File
... Daltons atomic theory was based on the following hypotheses : 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other ele ...
... Daltons atomic theory was based on the following hypotheses : 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other ele ...
Atomic Structure
... • The smallest part of an element is an _____________________ • All atoms consist of subatomic particles: – ________________ – ________________ – ________________ ...
... • The smallest part of an element is an _____________________ • All atoms consist of subatomic particles: – ________________ – ________________ – ________________ ...
Nuclear Chemistry - HCC Learning Web
... • A different unit is used for measuring the biological effects of radiation because the effects depend on the type and energy of the radiation • The sievert (Sv) is the SI unit of dose equivalent, H • The dose equivalent (in Sv) is a product of the absorbed dose (D) from some radiation source time ...
... • A different unit is used for measuring the biological effects of radiation because the effects depend on the type and energy of the radiation • The sievert (Sv) is the SI unit of dose equivalent, H • The dose equivalent (in Sv) is a product of the absorbed dose (D) from some radiation source time ...
isotopes - LCC1050
... • There in a short chapter (5 pages out of 900) in a book entitled A New System of Chemical Philosophy, Dalton established his reputation. ...
... • There in a short chapter (5 pages out of 900) in a book entitled A New System of Chemical Philosophy, Dalton established his reputation. ...
25 NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY NOTES __ /__ pts
... Directions: Use 100 pennies or other two sided object. Pick one side as radioactive and the other as non-radioactive. Put all the objects into a container and shake. Spread them out without adjusting sides. Pick out all the non-radioactive atoms and put the remaining “radioactive” atoms in the conta ...
... Directions: Use 100 pennies or other two sided object. Pick one side as radioactive and the other as non-radioactive. Put all the objects into a container and shake. Spread them out without adjusting sides. Pick out all the non-radioactive atoms and put the remaining “radioactive” atoms in the conta ...
February Valentine`s Day-10, 2010
... Like your social security number or a professional athlete’s jersey number, it identifies that element ...
... Like your social security number or a professional athlete’s jersey number, it identifies that element ...
9.3 Atoms and Elements notes
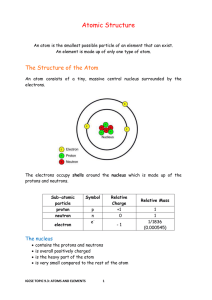
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
1. Structure and Properties of the Atom
... 19 electrons, should have an electronic configuration of 2 8 9. This, however would mean that the valence shell contains more than eight electrons. Therefore once the M shell contains the stable number of eight electrons, the next electron enters the N shell resulting in the configuration 2 8 8 1 fo ...
... 19 electrons, should have an electronic configuration of 2 8 9. This, however would mean that the valence shell contains more than eight electrons. Therefore once the M shell contains the stable number of eight electrons, the next electron enters the N shell resulting in the configuration 2 8 8 1 fo ...
Matter-Atoms PPT
... becomes positively charged (because the number of positively charged protons will be more the number of electrons) ...
... becomes positively charged (because the number of positively charged protons will be more the number of electrons) ...
Atom - Perry Local Schools
... -atom is mostly empty space through which electrons move -most of atom's positive charge and almost all of its mass were contained in a tiny dense region in the center of the atom-called the nucleus -negative particles are held within the atom by their attraction to positive nucleus Nucleus is very ...
... -atom is mostly empty space through which electrons move -most of atom's positive charge and almost all of its mass were contained in a tiny dense region in the center of the atom-called the nucleus -negative particles are held within the atom by their attraction to positive nucleus Nucleus is very ...
The Periodic Table - River Dell Regional School District
... (isotopes) 3. Not all atoms of an element have the same mass, but they all have a definite average mass which is characteristic. (isotopes) ...
... (isotopes) 3. Not all atoms of an element have the same mass, but they all have a definite average mass which is characteristic. (isotopes) ...
Science Notes September 09/06/2016
... Dalton expanded into elements classification chart called periodic table with different masses & properties …Everything may be split into atoms (smallest particles) & compounds – combinations of elements JJ Thomson experimented with rays/beams of light to determine - electrons hold negative charge - ...
... Dalton expanded into elements classification chart called periodic table with different masses & properties …Everything may be split into atoms (smallest particles) & compounds – combinations of elements JJ Thomson experimented with rays/beams of light to determine - electrons hold negative charge - ...
Ch. 5 Atomic Structure
... You don’t need to write. John Dalton (1766-1844), was an English schoolteacher. Performed experiments to test his atomic theory. ...
... You don’t need to write. John Dalton (1766-1844), was an English schoolteacher. Performed experiments to test his atomic theory. ...
What do I know about……
... minute (min), second (s) describe the structure of an atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and use symbols to describe particular nuclei understand the terms atomic (proton) number, mass (nucleon) number and isotope understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising rad ...
... minute (min), second (s) describe the structure of an atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and use symbols to describe particular nuclei understand the terms atomic (proton) number, mass (nucleon) number and isotope understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising rad ...
The discovery of the electron
... • Atoms are charged neutral. • The discovery of electron raised a question about the presence of a positive charge, to neutralize the negative charge of the electron. ...
... • Atoms are charged neutral. • The discovery of electron raised a question about the presence of a positive charge, to neutralize the negative charge of the electron. ...
ATOMS review
... What did Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr all have in common? • A. They each identified new elements. • B. They each identified new isotopes of atoms. • C. They each discovered something about what we know about atoms today. • D. They each were born in Greece.. ...
... What did Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr all have in common? • A. They each identified new elements. • B. They each identified new isotopes of atoms. • C. They each discovered something about what we know about atoms today. • D. They each were born in Greece.. ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.