COMMON SYNTHETIC SEQUENCES FOR OCHEM I
... take place in water as the medium, not in organic solvents like methylene chloride. Another difference is in the catalysis. In the vast majority of biological systems reactions are catalyzed by enzymes, which are organic macromolecules that have a high degree of specificity and precision. For exampl ...
... take place in water as the medium, not in organic solvents like methylene chloride. Another difference is in the catalysis. In the vast majority of biological systems reactions are catalyzed by enzymes, which are organic macromolecules that have a high degree of specificity and precision. For exampl ...
Week 10 Problem Set (Answers) (4/17, 4/18, 4/19) Reactions and
... The key transformation occurring is the breaking of the C2-N bond and the formation of the C6-O bond. There is an inversion of stereochem at the Br position, indicating an SN2 type reaction. A new pi bond is also made between C1-C2. This is a big clue. We know that we have to break the bond between ...
... The key transformation occurring is the breaking of the C2-N bond and the formation of the C6-O bond. There is an inversion of stereochem at the Br position, indicating an SN2 type reaction. A new pi bond is also made between C1-C2. This is a big clue. We know that we have to break the bond between ...
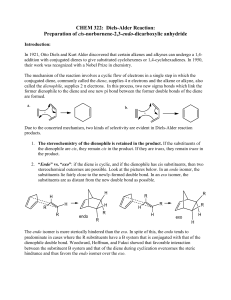
Diels-Alder Reaction:
... just a plain alkene (or alkyne), thus, they want electrons from the diene even more than a plain alkene (or alkyne). Even though s-trans conformation of dienes is more stable due to steric reasons, the s-cis conformation is needed to carry out the Diels-Alder reaction. The s-cis conformation of the ...
... just a plain alkene (or alkyne), thus, they want electrons from the diene even more than a plain alkene (or alkyne). Even though s-trans conformation of dienes is more stable due to steric reasons, the s-cis conformation is needed to carry out the Diels-Alder reaction. The s-cis conformation of the ...
Named Reactions Of Haloalkanes and haloarenes
... The reaction of joining two aromatic rings through –N=N- is known as coupling reaction. Arenediazonium salts react with phenols or aromatic amines to form ...
... The reaction of joining two aromatic rings through –N=N- is known as coupling reaction. Arenediazonium salts react with phenols or aromatic amines to form ...
Alkenes undergo Addition Reactions Predict the product of each
... 1. The growth hormone from the cecropia moth has the structure shown below. Express the stereochemistry of the double bonds according to the E-Z system. ...
... 1. The growth hormone from the cecropia moth has the structure shown below. Express the stereochemistry of the double bonds according to the E-Z system. ...
Arrows - Rutgers Chemistry
... each with a unique, specific meaning. The list below contains all the arrows that cost many 307 students valuable points. Be familiar with them and specific in their use. 1. The reaction arrow ...
... each with a unique, specific meaning. The list below contains all the arrows that cost many 307 students valuable points. Be familiar with them and specific in their use. 1. The reaction arrow ...
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides
... (which is not always the highest barrier) • This is the not the greatest difference but the absolute highest point (Figures 11.8 – the same step is rate-determining in both directions) ...
... (which is not always the highest barrier) • This is the not the greatest difference but the absolute highest point (Figures 11.8 – the same step is rate-determining in both directions) ...
T. V. RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed enolization, kinetic vs thermodynamic control Detailed mechanism of -substitution of a carbonyl compound (e. g., bromination) Ca ...
... Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed enolization, kinetic vs thermodynamic control Detailed mechanism of -substitution of a carbonyl compound (e. g., bromination) Ca ...
730-2005 topics
... Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed enolization, kinetic vs thermodynamic control Detailed mechanism of -substitution of a carbonyl compound (e. g., bromination) Ca ...
... Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed enolization, kinetic vs thermodynamic control Detailed mechanism of -substitution of a carbonyl compound (e. g., bromination) Ca ...
Lecture 14a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... (NMe2, NEt2): solution method works, but it is very slow; the microwave reaction is much faster The student has to be much more cautious ...
... (NMe2, NEt2): solution method works, but it is very slow; the microwave reaction is much faster The student has to be much more cautious ...
Chapter 14 Selenium reagents
... base, giving alkyl bromides: the overall reaction is ROH RBr with retention of configuration. • Aryl alkyl selenides are preparable either (as above) from electrophilic selenium reagents and carbon ncleophiles or from nucleophilic selenium reagents, e.g. ArSe-Na+, and carbon electrophiles. On oxidat ...
... base, giving alkyl bromides: the overall reaction is ROH RBr with retention of configuration. • Aryl alkyl selenides are preparable either (as above) from electrophilic selenium reagents and carbon ncleophiles or from nucleophilic selenium reagents, e.g. ArSe-Na+, and carbon electrophiles. On oxidat ...
Chemistry Crunch #12.2: Organic Reactions KEY Why? Learning
... 2. Describe what is going on between the molecules of pentene and hydrogen in this addition reaction. ...
... 2. Describe what is going on between the molecules of pentene and hydrogen in this addition reaction. ...
Microsoft Word
... generates a 2/1 mixture of bis- and mono-addition products whereas addition of excess iPrMgBr gives only the monoaddition product. This is presumably due to steric factors (quaternary center adjacent to the reaction site). Reduction of 2 (NaBH4/EtOH, rt. 2 h) produced the unsymmetrical 3,4-substitut ...
... generates a 2/1 mixture of bis- and mono-addition products whereas addition of excess iPrMgBr gives only the monoaddition product. This is presumably due to steric factors (quaternary center adjacent to the reaction site). Reduction of 2 (NaBH4/EtOH, rt. 2 h) produced the unsymmetrical 3,4-substitut ...
The Baylis–Hillman reaction is an organic reaction of an aldehyde
... The Henry Reaction is a base-catalyzed C-C bond-forming reaction between nitroalkanes and aldehydes or ketones. It is similar to the Aldol Addition, and also referred to as the Nitro Aldol Reaction. If acidic protons are available (i.e. when R = H), the products tend to eliminate water to give nitr ...
... The Henry Reaction is a base-catalyzed C-C bond-forming reaction between nitroalkanes and aldehydes or ketones. It is similar to the Aldol Addition, and also referred to as the Nitro Aldol Reaction. If acidic protons are available (i.e. when R = H), the products tend to eliminate water to give nitr ...
Exam 2
... Chern 24 2 (w 2016) exam #2B 1. (10 pts) Circle what is true about Substitution and elimination reactions. ...
... Chern 24 2 (w 2016) exam #2B 1. (10 pts) Circle what is true about Substitution and elimination reactions. ...
3672 been studied in detail by Kebarle, et al., who
... with both disulfides’ and peroxidess have been demonstrated to follow a mechanistically similar pathway. In direct analogy with these systems, the reaction of trimethyl phosphite with a sulfenate ester could, a priori, lead to the pentacoordinate phosphorane 1 and (or) the phosphonium salts 2-4 whic ...
... with both disulfides’ and peroxidess have been demonstrated to follow a mechanistically similar pathway. In direct analogy with these systems, the reaction of trimethyl phosphite with a sulfenate ester could, a priori, lead to the pentacoordinate phosphorane 1 and (or) the phosphonium salts 2-4 whic ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed enolization, kinetic vs thermodynamic control Detailed mechanism of -substitution of a carbonyl compound (e. g., bromination) Car ...
... Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed enolization, kinetic vs thermodynamic control Detailed mechanism of -substitution of a carbonyl compound (e. g., bromination) Car ...
Topic 8 Assessed Homework Task - A
... Ethanol is an important fuel. A dilute aqueous solution of ethanol can be produced by the fermentation of an aqueous solution of glucose. It is claimed that the ethanol obtained from this solution is a carbon-neutral biofuel. Write an equation for this fermentation reaction. Give two other essential ...
... Ethanol is an important fuel. A dilute aqueous solution of ethanol can be produced by the fermentation of an aqueous solution of glucose. It is claimed that the ethanol obtained from this solution is a carbon-neutral biofuel. Write an equation for this fermentation reaction. Give two other essential ...
Chapter 9-Additions to Alkenes I
... σ bond. As a result it can act as a nucleophile towards various electrophilic species. When a C=C π bond acts as a nucleophile, one of the C atoms takes the π electrons away from the other C and uses them to make a bond to the electrophile. The other C atom either ...
... σ bond. As a result it can act as a nucleophile towards various electrophilic species. When a C=C π bond acts as a nucleophile, one of the C atoms takes the π electrons away from the other C and uses them to make a bond to the electrophile. The other C atom either ...
Classification of Halogen Derivatives
... kCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution, which is ambident nucleophile and bind with carbon side to form as the major product, while AgCN is covalent and form isocyanide as the major product. Like KCN, KNO2 form R-ONO while AgNO2 produces R-NO2 as product. Vinyl chloride is ...
... kCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution, which is ambident nucleophile and bind with carbon side to form as the major product, while AgCN is covalent and form isocyanide as the major product. Like KCN, KNO2 form R-ONO while AgNO2 produces R-NO2 as product. Vinyl chloride is ...
Lecture #
... Other nucleophiles for conjugate additions: organocuprates, thiols Conjugate additions of enolates: Michael reaction and Robinson annulation (again) Mechanism clinic: acetylcholinesterase ...
... Other nucleophiles for conjugate additions: organocuprates, thiols Conjugate additions of enolates: Michael reaction and Robinson annulation (again) Mechanism clinic: acetylcholinesterase ...
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 21 – Phenoles and Aryl
... – These compounds serve to transport electrons between substrates in enzyme-catalyzed oxidation-reduction reactions ...
... – These compounds serve to transport electrons between substrates in enzyme-catalyzed oxidation-reduction reactions ...
Study_guide_2010-01
... Other nucleophiles for conjugate additions: organocuprates, thiols Conjugate additions of enolates: Michael reaction and Robinson annulation (again) Mechanism clinic: acetylcholinesterase ...
... Other nucleophiles for conjugate additions: organocuprates, thiols Conjugate additions of enolates: Michael reaction and Robinson annulation (again) Mechanism clinic: acetylcholinesterase ...
Organic Reactions
... 1. To what class of organic compounds does reactant 1 belong? 2. To what class of organic compounds does reactant 2 belong? 3. To what class of organic compounds does the product (not water) belong? ...
... 1. To what class of organic compounds does reactant 1 belong? 2. To what class of organic compounds does reactant 2 belong? 3. To what class of organic compounds does the product (not water) belong? ...
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement

The vinylcyclopropane rearrangement or vinylcyclopropane-cyclopentene rearrangement is a ring expansion reaction, converting a vinyl-substituted cyclopropane ring into a cyclopentene ring.Intense experimental as well as computational investigations have revealed that mechanistically, the vinylcyclopropane rearrangement can be thought of as either a diradical-mediated two-step and/or orbital-symmetry-controlled pericyclic process. The amount by which each of the two mechanisms is operative is highly dependent on the substrate.Due to its ability to form cyclopentene rings the vinylcyclopropane rearrangement has served several times as a key reaction in complex natural product synthesis.