Atomic Number
... 2. Electrical charges are carried by matter 3. Electrical charges always exist in whole numbers 4. # of negatively charged particles = # of positively charged particles = neutral atom ...
... 2. Electrical charges are carried by matter 3. Electrical charges always exist in whole numbers 4. # of negatively charged particles = # of positively charged particles = neutral atom ...
Matter – Properties and Changes
... the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that element. Chemists have taken samples of the different isotopes of a given element, for example Potassium-39, Potassium40, and Potassium-41, and have averaged the masses to determine atomic mass. That is different from mass number, which is the mass o ...
... the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that element. Chemists have taken samples of the different isotopes of a given element, for example Potassium-39, Potassium40, and Potassium-41, and have averaged the masses to determine atomic mass. That is different from mass number, which is the mass o ...
File
... Mass Number Mass number: (symbol: A) total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus (not listed on the periodic table, since it varies). NOTE this number is a whole number. Atomic Mass is different. Atoms of the same element have the same atomic number, but may have different mass numbers. ...
... Mass Number Mass number: (symbol: A) total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus (not listed on the periodic table, since it varies). NOTE this number is a whole number. Atomic Mass is different. Atoms of the same element have the same atomic number, but may have different mass numbers. ...
How many protons, electrons and neutrons are in an atom of krypton
... electrons from an atom does not change which element it is, just its net charge. For example, removing an electron from an atom of krypton forms a krypton ion, which is usually written as Kr+. The plus sign means that this is a positively charged ion. It is positively charged because a negatively ch ...
... electrons from an atom does not change which element it is, just its net charge. For example, removing an electron from an atom of krypton forms a krypton ion, which is usually written as Kr+. The plus sign means that this is a positively charged ion. It is positively charged because a negatively ch ...
Example of calculating average atomic mass
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. ...
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. ...
What is an atom?
... Neils Bohr devised a method for drawing models to represent the atoms nucleus and their electron arrangement because the atoms are too small to see. These models are easy to draw – if you follow the steps! ...
... Neils Bohr devised a method for drawing models to represent the atoms nucleus and their electron arrangement because the atoms are too small to see. These models are easy to draw – if you follow the steps! ...
Date
... Elements forming one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. A positively or negatively charged atom due to gain or loss of electrons. One of two or more atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to more or less neutrons. There are 275 isotopes of the 81 stable elemen ...
... Elements forming one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. A positively or negatively charged atom due to gain or loss of electrons. One of two or more atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to more or less neutrons. There are 275 isotopes of the 81 stable elemen ...
Atom
... • Each element has a unique name and symbol. • All of this data, and more, are collected in an organized table called the periodic table of elements. ...
... • Each element has a unique name and symbol. • All of this data, and more, are collected in an organized table called the periodic table of elements. ...
atom
... and other properties. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. ...
... and other properties. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductors? G 7. Which elements are considered poor conductors? F, B, A,H 8. Which element is considered met ...
... H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductors? G 7. Which elements are considered poor conductors? F, B, A,H 8. Which element is considered met ...
11129_evl_ch1_ste_corr
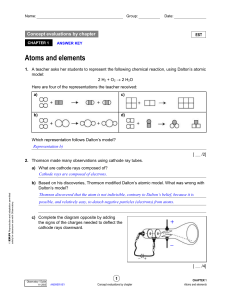
... d) Based on his discoveries, Rutherford modified Thomson’s atomic model. What was wrong with Thomson’s model? The deflection of some alpha particles indicated that they had struck an object that was both dense and positively charged—an idea that did not fit with the image of a “positive dough” in Th ...
... d) Based on his discoveries, Rutherford modified Thomson’s atomic model. What was wrong with Thomson’s model? The deflection of some alpha particles indicated that they had struck an object that was both dense and positively charged—an idea that did not fit with the image of a “positive dough” in Th ...
Prior knowledge catch-up student sheet for Chapter 3 Quantitative
... For example, the atomic number of sodium is 11 and the mass number is 23. Number of protons = 11 Number of electrons = 11 Number of neutrons = 23 − 11 = 12 Chemical reactions can be represented using a formula to show reactants and products in a chemical equation, with an arrow in between. An equati ...
... For example, the atomic number of sodium is 11 and the mass number is 23. Number of protons = 11 Number of electrons = 11 Number of neutrons = 23 − 11 = 12 Chemical reactions can be represented using a formula to show reactants and products in a chemical equation, with an arrow in between. An equati ...
The Atom
... what is the charge of the resulting ion? 2) How many electrons would be found in the ion O2-? 3) If an ion has 28 protons and 26 electrons, what is its charge? What is its symbol (including charge)? ...
... what is the charge of the resulting ion? 2) How many electrons would be found in the ion O2-? 3) If an ion has 28 protons and 26 electrons, what is its charge? What is its symbol (including charge)? ...
THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... • When dealing with the masses of atoms, we are dealing with extremely small numbers. • Because of these extremely small masses are very difficult to deal with chemists have developed a method of measuring the mass of an atom relative to the mass of a specific standard. • Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – de ...
... • When dealing with the masses of atoms, we are dealing with extremely small numbers. • Because of these extremely small masses are very difficult to deal with chemists have developed a method of measuring the mass of an atom relative to the mass of a specific standard. • Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – de ...
Atomic Number
... Protons and neutrons are responsible for most of the atomic mass of an atom, while electrons contribute a very small amount of mass(9.108 X 10-28 grams). ...
... Protons and neutrons are responsible for most of the atomic mass of an atom, while electrons contribute a very small amount of mass(9.108 X 10-28 grams). ...
Atomic Structure and Elements
... Neils Bohr devised a method for drawing models to represent the atoms nucleus and their electron arrangement because the atoms are too small to see. These models are easy to draw – if you follow the steps! ...
... Neils Bohr devised a method for drawing models to represent the atoms nucleus and their electron arrangement because the atoms are too small to see. These models are easy to draw – if you follow the steps! ...
atoms - Somerset Academy Silver Palms Middle/High
... properties as he arrange elements by atomic mass. 2. Elements were rearranged by atomic number after the proton was discovered. 3. The properties of an element can be predicted from its location in the periodic table. 4. Each horizontal row of the table is called a period. 5. The elements in a colum ...
... properties as he arrange elements by atomic mass. 2. Elements were rearranged by atomic number after the proton was discovered. 3. The properties of an element can be predicted from its location in the periodic table. 4. Each horizontal row of the table is called a period. 5. The elements in a colum ...
Chapter 11 section 2 questions - the atom
... Electrons are the negatively charged particles found in the energy levels that surround the nucleus - this like the rings on a target! Electrons have a VERY small mass - almost inconsequential to the atomic mass. Electrons carry a negative charge and are held in place by the positively charged proto ...
... Electrons are the negatively charged particles found in the energy levels that surround the nucleus - this like the rings on a target! Electrons have a VERY small mass - almost inconsequential to the atomic mass. Electrons carry a negative charge and are held in place by the positively charged proto ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.