Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... – Calculate the number of neutrons in an atom. – Calculate the atomic mass of an element. – Explain why chemists use the periodic ...
... – Calculate the number of neutrons in an atom. – Calculate the atomic mass of an element. – Explain why chemists use the periodic ...
Document
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
... positively charged particles in the nucleus called protons. • James Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935 for discovering the existence of neutrons, neutral particles in the nucleus which accounts for the remainder of an atom’s mass. ...
Atomic Structure Atomic_Structure
... 1. What is meant when an atom is said to be in its ground state? CORRECT: The state an atom is found naturally. 3. The subatomic particle(s) found in the nucleus of an atom are CORRECT: protons and neutrons. 5. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy an atomic orbital? CORRECT: 2, 6 ...
... 1. What is meant when an atom is said to be in its ground state? CORRECT: The state an atom is found naturally. 3. The subatomic particle(s) found in the nucleus of an atom are CORRECT: protons and neutrons. 5. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy an atomic orbital? CORRECT: 2, 6 ...
Makeup of Atoms - chemmybear.com
... isotopes. This mass is due to the protons and neutrons. The number of neutrons is the mass number - the atomic number. 33 - 16 = 17 neutrons. Since the charge is 2-, there are 2 more electrons than protons. In this case, there are 18 electrons. ...
... isotopes. This mass is due to the protons and neutrons. The number of neutrons is the mass number - the atomic number. 33 - 16 = 17 neutrons. Since the charge is 2-, there are 2 more electrons than protons. In this case, there are 18 electrons. ...
Unit 2 Spiraling
... Read Pages 401-403 in the textbook. Answer Questions 21-25 on page 404. Read Pages 520-523 in the textbook. Answer Questions a, b, and c on page 523 Interpreting Graphs ...
... Read Pages 401-403 in the textbook. Answer Questions 21-25 on page 404. Read Pages 520-523 in the textbook. Answer Questions a, b, and c on page 523 Interpreting Graphs ...
Structure of Atoms
... Quarks are the tiniest subatomic particles that make up protons and neutrons There are three quarks in every proton and three quarks in every neutron There are six different kinds of quarks (copy into notes) ...
... Quarks are the tiniest subatomic particles that make up protons and neutrons There are three quarks in every proton and three quarks in every neutron There are six different kinds of quarks (copy into notes) ...
Structure of Atoms
... Quarks are the tiniest subatomic particles that make up protons and neutrons There are three quarks in every proton and three quarks in every neutron There are six different kinds of quarks (copy into notes) ...
... Quarks are the tiniest subatomic particles that make up protons and neutrons There are three quarks in every proton and three quarks in every neutron There are six different kinds of quarks (copy into notes) ...
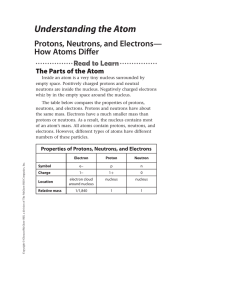
Understanding the Atom
... You can determine any one of these three quantities if you know the value of the other two quantities. For example, to determine the mass number of an atom, you must know the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the atom. The mass numbers of the isotopes of carbon are shown in the table a ...
... You can determine any one of these three quantities if you know the value of the other two quantities. For example, to determine the mass number of an atom, you must know the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the atom. The mass numbers of the isotopes of carbon are shown in the table a ...
Chapter 16 - Structure of an Atom - from class 4/13/15
... 1. protons 2. neutrons 3. electrons nucleus -- core of the atom, it is positively charged. 99.9 % of the atoms mass is in the nucleus. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus. Label the nucleus on your diagram. ...
... 1. protons 2. neutrons 3. electrons nucleus -- core of the atom, it is positively charged. 99.9 % of the atoms mass is in the nucleus. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus. Label the nucleus on your diagram. ...
C. - Taylor County Schools
... • Almost all of the atom's positive charge and almost all of its mass is contained in a dense region in the center of the atom called the nucleus. • Electrons are held within the atom by their attraction to the positively charged nucleus. ...
... • Almost all of the atom's positive charge and almost all of its mass is contained in a dense region in the center of the atom called the nucleus. • Electrons are held within the atom by their attraction to the positively charged nucleus. ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
Decommissioning a nuclear reactor
... the half-life and is characteristic of that particular radionuclide. For example, the half-life of radium is about 1600 years, so 1 g of radium decays to 0.5 g in 1600 years and to 0.25 g in 3200 years. Of course the radium does not disappear — it changes into its daughter products. The total mass d ...
... the half-life and is characteristic of that particular radionuclide. For example, the half-life of radium is about 1600 years, so 1 g of radium decays to 0.5 g in 1600 years and to 0.25 g in 3200 years. Of course the radium does not disappear — it changes into its daughter products. The total mass d ...
Topic 1 – Atomic structure and the periodic table
... o sometimes broke the ‘increasing atomic mass rule’ e.g he switched tellurium and iodine around so that they would be in the same groups as elements with similar properties (i.e by switching them, iodine was next to bromine, chlorine, fluorine…) o realised from the big jumps in atomic mass that th ...
... o sometimes broke the ‘increasing atomic mass rule’ e.g he switched tellurium and iodine around so that they would be in the same groups as elements with similar properties (i.e by switching them, iodine was next to bromine, chlorine, fluorine…) o realised from the big jumps in atomic mass that th ...
atomic number - s3.amazonaws.com
... Nuclear Fission A chain reaction is a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction. The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons needed to sustain a chain reaction is called the critical mass. Nuclear react ...
... Nuclear Fission A chain reaction is a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction. The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons needed to sustain a chain reaction is called the critical mass. Nuclear react ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
Nuclear Chem Notes - Warren County Schools
... Nuclear energy generates about 21 percent of the electricity produced in the United States. Questions of safety, costs, and nuclear waste disposal have halted construction of nuclear reactors in the United States. ...
... Nuclear energy generates about 21 percent of the electricity produced in the United States. Questions of safety, costs, and nuclear waste disposal have halted construction of nuclear reactors in the United States. ...
Atomic structure - s3.amazonaws.com
... they passed through a thin foil of gold. Rutherford was aware of Thomson’s “plum pudding” model and expected only minor deflections of alpha particles. ...
... they passed through a thin foil of gold. Rutherford was aware of Thomson’s “plum pudding” model and expected only minor deflections of alpha particles. ...
Protons, Neutrons and Electrons
... To determine the number of neutrons, you need to do a little subtraction. First round the mass number to the nearest whole number (because you either have a proton or neutron or you do not) Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) = neutrons ...
... To determine the number of neutrons, you need to do a little subtraction. First round the mass number to the nearest whole number (because you either have a proton or neutron or you do not) Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) = neutrons ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.