetics 03
... methanogenesis is from proton translocation via electron transfer to the methyl group generated during metabolism. Methanogenesis = anaerobic methyl respiration ...
... methanogenesis is from proton translocation via electron transfer to the methyl group generated during metabolism. Methanogenesis = anaerobic methyl respiration ...
enzymatic And Limited Industrial Use
... A stereospecific reaction is one in which a single starting material yields only a single stereoisomer ...
... A stereospecific reaction is one in which a single starting material yields only a single stereoisomer ...
Mass Spec - Fragmentation
... 1. The relative height of the M+ peak is greatest for straightchain molecules and decreases as the branching increases. 2. The relative height of the M+ peak decreases with chain length for a homologous series. 3. Cleavage is favoured at alkyl-substituted carbons, with the probability of cleavage in ...
... 1. The relative height of the M+ peak is greatest for straightchain molecules and decreases as the branching increases. 2. The relative height of the M+ peak decreases with chain length for a homologous series. 3. Cleavage is favoured at alkyl-substituted carbons, with the probability of cleavage in ...
Chapter 10 Outline: Alcohols
... Alcohol Reactions. Provide correct organic product(s) and the mechanism for the following reactions. If stereochemistry pertains, ensure it is clearly demonstrated. If there is more than one product, then circle the major product. ...
... Alcohol Reactions. Provide correct organic product(s) and the mechanism for the following reactions. If stereochemistry pertains, ensure it is clearly demonstrated. If there is more than one product, then circle the major product. ...
Alcohols - City University of New York
... Increasing Basicity of Alkoxide Anion, the conjugate base Increasing Acidity of the alcohol Alkoxides can be produced in several ways… Recall: H2O + Na Na+ + OH- + ½ H2(g) ...
... Increasing Basicity of Alkoxide Anion, the conjugate base Increasing Acidity of the alcohol Alkoxides can be produced in several ways… Recall: H2O + Na Na+ + OH- + ½ H2(g) ...
Organometallic Compounds
... The next slides recall the diversity of nucleophiles that may be used. Observe that there is limited opportunity of creating new C-C bonds, welding together two R groups. We seem to be somewhat lacking in simple carbon based nucleophiles. ...
... The next slides recall the diversity of nucleophiles that may be used. Observe that there is limited opportunity of creating new C-C bonds, welding together two R groups. We seem to be somewhat lacking in simple carbon based nucleophiles. ...
Alkenes Key features sp -hybridized carbons, 120 bond angles
... Regioselectivity of reactions: Which side does the nucleophile end up? Some reactions favor reaction to occur with a particular orientation, where a given region of the molecule is more likely to participate in bond formation. This regioselectivity occurs with hydrogen halide addition to alkenes, s ...
... Regioselectivity of reactions: Which side does the nucleophile end up? Some reactions favor reaction to occur with a particular orientation, where a given region of the molecule is more likely to participate in bond formation. This regioselectivity occurs with hydrogen halide addition to alkenes, s ...
Exam 1 Review Sheet Chapter 15 Chemistry 110b
... syntheses using SN2 chemistry; ester syntheses using activated carbonyl groups. Mechanism of basic saponification of esters, use of isotopes to support mechanisms of acyl vs. alkyl attack, be aware of an example where alkyl attack is favored and why. Lactones-- know the relevant nomenclature, proper ...
... syntheses using SN2 chemistry; ester syntheses using activated carbonyl groups. Mechanism of basic saponification of esters, use of isotopes to support mechanisms of acyl vs. alkyl attack, be aware of an example where alkyl attack is favored and why. Lactones-- know the relevant nomenclature, proper ...
Origin of the Diastereoselection in the Indium
... In summary, the In-mediated addition reaction of the haloallylic sulfones 1 to aldehydes 2 efficiently produces the homoallylic alcohols 3 containing a homoallylic sulfone moiety, which are useful building blocks in organic synthesis. This reaction is highly anti-stereoselective (13:1) when the R1 s ...
... In summary, the In-mediated addition reaction of the haloallylic sulfones 1 to aldehydes 2 efficiently produces the homoallylic alcohols 3 containing a homoallylic sulfone moiety, which are useful building blocks in organic synthesis. This reaction is highly anti-stereoselective (13:1) when the R1 s ...
Mechanisms of Alkenes
... Base (must have a lone pair) and is called the “nucleophile”. • The electron-poor species is a Lewis Acid (must have empty orbital) and is called the “electrophile”. ...
... Base (must have a lone pair) and is called the “nucleophile”. • The electron-poor species is a Lewis Acid (must have empty orbital) and is called the “electrophile”. ...
Hmwk_4-09 Key
... b) Suggest how the Vo versus pH plots might look for [S]o >> KM and [S]o << KM (i.e., draw them). Explain your answer. You might have to make some assumptions about pKa values. If so, state them. Also, you may confine your comments to ionizations that occur on the enzyme (or ES complex) and ignore ...
... b) Suggest how the Vo versus pH plots might look for [S]o >> KM and [S]o << KM (i.e., draw them). Explain your answer. You might have to make some assumptions about pKa values. If so, state them. Also, you may confine your comments to ionizations that occur on the enzyme (or ES complex) and ignore ...
Substitution Reactions of Alcohols
... Substitution Reactions of Alcohols – Converting Alcohols to Alkyl Halides Sulfonate esters make good leaving groups because the pKa of their conjugate acids is ~-6.5, roughly the same as that for Cl-. As such, another strategy for making alcohols a better leaving group is to convert them into a hal ...
... Substitution Reactions of Alcohols – Converting Alcohols to Alkyl Halides Sulfonate esters make good leaving groups because the pKa of their conjugate acids is ~-6.5, roughly the same as that for Cl-. As such, another strategy for making alcohols a better leaving group is to convert them into a hal ...
Converting Alcohols to Alkyl Halides – The Mitsunobu Reaction
... Substitution Reactions of Alcohols – Converting Alcohols to Alkyl Halides Sulfonate esters make good leaving groups because the pKa of their conjugate acids is ~-6.5, roughly the same as that for Cl-. As such, another strategy for making alcohols a better leaving group is to convert them into a hal ...
... Substitution Reactions of Alcohols – Converting Alcohols to Alkyl Halides Sulfonate esters make good leaving groups because the pKa of their conjugate acids is ~-6.5, roughly the same as that for Cl-. As such, another strategy for making alcohols a better leaving group is to convert them into a hal ...
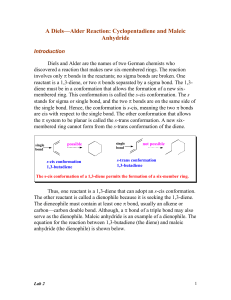
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
... discovered a reaction that makes new six-membered rings. The reaction involves only bonds in the reactants; no sigma bonds are broken. One reactant is a 1,3-diene, or two bonds separated by a sigma bond. The 1,3diene must be in a conformation that allows the formation of a new sixmembered ring. ...
... discovered a reaction that makes new six-membered rings. The reaction involves only bonds in the reactants; no sigma bonds are broken. One reactant is a 1,3-diene, or two bonds separated by a sigma bond. The 1,3diene must be in a conformation that allows the formation of a new sixmembered ring. ...
NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION & ELIMINATION ON Csp 3
... SN2 – putting it all (almost) together: - The substrate: 1o C (or, not so good, 2º C) - The nucleophile: good - The leaving group: low pKa of conjugate acid - The solvent: polar, aprotic (next slides) The reaction flow & the transition state: ...
... SN2 – putting it all (almost) together: - The substrate: 1o C (or, not so good, 2º C) - The nucleophile: good - The leaving group: low pKa of conjugate acid - The solvent: polar, aprotic (next slides) The reaction flow & the transition state: ...
CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I)
... ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: Laboratory Experiments by Schoffstall, Barbara and Melvin(2nd Edn) Learning Objectives: The principal objective of this course is to get familiar with the C compounds, their nomenclature, functional groups, structures, stereochemistry, their syntheses and reactions. The C compound ...
... ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: Laboratory Experiments by Schoffstall, Barbara and Melvin(2nd Edn) Learning Objectives: The principal objective of this course is to get familiar with the C compounds, their nomenclature, functional groups, structures, stereochemistry, their syntheses and reactions. The C compound ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... is chiral (in principle but not in practice): the lone pair of electrons is the fourth substituent Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N are not resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
... is chiral (in principle but not in practice): the lone pair of electrons is the fourth substituent Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N are not resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
Mechanism
... Industrial Application- An enantioselective aldol addition product can be obtained in asymmetric synthesis by reaction of benzaldehyde with nitromethane and the a catalyst system consisting of a zinc triflate salt / the base diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) and as chiral ligand is the N-methyl derivati ...
... Industrial Application- An enantioselective aldol addition product can be obtained in asymmetric synthesis by reaction of benzaldehyde with nitromethane and the a catalyst system consisting of a zinc triflate salt / the base diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) and as chiral ligand is the N-methyl derivati ...
11.Unit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes.
... Q3. When an alkyl halide is treated with ethanolic solution of KCN, the major product is alkylcyanide where as if alkyl halide is treated with AgCN, the major product is alkyl isocyanide. Ans. KCN is ionic they can attach through C or N but C-C bond is stronger than C-N bond. So RCN is major produc ...
... Q3. When an alkyl halide is treated with ethanolic solution of KCN, the major product is alkylcyanide where as if alkyl halide is treated with AgCN, the major product is alkyl isocyanide. Ans. KCN is ionic they can attach through C or N but C-C bond is stronger than C-N bond. So RCN is major produc ...
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement

The vinylcyclopropane rearrangement or vinylcyclopropane-cyclopentene rearrangement is a ring expansion reaction, converting a vinyl-substituted cyclopropane ring into a cyclopentene ring.Intense experimental as well as computational investigations have revealed that mechanistically, the vinylcyclopropane rearrangement can be thought of as either a diradical-mediated two-step and/or orbital-symmetry-controlled pericyclic process. The amount by which each of the two mechanisms is operative is highly dependent on the substrate.Due to its ability to form cyclopentene rings the vinylcyclopropane rearrangement has served several times as a key reaction in complex natural product synthesis.