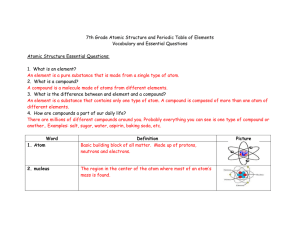
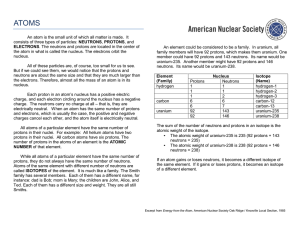
1.2--NOTES--Basic Atomic Structure
... • neutron number varies with the type of isotope (more on this later) • electron number is the same as proton number for uncharged (neutral) atoms (also, more on this later) Part II: Atomic Structure • the atom has two distinct areas: the nucleus and the electron cloud. • nucleus = center of the ato ...
... • neutron number varies with the type of isotope (more on this later) • electron number is the same as proton number for uncharged (neutral) atoms (also, more on this later) Part II: Atomic Structure • the atom has two distinct areas: the nucleus and the electron cloud. • nucleus = center of the ato ...
Atomic Nature of Matter
... Nuclides are atoms that contain a particular number of protons and neutrons. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in the nucleus. The mass number of an at ...
... Nuclides are atoms that contain a particular number of protons and neutrons. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in the nucleus. The mass number of an at ...
Atom - Perry Local Schools
... positions. In contrast, Rutherford's model states that an atom is mostly empty space, with a small, dense, central nucleus containing all of an atom's positive charge and most of its mass. The negatively charged electrons move through the empty space and are held in the atom by their attraction to t ...
... positions. In contrast, Rutherford's model states that an atom is mostly empty space, with a small, dense, central nucleus containing all of an atom's positive charge and most of its mass. The negatively charged electrons move through the empty space and are held in the atom by their attraction to t ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... number of 53. Determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an atom of this isotope and write its symbol. 2) The other three naturally occurring isotopes of chromium have mass number of 50, 52, and 54. Describe how atoms of these isotopes differ from the isotope mentioned in example ...
... number of 53. Determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an atom of this isotope and write its symbol. 2) The other three naturally occurring isotopes of chromium have mass number of 50, 52, and 54. Describe how atoms of these isotopes differ from the isotope mentioned in example ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass,and other properties. Atoms of different elements are different. Atoms cannot be subdivided, ...
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass,and other properties. Atoms of different elements are different. Atoms cannot be subdivided, ...
Atomic Concepts and Nuclear Chemistry Regents Review Page 1 A
... 67. Explain why the U-238 disintegration series ends with the nuclide Pb-206. 68. Based on this graph, what particle is emitted during the nuclear decay of a Po-218 atom? ...
... 67. Explain why the U-238 disintegration series ends with the nuclide Pb-206. 68. Based on this graph, what particle is emitted during the nuclear decay of a Po-218 atom? ...
Chapter 4
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass, & chemical properties. Atoms of a specific element are different from those of any other element Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, or destro ...
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass, & chemical properties. Atoms of a specific element are different from those of any other element Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, or destro ...
Multiple Choice Questions
... (3) unstable nuclei emit alpha particles (4) unstable nuclei emit beta particles 8. Alpha particles are emitted during the radioactive decay of (1) carbon-14 (2) neon-19 (3) calcium-37 ...
... (3) unstable nuclei emit alpha particles (4) unstable nuclei emit beta particles 8. Alpha particles are emitted during the radioactive decay of (1) carbon-14 (2) neon-19 (3) calcium-37 ...
isotopes
... neutrons does sodium-23 have? Why is a magnesium-24 atom magnesium and why is a sodium-23 atom sodium? ...
... neutrons does sodium-23 have? Why is a magnesium-24 atom magnesium and why is a sodium-23 atom sodium? ...
Concepts to know for the Unit 3 test
... 6. Use the periodic table to correlate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. a. Atomic number: Number of protons b. Mass number: Number of protons + number of neutrons c. Number of electrons: Same as # of protons in neutral atom a. # Electrons > # Protons NEGATIVE charge b. # ...
... 6. Use the periodic table to correlate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. a. Atomic number: Number of protons b. Mass number: Number of protons + number of neutrons c. Number of electrons: Same as # of protons in neutral atom a. # Electrons > # Protons NEGATIVE charge b. # ...
Build an Atom - Sterlingwikisci
... 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of __________________. 3. Adding or removing protons from an atom does what to the atom? _________________________________. 4. An atom with the same number of protons and electrons has a charge of _________. 5. Adding two electrons to ...
... 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of __________________. 3. Adding or removing protons from an atom does what to the atom? _________________________________. 4. An atom with the same number of protons and electrons has a charge of _________. 5. Adding two electrons to ...
Unit 3 Notes only
... 1) Explain how the following terms are related – Atomic number and proton – the atomic number tells you how many protons there are in an element – Isotope and neutron – isotopes are based on different number of neutrons – Electrons and energy levels – electrons are found in energy levels. Energy l ...
... 1) Explain how the following terms are related – Atomic number and proton – the atomic number tells you how many protons there are in an element – Isotope and neutron – isotopes are based on different number of neutrons – Electrons and energy levels – electrons are found in energy levels. Energy l ...
Name Date: __ ______ Chemistry Semester I Final Exam Review
... The columns on the periodic table are called ________________. 36. Write the correct charge and name for the following ions. ...
... The columns on the periodic table are called ________________. 36. Write the correct charge and name for the following ions. ...
Notes for the Structure of Atoms (Chapter 4, Sect
... change but atomic number increases by one, causing the atom to change to a different element. 3. What happens during alpha decay? – mass number and atomic number change C. half-life The time it takes for half of a sample of a radioactive isotope to break down by radioactive decay. Can be a nanosecon ...
... change but atomic number increases by one, causing the atom to change to a different element. 3. What happens during alpha decay? – mass number and atomic number change C. half-life The time it takes for half of a sample of a radioactive isotope to break down by radioactive decay. Can be a nanosecon ...
Atomic structure packets
... 1. Three isotopes of argon occur in nature – Argon-36, Argon-38, and Argon-40. Calculate the average atomic mass of argon to two decimal places, given the following relative atomic masses and abundances of each of the isotopes: argon-36 (35.97 amu; 0.337%), argon-38 (37.96 amu; 0.063%), and argon-40 ...
... 1. Three isotopes of argon occur in nature – Argon-36, Argon-38, and Argon-40. Calculate the average atomic mass of argon to two decimal places, given the following relative atomic masses and abundances of each of the isotopes: argon-36 (35.97 amu; 0.337%), argon-38 (37.96 amu; 0.063%), and argon-40 ...
atomic mass
... Mass number can be estimated from the atomic mass by rounding to the nearest integer. ...
... Mass number can be estimated from the atomic mass by rounding to the nearest integer. ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.