Nuclear chemistry – the study of nuclear reactions and their uses in
... All spontaneous nuclear reactions are exothermic. The masses of nuclei are always less than the masses of the individual nucleons of which they are composed. i. Helium-4 (2protons, 2 neutrons, 2 electrons) has a mass of 4.00150 amu ii. The mass of 2 protons and 2 neutrons is 4.03188 amu. 1. The mass ...
... All spontaneous nuclear reactions are exothermic. The masses of nuclei are always less than the masses of the individual nucleons of which they are composed. i. Helium-4 (2protons, 2 neutrons, 2 electrons) has a mass of 4.00150 amu ii. The mass of 2 protons and 2 neutrons is 4.03188 amu. 1. The mass ...
Achievement Scale - Mayfield City Schools
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: The student: Can state the timeline associated with the key theories or experiments associated with Dalton, Rutherford, Thomson, and Bo ...
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: The student: Can state the timeline associated with the key theories or experiments associated with Dalton, Rutherford, Thomson, and Bo ...
Atomic Structure Notes Blank
... c. Very dense (Extremely small % of total volume of atom, BUT 99.97% of its _________) 2. Outside nucleus a. 99.9% of atom is this empty space through which the _____________ travel. b. Overall __________________ charge C. How they fit together 1. Electrons are held within the atom due to their attr ...
... c. Very dense (Extremely small % of total volume of atom, BUT 99.97% of its _________) 2. Outside nucleus a. 99.9% of atom is this empty space through which the _____________ travel. b. Overall __________________ charge C. How they fit together 1. Electrons are held within the atom due to their attr ...
The Modern View of Atomic Structure
... Because in the real world we use large amounts of atoms and molecules, we use average masses in calculations. Average mass is calculated from the isotopes of an element weighted by their relative abundances. ...
... Because in the real world we use large amounts of atoms and molecules, we use average masses in calculations. Average mass is calculated from the isotopes of an element weighted by their relative abundances. ...
03 PowerPoint
... mass number (A) - sum of the protons and neutrons in a nucleus this number is rounded from atomic mass due to the fact that there are isotopes # neutrons = A - Z example - # of neutrons in Li = 6.941-3 = 3.941 rounds to 4 Ion – a charged atom. Atoms become charged by gaining electrons (become a nega ...
... mass number (A) - sum of the protons and neutrons in a nucleus this number is rounded from atomic mass due to the fact that there are isotopes # neutrons = A - Z example - # of neutrons in Li = 6.941-3 = 3.941 rounds to 4 Ion – a charged atom. Atoms become charged by gaining electrons (become a nega ...
Intro to Chemistry
... available for interaction with other atoms. As a result, they behave in similar ways. Any elements after atomic number 92 are extremely unstable. ...
... available for interaction with other atoms. As a result, they behave in similar ways. Any elements after atomic number 92 are extremely unstable. ...
Atomic Structure Power Point File
... • The mass of each is approximately 1,836 times greater than the mass of the electron. • Electrons are so small they do not contribute to the atomic mass ...
... • The mass of each is approximately 1,836 times greater than the mass of the electron. • Electrons are so small they do not contribute to the atomic mass ...
Ions - amyschaefer24
... element but have different masses. •Atoms that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. •Why doesn’t an isotope form if we change the number of protons? ...
... element but have different masses. •Atoms that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. •Why doesn’t an isotope form if we change the number of protons? ...
Document
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
Chpt. 5 Study Guide for Fall Final
... 6) Who was the first person to suggest the idea of atoms, in the fourth century B. C.? A) Democritus B ) Dalton C) Thomson D) Galileo E) Atomos 7) What particles form the nucleus of an atom? A) neutrons and electrons B ) protons and neutrons C) protons and electrons D) electrons only E) None of the ...
... 6) Who was the first person to suggest the idea of atoms, in the fourth century B. C.? A) Democritus B ) Dalton C) Thomson D) Galileo E) Atomos 7) What particles form the nucleus of an atom? A) neutrons and electrons B ) protons and neutrons C) protons and electrons D) electrons only E) None of the ...
Atom
... determines atom’s chemical properties participate in chemical bonding Every atom has between one and eight ...
... determines atom’s chemical properties participate in chemical bonding Every atom has between one and eight ...
CMC Chapter 04
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
Chapter 4 power point notes
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
ch 4 ppt - Madison County Schools
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
Chapter 4 PPT
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
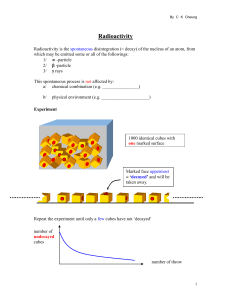
Radioactivity
... By measuring the activity of some furniture from an ancient village age of the furniture can be estimated within the range of 1000 to 5000 years. ...
... By measuring the activity of some furniture from an ancient village age of the furniture can be estimated within the range of 1000 to 5000 years. ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... γ has no mass ( ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
... γ has no mass ( ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
electrons = # protons
... This energy is seen as light. While the light appears as one color, it is actually composed of many different wavelengths, each of which is seen as a different line when viewed through an instrument called a spectroscope. ...
... This energy is seen as light. While the light appears as one color, it is actually composed of many different wavelengths, each of which is seen as a different line when viewed through an instrument called a spectroscope. ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.